Learn about biometric payments, the technology behind them, how they boost security and convenience in transactions, their types, pros and cons and more.

Biometrics Payments: Everything You Need to Know
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

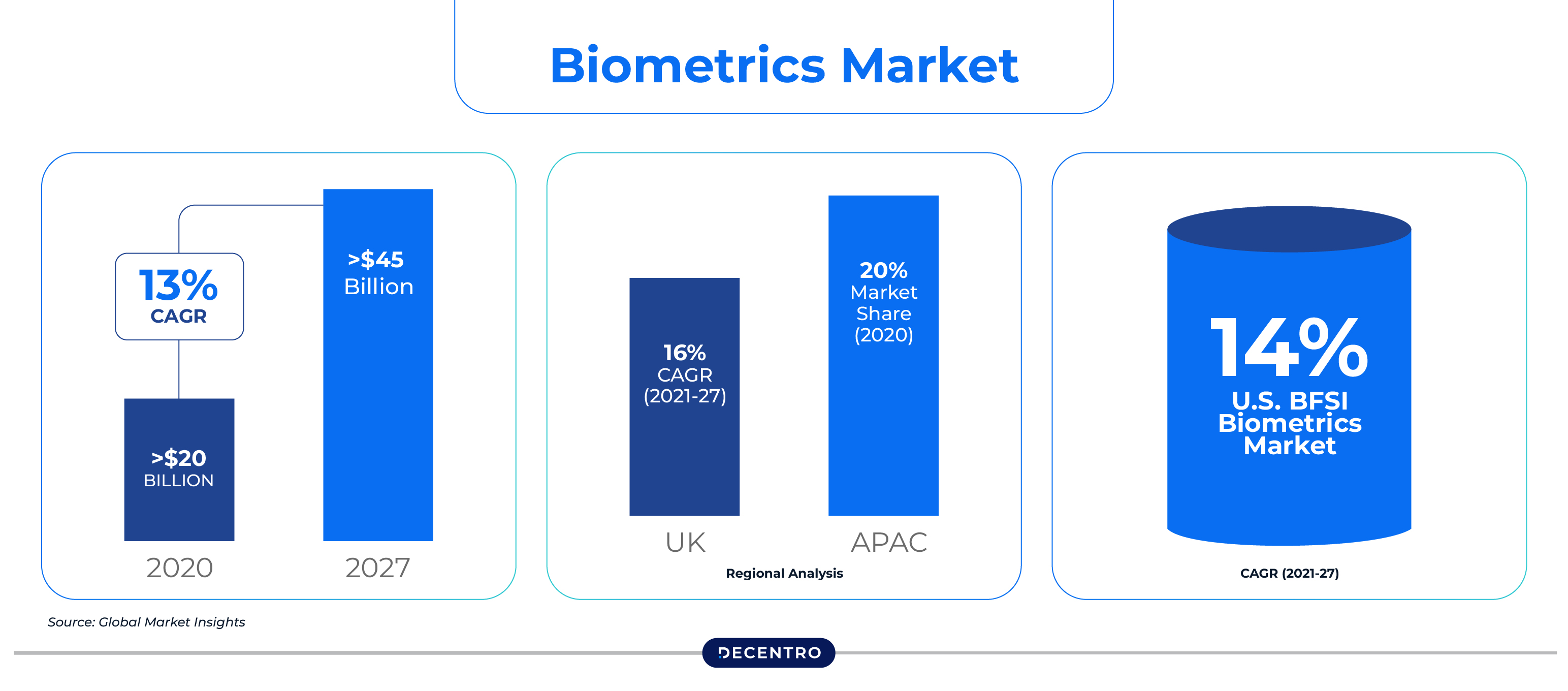
In today’s digital age, payment authentication methods are rapidly progressing, with biometric payments gaining increasing acceptance across industries. By leveraging unique biological traits like fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice identification, biometric technology is revolutionising the way consumers make purchases.
With their rapid integration in e-commerce and mobile payments, biometric systems provide a faster, more secure, and convenient way to verify identities. Apart from this, the increasing preference among consumers for fast, contactless and streamlined payment experiences is serving as a key driver for biometric payment adoption.
Thus, in order to remain competitive, businesses should explore the technology behind biometric payments, how they work, their merits, drawbacks, use cases and more.
Keep reading!
What are Biometric Payments?
Biometric payment systems represent a secure transaction technique by leveraging an individual’s various biological characteristics like facial recognition, fingerprints, iris scans, voice patterns, etc.
This helps authenticate their identity prior to completing a payment. Unlike conventional payment methods that depend on physical cards, passwords, or PINs, biometric payments use inherent personal traits for identity verification.
This approach enhances the security of the payment process, considerably reducing the likelihood of fraudsters successfully impersonating legitimate users. Currently, the most prevalent biometric identifiers include fingerprints, facial features, voice, iris patterns, vein recognition, and hand geometry.
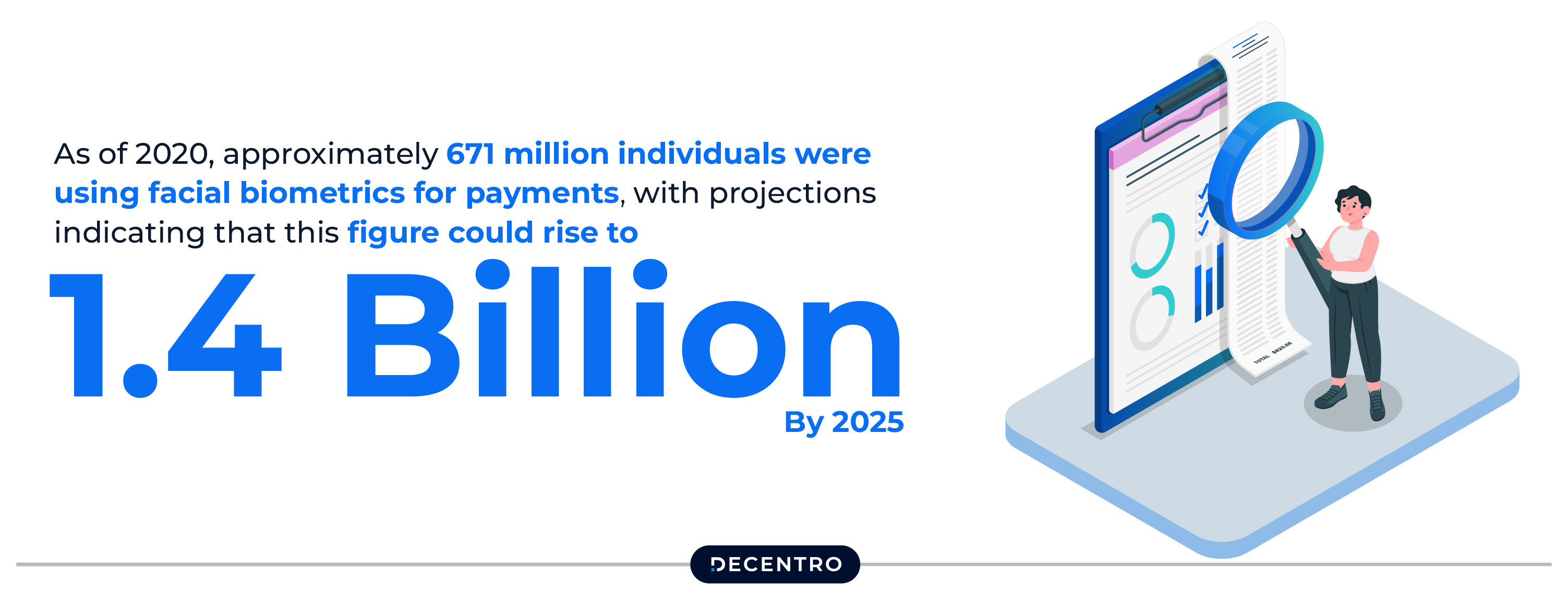
Note: As of 2020, approximately 671 million individuals were using facial biometrics for payments, with projections indicating that this figure could rise to 1.4 billion by 2025.
Difference Between Biometric Payments and Traditional Payment Methods
Biometric payments offer stronger security than traditional options like cash or credit cards. They use unique biological traits that are hard to copy or steal, which lowers the chances of fraud and identity theft. Unlike passwords that can be hacked, biometrics do not need users to remember complicated codes.
They also eliminate the need for physical cards, curbing the theft risk and making payments easier for customers. Once set up, biometric authentication provides fast and smooth accessibility, improving the shopping experience by expediting checkout times.
Moreover, it offers better access, especially for those who find regular banking complicated. With the development of biometric payment systems, people who previously considered banking systems to be complicated are finding it easier to transact online due to this advanced payment procedure.
Examples of Biometric Authentication Used for Payments
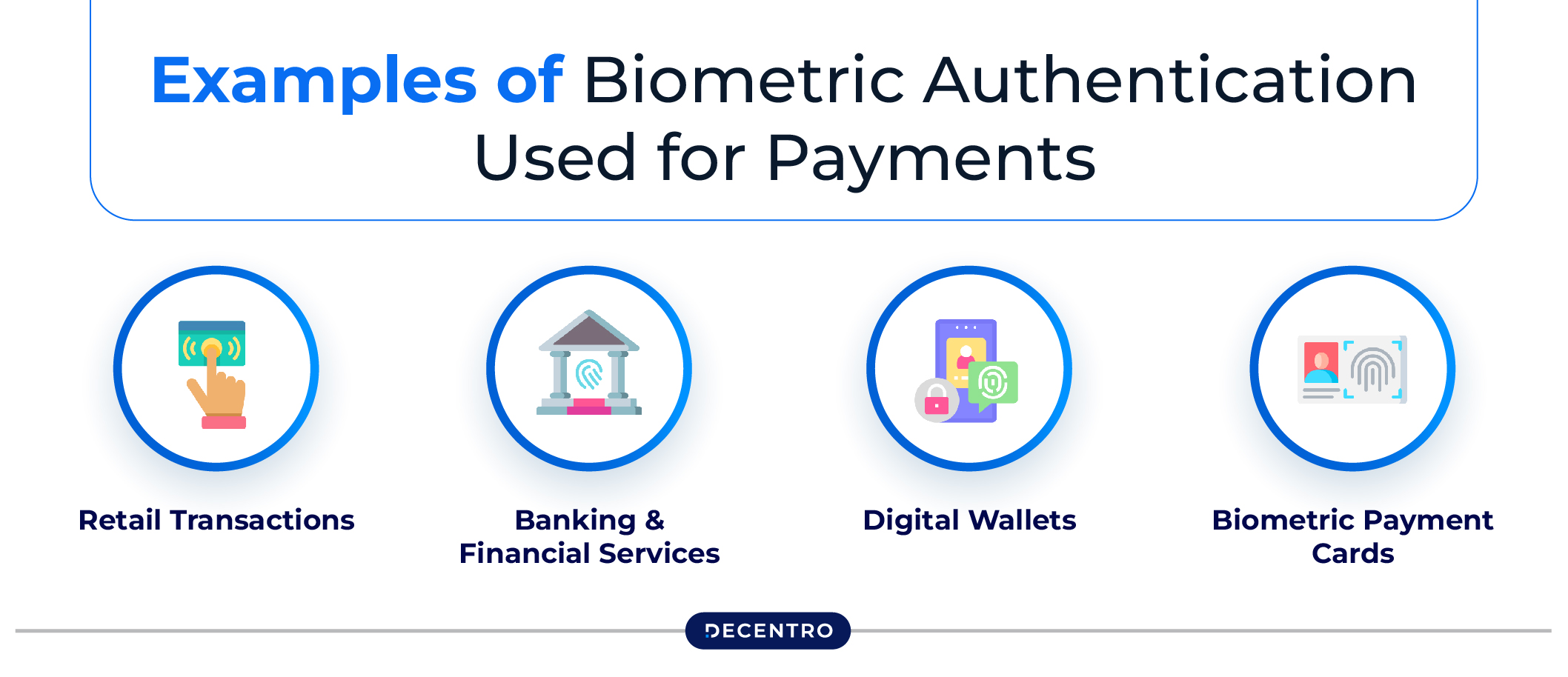
As biometric authentication technology develops, it is becoming an extensively implemented method for securing transactions across different payment platforms. Following are some major examples of how biometric technology is being incorporated into payment systems:
- Retail Transactions
When it comes to retail transactions, biometric fingerprint payment systems streamline the checkout experience while bringing an advancement in security. Customers can carry out transactions by scanning their fingerprints, reducing the need to carry cash or physical cards.
- Banking and Financial Services
Financial institutions and banks implement biometric authentication to improve online banking and safeguard ATM transactions, and mobile banking apps. This method helps prevent unauthorised access to sensitive financial data and strengthens overall security.
- Digital Wallets
Digital wallet platforms gradually incorporate biometric payment features, enabling users to authenticate transactions via facial recognition or fingerprint scans. This perfect blend of security and convenience significantly enhances the experience of online payment through smartphones.
- Biometric Payment Cards
These days, many payment card issuers provide cards with in-built fingerprint sensors. These biometric payment cards allow users to authorise transactions with a simple touch, thereby offering a safer alternative to conventional chip-and-PIN methods.
How Biometric Payments Work?
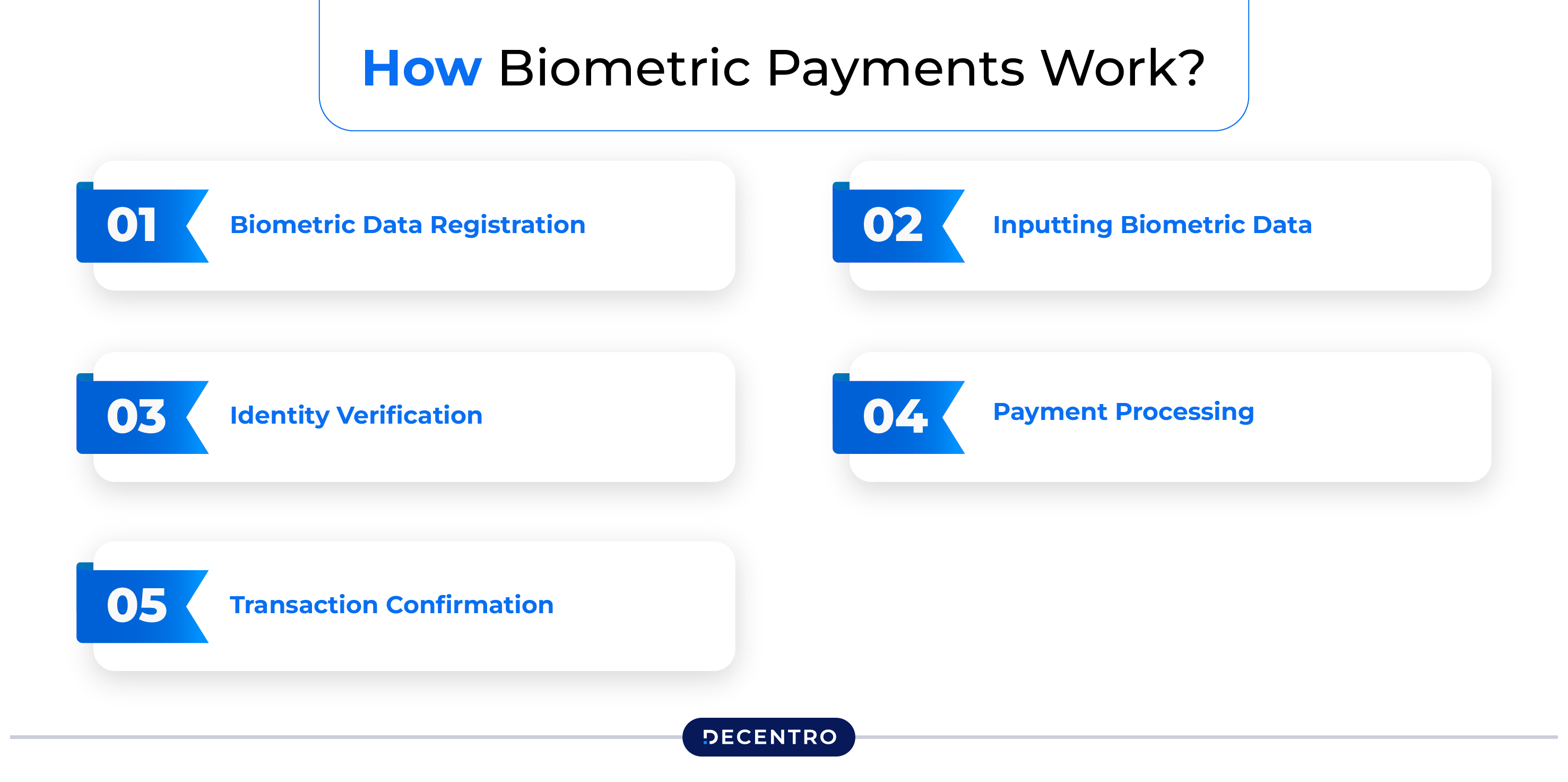
When biometric payments are initiated, they are processed in the following manner:
Step 1: Biometric Data Registration
The process begins with the user registering their respective biometric data, such as facial recognition or fingerprint, with the payment service provider. This information is confidentially stored for future transactions.
Step 2: Inputting Biometric Data
During the payment procedure, the user provides their registered biometric feature, which may include scanning their fingerprint or using facial recognition technology at a designated scanner or camera.
Step 3: Identity Verification
The system uses sophisticated algorithms to analyse the captured biometric data against the stored template, ensuring a precise and secure identity verification process.
Step 4: Payment Processing
Once identity verification is completed successfully, the payment is authorised, and the associated payment method, such as a credit card or bank account, is debited accordingly.
Step 5: Transaction Confirmation
The user receives a confirmation regarding the transaction completion, which may be provided as a digital notification or a printed receipt.
Types of Biometric Payment Methods

Various biometric authentication methods are employed in biometric payment systems, such as:
- Fingerprint Recognition
This technique captures the unique ridge and valley patterns on a user’s fingertip to confirm their identity. It is among the most prevalent and dependable forms of biometric authentication, frequently utilised in smartphones and payment devices.
- Facial Recognition
Facial recognition evaluates specific characteristics of a user’s face, including the eyes’ spacing and the jaw’s contour, to facilitate payment authentication. Its popularity is growing in mobile payment applications, providing a swift, contactless payment option.
- Iris or Retina Recognition
Iris and retina recognition systems authenticate users by examining the distinct patterns found in their eyes. Although this method is highly precise, it is less commonly used in standard payment systems due to the requirement for specialised equipment.
- Signature Recognition
Signature recognition analyses an individual’s handwritten signature, paying attention to aspects like speed, pressure, and the order of strokes. Although it is rarely used, it is still applied in some payment systems that strictly require physical or digital signatures.
- Vein Recognition
This technique scans the unique vein patterns in a person’s palm or finger for identification. Vein recognition is very secure because these patterns are hard to duplicate and can only be taken from a living individual.
- Voice Recognition
Voice recognition identifies a person by their voice features, including pitch, tone, and rhythm. It is usually used for hands-free payments or through phone systems, like at drive-throughs or with virtual assistants.
Components of Biometric Payments
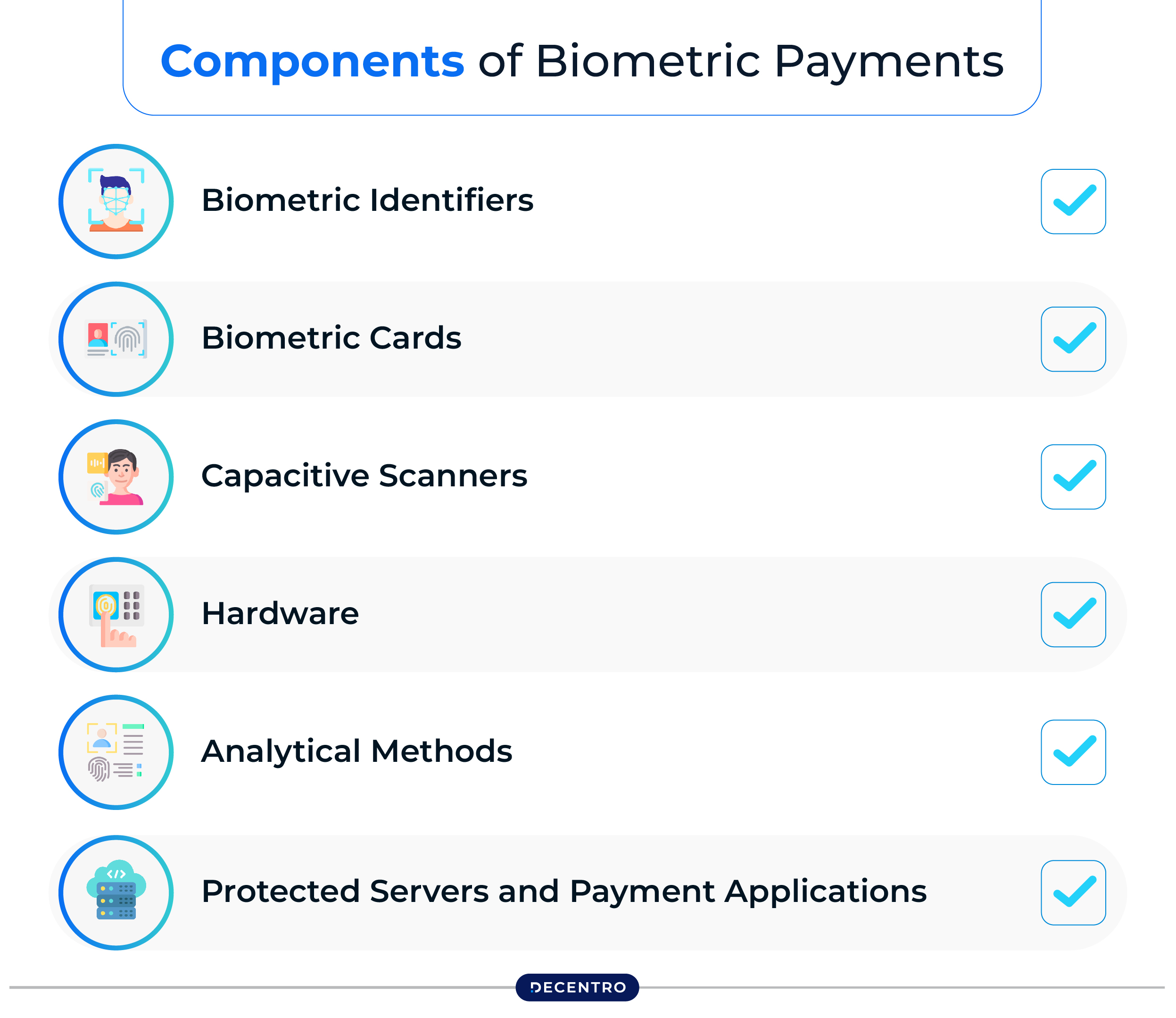
A biometric payment system is made up of several essential elements that collaborate to provide secure and efficient transactions:
- Biometric Identifiers
These are distinct biological traits, like fingerprints or facial features, utilised to confirm a user’s identity.
- Biometric Cards
Certain payment cards are now equipped with in-built fingerprint sensors, which enable individuals to authenticate transactions with just a touch.
- Capacitive Scanners
Capacitive scanners are commonly employed to gather fingerprint data for biometric verification. They utilise electrical currents in order to generate a precise image of the fingerprint.
- Hardware
Biometric payment systems rely on specific equipment, including fingerprint sensors and facial recognition cameras, in order to collect, process and authenticate biometric information.
- Analytical Methods
Advanced analytical methods are adopted to assess and compare biometric data, ensuring flawless and confidential authentication.
- Protected Servers and Payment Applications
Biometric information is safely stored on secure servers or within payment applications, thus protecting sensitive data from illegal access.
Benefits of Biometric Payments
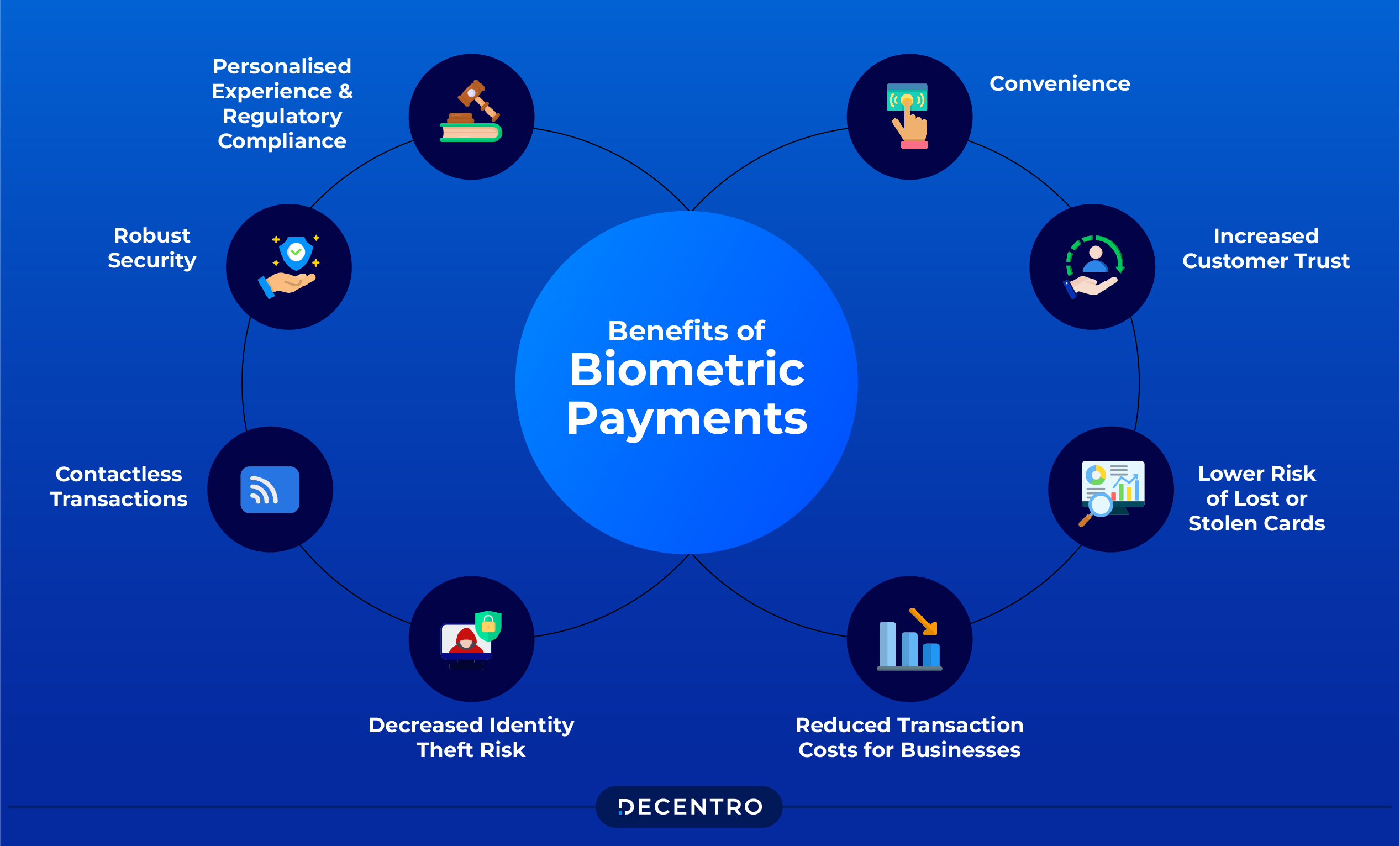
Biometric payment systems offer a wide array of benefits compared to conventional payment modes. They are as follows:
- Convenience
Biometric payments enable users to authenticate transactions instantly and effortlessly, eliminating the need to remember complex passwords or carry physical cards.
- Robust Security
Biometric identifiers are unique to each individual and can hardly be duplicated or stolen, making this form of authentication safer than traditional PINs or passwords.
- Contactless Transactions
Many biometric payment options, including vein scanning and facial recognition, facilitate contactless transactions, which are both more user-friendly and hygienic.
- Decreased Identity Theft Risk
Biometric systems significantly lower the chances of identity theft and fraudulent activities as it is difficult to steal or replicate an individual’s biometric data.
- Reduced Transaction Costs for Businesses
By diminishing the risks associated with scams and chargebacks, biometric payment systems can help businesses reduce transaction costs and boost profitability.
- Lower Risk of Lost or Stolen Cards
With biometric payments, users can stay away from the headaches of losing their physical payment cards, as their biometric information is much harder to decipher.
- Increased Customer Trust
By adopting a biometric payment system, businesses can enhance customer trust by showcasing their strong security and technological advancement.
- Personalised Experience and Regulatory Compliance
Biometric payment systems can provide tailored user experiences while ensuring adherence to strict security regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Drawbacks in Adopting Biometric Payments
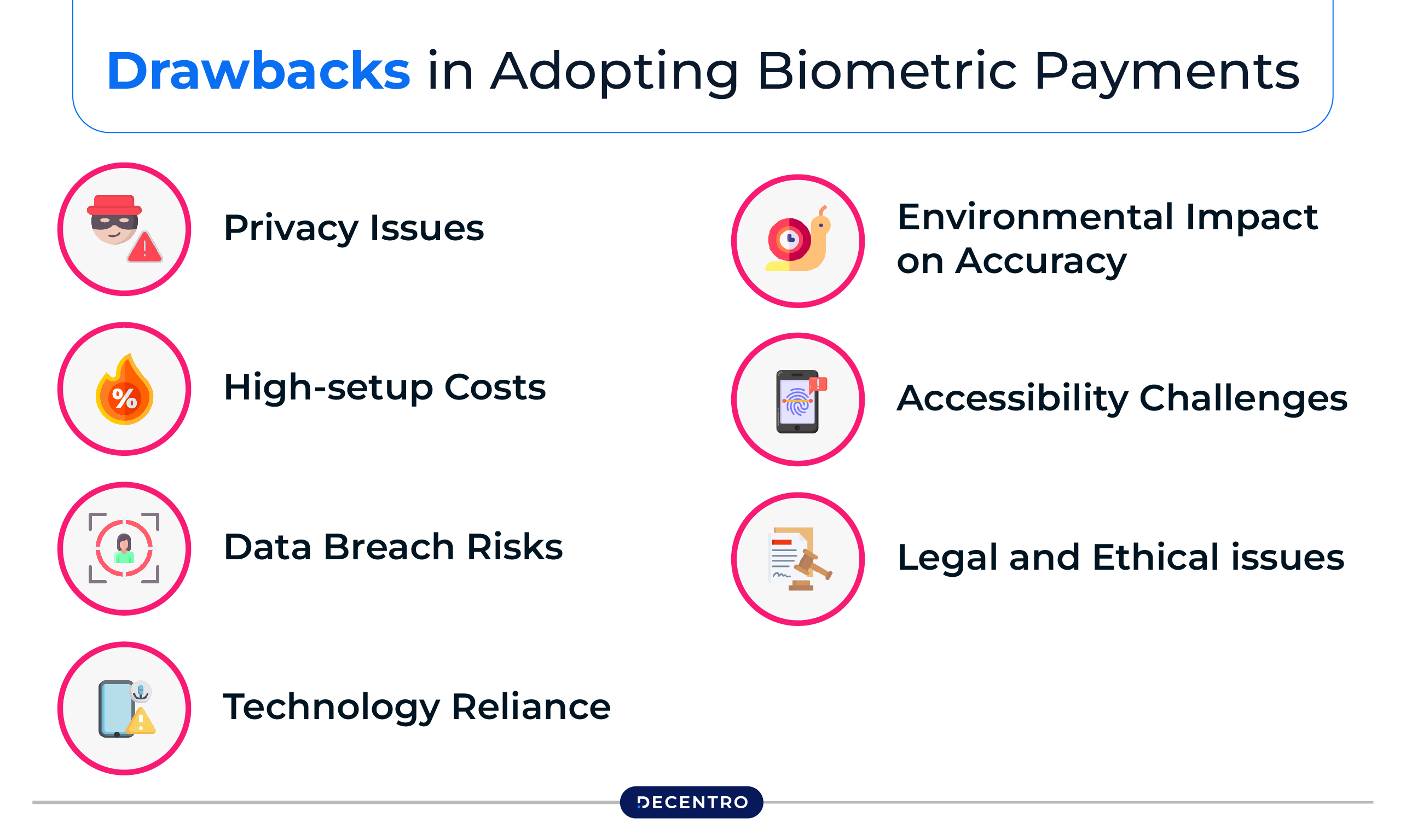
Biometric payment systems may be advantageous, but there are also some drawbacks to keep in mind:
- Privacy Issues
Some people may be reluctant to share their biometric information as they feel concerned about their privacy and potential misuse of their personal data.
- High-setup Costs
Implementing a biometric payment system can be expensive as it requires dedicated hardware, software, and specialised training.
- Data Breach Risks
Even though biometric data is generally more secure than traditional methods, it can still be vulnerable to breaches. In case your biometric data is stolen by any chance, it cannot be changed like a password.
- Technology Reliance
Biometric payment systems depend on advanced technology, which can experience technological glitches, failures, or compatibility problems.
- Environmental Impact on Accuracy
Factors like dirt, moisture, or improper lighting can affect the performance of biometric scanners, leading to incorrect rejections or acceptances.
- Accessibility Challenges
Individuals with certain skin conditions or disabilities may struggle to use specific biometric scanners, creating accessibility challenges.
- Legal and Ethical issues
The gathering, storage, and utilisation of biometric data come up with significant legal and ethical concerns, including user consent, data ownership, and the risk of misuse by companies or establishments.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Biometric Payments
Certain regulatory bodies administer the applicability of biometric data for payment systems. It is essential for them to ensure that proper jurisdiction principles are in place for the safe and seamless use of such sensitive data.
Some of the existing regulations in this area include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and many other regional laws that govern the collection, storage, and processing of biometric information.
The GDPR lists biometric data as sensitive personal data, requiring any application involving it to have explicit consent from the person concerned with stringent restrictions on data handling. PCI DSS ensures that payment systems must comply with several strict security requirements, including the encryption of sensitive information such as biometric identifiers.
Furthermore, there are extensive consumer trust regulation measures, the non-adherence to which may incur serious penalties, including fines of up to €20 million, or up to 4% of the global turnover, under GDPR.
All these measures curb the risks of exposing private or commercial information through data leaks. This encourages consumers to choose biometric payment, which, in turn, increases its widespread popularity and acceptance.
Use Cases of Biometric Payments
Listed below are some of the common use cases of biometric payments:
- Online Shopping
Biometric payments provide superior security and convenience for online shoppers. By integrating with mobile payment systems, they offer a quick and user-friendly experience, allowing customers to make transactions easily with a simple biometric scan, such as facial recognition or fingerprint.
- Banking
Banks utilise biometric payment technology to protect customer data and prevent fraud. Technologies like biometric bank cards, facial recognition, and fingerprint scanning enable secure, faster transactions, enhancing both user safety and banking efficiency.
- Retail Stores
In the retail industry, biometric payments speed up the checkout process by allowing customers to pay via biometric authentication at EMV (Europay, MasterCard, and Visa) terminals. This reduces wait times and eliminates the need for physical cards while creating a seamless andsecure shopping experience.
- Transportation (Ticketless Travel Payments)
Biometric payments streamline travel by allowing passengers to board trains or flights using only their face or fingerprint for identity verification. This eliminates the need for physical tickets, offering a smoother, faster, and more secure travel experience. This approach not only saves valuable time but also boosts security with cutting-edge encryption technologies.
- Healthcare
In healthcare, biometric payments enable secure patient identification and payment processing. Patients can use fingerprints or facial recognition to book appointments or pay for services, reducing fraud risks and ensuring accurate identification for better healthcare delivery.
- Education
Educational institutions are adopting biometric payment systems for students to pay for meals, books, and services with a simple biometric scan. This system simplifies transactions, improves efficiency, and reduces administrative burdens for schools and universities.
Best Practices for Businesses Adopting Biometric Payments
Here are the best practices businesses can follow while adopting biometric payment systems:
- Ensure Compliance with Data Protection Laws
Implement a biometric payment system by complying with Indian data protection laws, such as the Personal Data Protection Bill, to protect customer data, especially their biometric information. This reduces the risk of violating the rules and creates an impression that customers’ sensitive information is protected as per the highest legal standards.
- Educate Customers About Biometric Payment Benefits
Businesses should make sure that their customers are adequately informed of the convenience, security, and speed with which biometric payments may be executed. By explaining to customers how it operates and its advantages that do not require physical cards or PINs, businesses can encourage more people to accept and use this system.
- Partner with Trusted Technology Providers Like Decentro
Partnering with reputable and trusted technology providers like Decentro can help businesses successfully implement secure and efficient biometric payment solutions. They will ensure the robustness, scalability, and end-to-end compliance of the technology to all relevant regulations.
In this way, a business can be assured that the solution is trustworthy and convenient for both the company and its customers.
The Future of Biometric Payments
With the progression of technology, the future of biometric payment systems looks promising. Here are some noteworthy trends and advancements to keep an eye on:
- Increased Business Integration of Biometric Payments
A growing number of businesses and payment providers have gradually begun embracing biometric systems in their operations. This is because of the advancement of technology, alongside its cost-effective, dependable, and user-friendly nature.
- Improved Security through Multimodal Authentication
The execution of various biometric traits, such as the combination of facial recognition and fingerprint, ensures enhanced security and accuracy in payment processes.
- Convergence with Cutting-Edge Technologies
Biometric payments are likely to integrate with advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things, creating seamless, intelligent and secure payment experiences.
- Continuous Innovations in Biometric Authentication
Researchers are exploring new biometric techniques, including heartbeat and brainwave analysis so that biometric systems can become more powerful and versatile in terms of reliability, security, and convenience of payment.
- Developing Regulatory Frameworks for Biometric Data
As the adoption of biometric systems develops, governments and regulatory agencies are expected to establish new laws and guidelines in order to protect user privacy and ensure the ethical management of biometric data.
How Decentro Can Simplify Biometric Payment Adoption?
Decentro offers strong API solutions that make it easy to incorporate secure biometric payment systems. Our platform allows businesses to connect biometric authentication systems seamlessly with payment gateways, ensuring safe and smooth transactions for customers and merchants.
Furthermore, our APIs are a simple solution for integrating banking services while ensuring compliance. For instance, our KYC stack enables us to process more than 400 identity validations, 250 image recognitions, and 300 repository fetches each hour.
Also, our payment collection APIs are fully compliant with the RBI’s latest regulations, enabling you to negate the chances of non-compliance and focus fully on your core operations. This makes us fully capable of guiding you in your verification and validation efforts.
Ready to introduce biometric payments into your business operations?