Learn how fraud detection works, common fraud types, and best practices to protect your business and personal data from financial crimes and cyber threats.

Fraud Detection Explained: What You Need to Know to Stay Protected
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

As an increasing number of individuals are becoming victims of scams, financial fraud, and cybercrimes, fraud detection is becoming necessary. According to recent statistics, the year 2023-24 witnessed a 27% increase in bank fraud cases compared to the previous year.
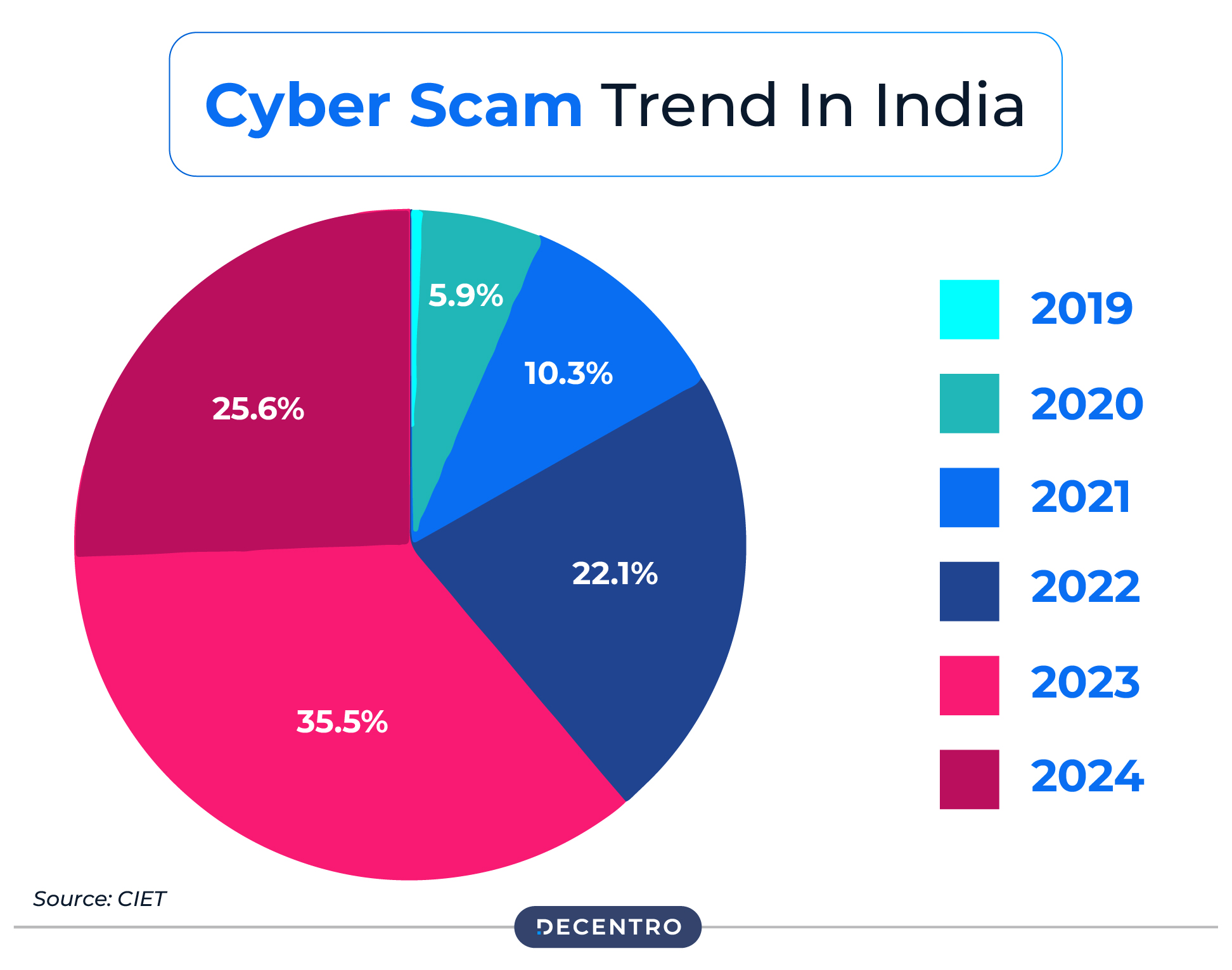
This highlights the growing need for robust fraud detection systems, along with the need to understand how fraud detection works and how to stay protected. This guide covers fraud detection, its common types, how it works, and other crucial aspects.
Keep reading!
Fraud Detection: An Overview
Fraud detection helps to locate and prevent fraudulent individuals from illegally acquiring money or assets. It involves actions performed to monitor and curb fraud activities. This process is extensively implemented in the fields of banking, insurance, healthcare, government activities, and even law enforcement.
Now, fraud comes in various forms, such as money laundering, cyberattacks, false banking claims, fake cheques, and identity theft. Thus, to combat the increase in fraud, companies need to adopt new detection methods, cutting-edge technologies, and risk management plans.
How Fraud Detection Differs from Fraud Prevention?
Let’s check out the key differences between fraud detection and fraud prevention:
| Aspects | Fraud Detection | Fraud Prevention |
| Aim | Detect and respond to fraud after it has occurred. | Prevent fraud before it occurs. |
| Timing | Implemented after the occurrence of fraud. | Implemented before fraud occurs. |
| Nature of Activities | Steps include monitoring, analysis, and investigation of transactions or behaviour. | Steps include identity verification, access grants, and user education. |
| Proactiveness | Acts in response to a fraud incident. | Seeks to actively mitigate the risk of fraud. |
| Long-term Impact | Assists in reducing losses and preventing future fraud. | Helps in building a strong and fraud-resistant system. |
| Costs | Initial costs are lesser than fraud prevention. It involves costs associated with the investigation and correction of fraud cases. | There could be high initial costs in fraud prevention for implementing preventive tools and processes. |
| Examples | Fraud data analysis, detection of anomalous behaviour, and forensic analysis. | Enhanced identity verification, fraud awareness training, and transaction monitoring systems. |
What are the Common Types of Fraud?
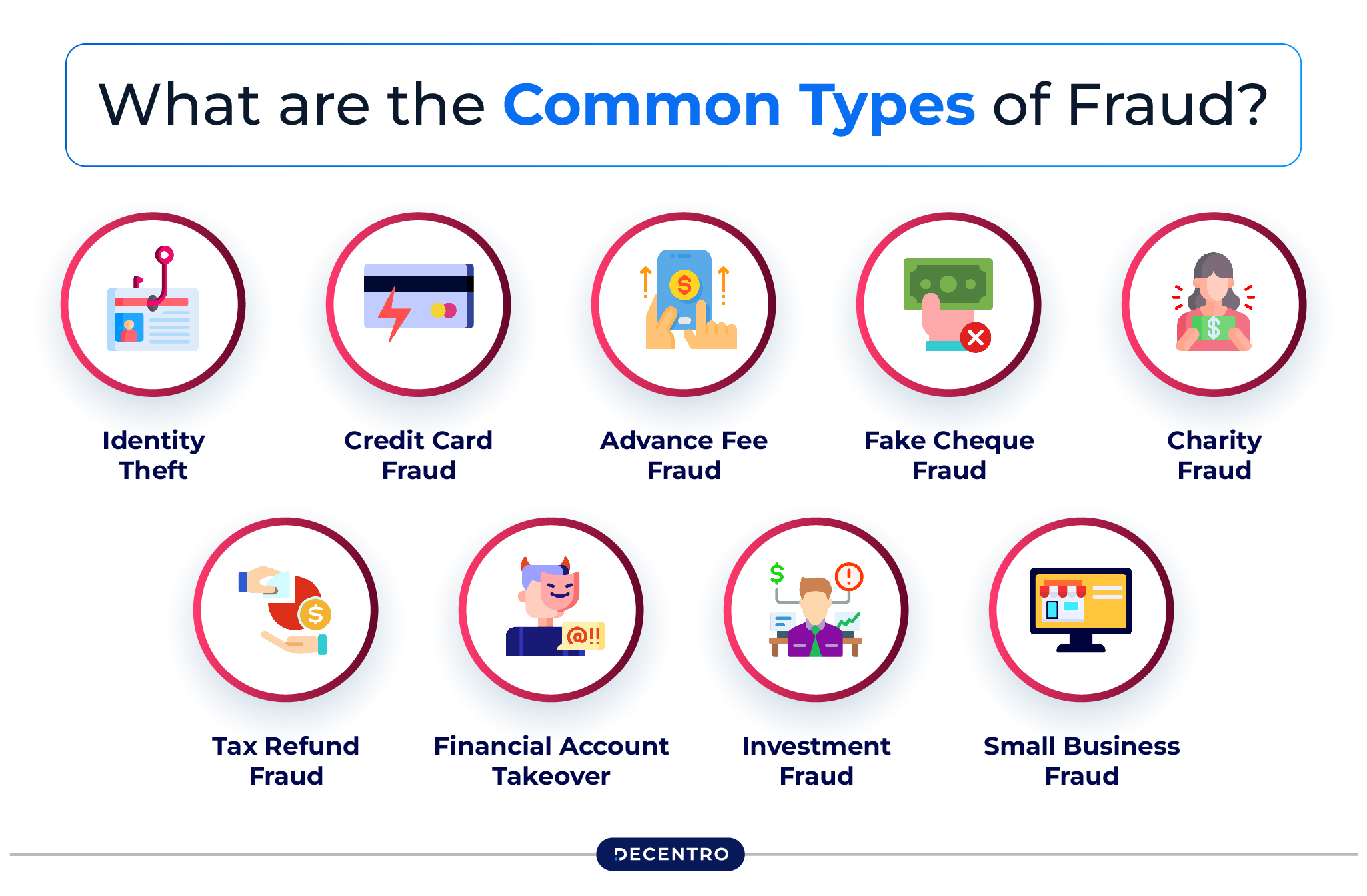
Following are the major types of fraudulent activities that are detected during the fraud detection process:
- Identity Theft
Identity theft occurs when fraudsters use your personal information to commit fraud or other illegal activities. It could include taking your private details to open new accounts, misusing your existing accounts, or seeking medical services.
Broadly speaking, any instance where an individual uses your identity to commit crimes in your name can be termed identity theft.
- Credit Card Fraud
Credit card fraud involves someone using your credit card or its details without permission to obtain money or acquire something. Fraudsters generally steal people’s credit card information using online hacking techniques. This enables them to make purchases on another person’s account.
- Advance Fee Fraud
Advance fee fraud is a type of scam in which an individual asks for an upfront fee with a promise to help gain an enormous amount later, which never happens.
The scammers reach out to people by making claims that the fee is just a tiny fraction of a much larger sum of money that will be unlocked through its payment. If the victim gets scammed and pays that fee, the scammer disappears from the scene.
- Fake Cheque Fraud
Fake cheque fraud is associated with using fake cheques to purchase goods and services or enticing an individual to cash a counterfeit cheque and send back a portion of the money.
Earlier, the detection of false cheques was a challenge for financial institutions. However, with the advent of technologies powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), banks can easily identify them.
- Charity Fraud
Charity fraud refers to a scam where an individual asks for a certain amount of donation for a charity that does not even exist, especially after various disasters and tragedies. Individuals may even get calls, emails, or online messages where someone claims to gather money for relief for the victims. Unfortunately, all the funds go to the scammer.
- Tax Refund Fraud
Tax refund fraud is another type of scam that occurs when an individual files a fraudulent tax return by using a different person’s personal information. They file for tax refunds on the latter’s behalf, which they collect for themselves. Scammers can easily do that by acquiring personal information related to their victims.
- Financial Account Takeover
This situation arises when someone illegally accesses another individual’s financial accounts and then uses them to execute unauthorised transactions. These incidents typically occur through privacy breaches, which constitute one of the many fraud risks that financial institutions need to effectively supervise.
- Investment Fraud
Such fraud occurs when a criminal convinces victims to invest money in a false scheme. The money may be used to fund the fraudster’s lifestyle or may simply be stolen completely.
- Small Business Fraud
It refers to fraudulent activities that generally occur within a small business. This involves employees or business owners stealing funds, misrepresenting information, or engaging in deceptive practices for personal gain.
Why is Fraud Detection Important for Businesses?
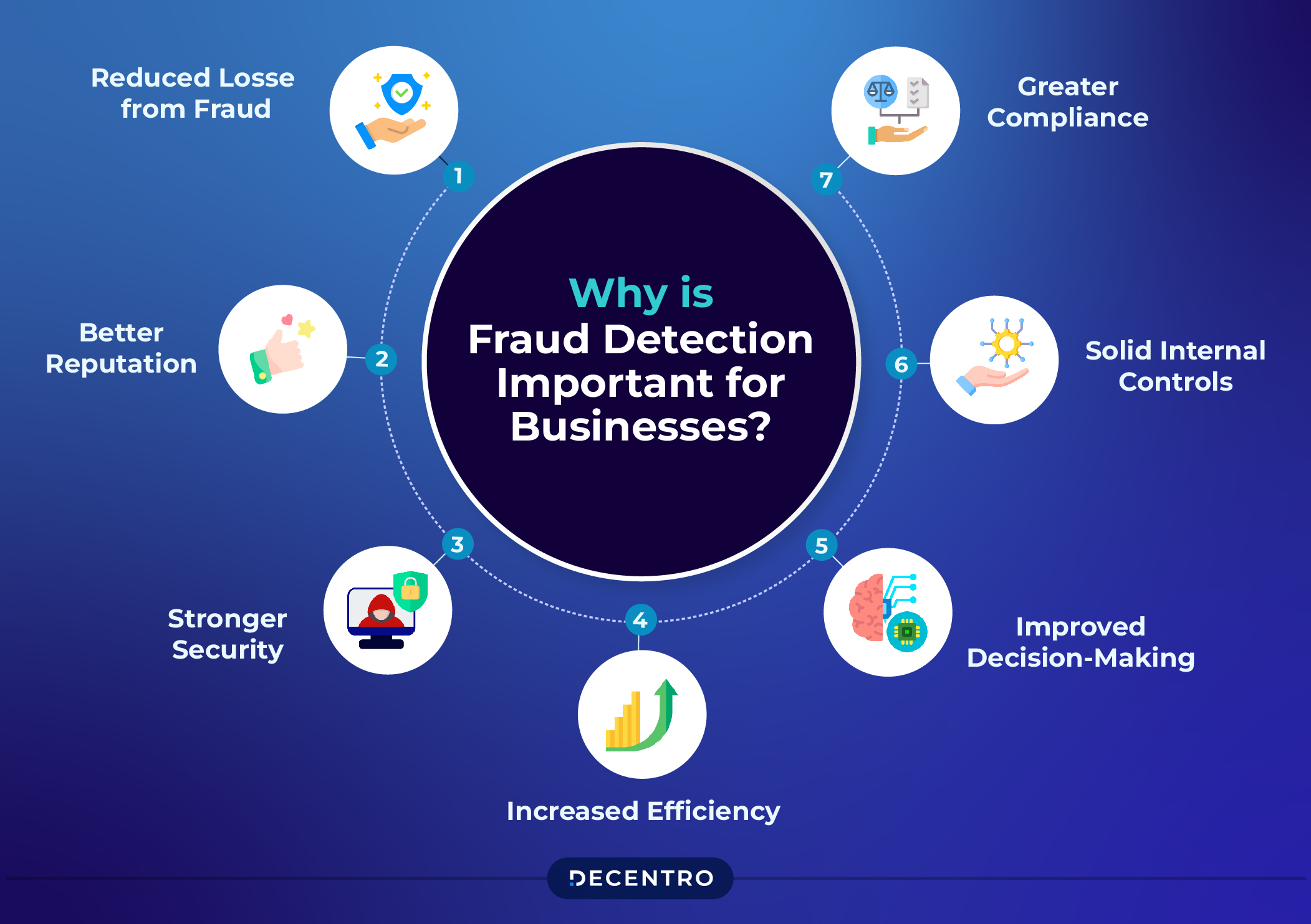
As per PwC’s ‘Global Economic Crime Survey 2024’, almost 59% of Indian entities faced financial or economic fraud in the last 2-3 years. Following are some of the major reasons why fraud detection mechanisms are crucial for businesses:
- Reduced Losses from Fraud: Implementing fraud detection mechanisms helps an organisation detect and prevent fraud, thus reducing the chances of financial loss.
- Better Reputation: Companies that seek to actively detect fraud and prevent it usually gain a better reputation from customers and the public, resulting in better interactions.
- Stronger Security: Fraud detection enables business entities to enhance their security by identifying and addressing potential risks as soon as possible.
- Increased Efficiency: By detecting and preventing frauds on time, organisations can function more efficiently as they save time and other resources that can be utilised for improving their market position.
- Improved Decision-Making: A business capable of detecting fraud is better able to make informed resource allocation and risk management decisions.
- Solid Internal Controls: Fraud detection enables organisations to identify and correct weaknesses in their internal systems, thereby reducing the possibility of future fraud.
- Greater Compliance: Firms that can determine and avert fraud are likely to better comply with laws and regulations associated with preventing fraudulent activities.
How Fraud Detection Works?
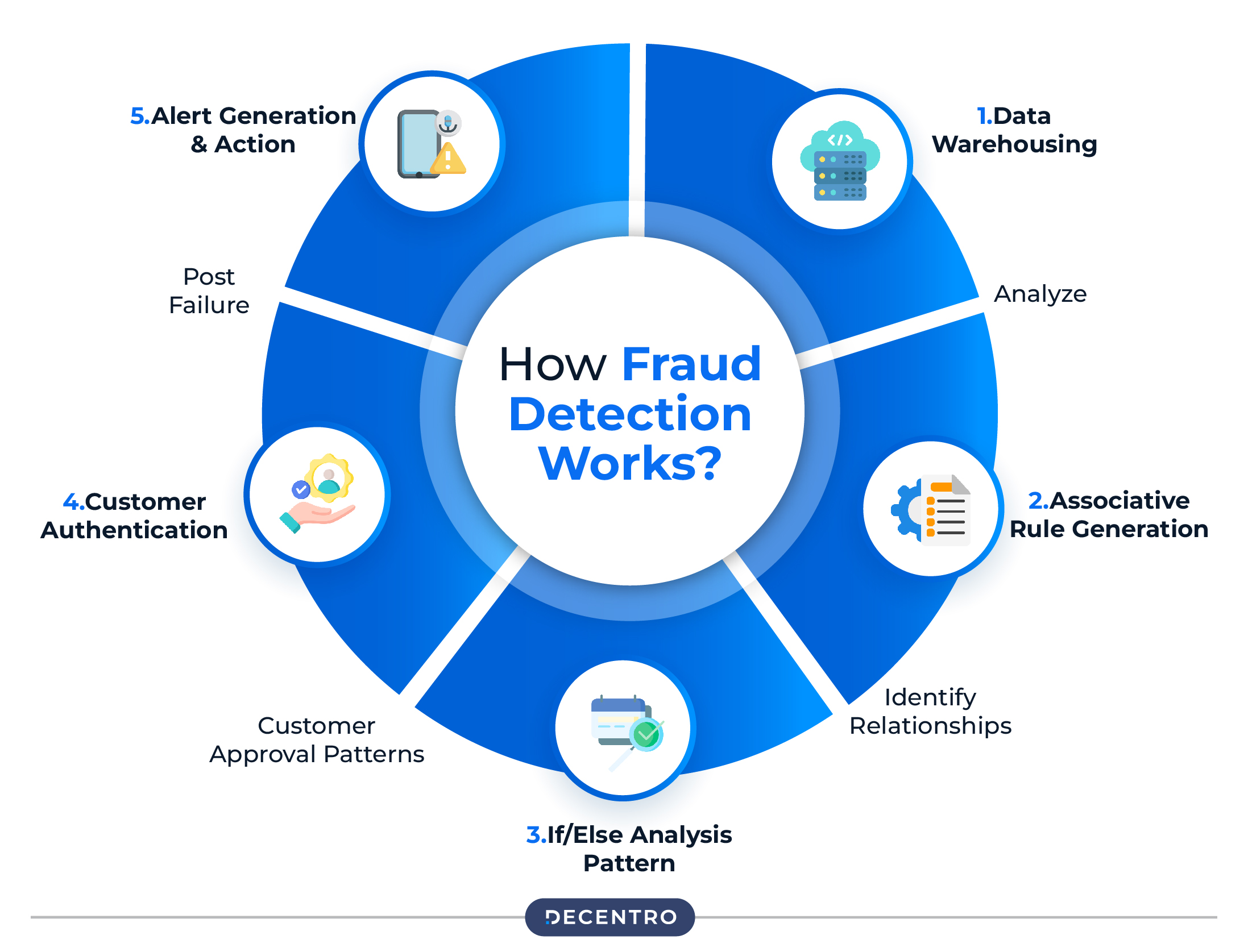
Here is a step-by-step discussion regarding how fraud detection works:
Step 1: Data Warehousing and Analysis
This includes gathering and processing large amounts of data, like transaction records and customer behaviour. Advanced analytics techniques are applied to look for fraud indicator patterns and to flag suspicious activities.
Step 2: Associative Rule Generation
An algorithm is used to identify a relationship between a number of variables like transaction amount and customer demographics. By finding the patterns, the system detects abnormalities that imply fraudulent activity.
Step 3: Pattern Recognition with If/Else Analysis
After this, the system uses sophisticated algorithms to analyse patterns of customer approval in comparison with deviations from typical transaction behaviours. It helps distinguish legitimate transactions from suspicious ones that require closer examination.
Step 4: Customer Authentication & Verification
Once the system identifies the potential fraud, it initiates authentication processes to confirm the customer’s identity and validate the transaction details. This also ensures that only the legal transactions are passed.
Step 5: Alert Generation & Action
After noticing any suspicious behaviour, the system sends automated alerts to allow stakeholders to follow up on the case. The system sends out quick alerts regarding scams, stopping money loss and reducing the impact of fraudulent activities.
Best Practices for Fraud Detection
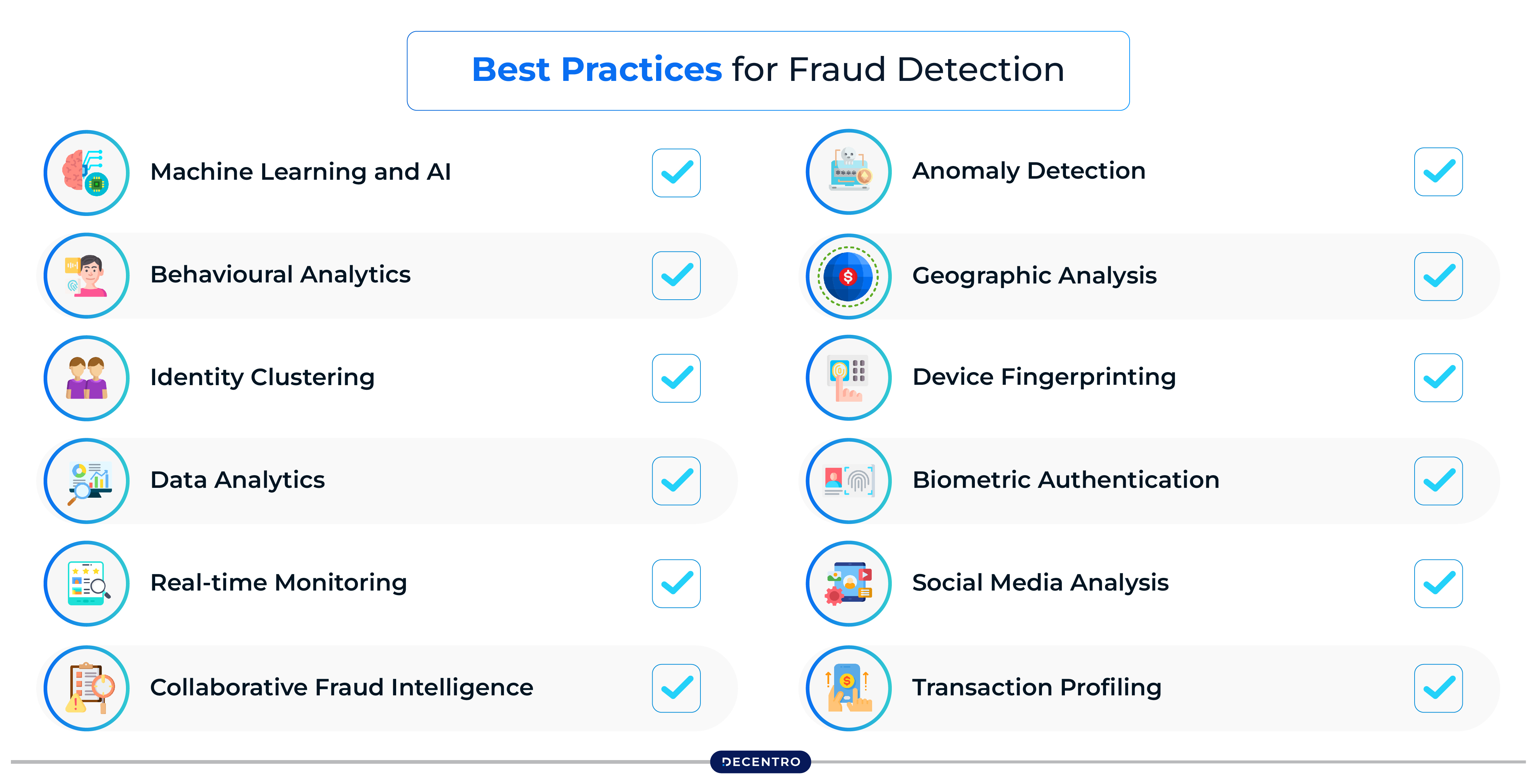
Discussed below are some of the most ideal methods that help in fraud detection:
- Machine Learning and AI
By applying machine learning and artificial intelligence, fraud can be detected quite efficiently. For instance, high data volumes can be processed in no time by such technologies, recognising patterns, and unknown activities that are suspected to be fraudulent actions.
- Behavioural Analytics
Through comprehensive user behaviour analysis, a company can find if the action has been taken beyond the legal boundaries. Behavioural analytics can reflect suspicious activities, such as logins from unknown locations, sudden changes in spending patterns, or larger transactions.
- Identity Clustering
When businesses combine users with similar characteristics into groups, they can detect suspicious patterns that are connected to fraudulent behaviour. Identity clustering serves well in uncovering both cybercriminal and organised crime activities.
- Data Analytics
Advanced data analysis tools can sort through vast amounts of data to identify fraud indicators. Companies can collect information from different sources and gain valuable insights, staying ahead of fraudsters.
- Real-time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring is one of the best methods of fraud detection. This method monitors activities live so that it can instantly locate and send alerts if any fraudulent activity is discovered.
- Collaborative Fraud Intelligence
Information sharing among organisations and the industry regarding fraudulent activities tends to improve their understanding of emerging fraud methods. Collaboration helps businesses prevent such crimes effectively and defend better against fraudsters.
- Anomaly Detection
This approach is based on creating a benchmark for normal activities and detecting any significant deviation beyond expectation. Anomalies can indicate fraudulent transactions, irregular login attempts, or other kinds of malicious activities.
- Geographic Analysis
Connecting locations associated with a transaction may point out suspicious patterns, such as those coming from risky or unusual geographic regions. It may also help identify differences between the reported locations and the actual origins of the transactions.
- Device Fingerprinting
By assigning unique codes to every device (computers or smartphones) used in payments, businesses can track when unauthorised access or strange actions occur.
- Biometric Authentication
The use of biometric methods, like fingerprint or facial recognition, can increase fraud detection since it verifies who is making the transactions. This adds a layer of security since each person must have a unique physical feature.
- Social Media Analysis
The usage of social media sites can provide valuable hints or mentions related to fraud that can come in handy in the detection process. This may reveal crucial information regarding the potential fraudsters, their methodologies, and their target so that the mishap can be prevented as early as possible.
- Transaction Profiling
Through transaction profiling, companies create profiles of ordinary transactions based on the behaviour of individual users or accounts. In light of past transaction data, it helps detect any unusual activities that may indicate fraud.
Key Challenges in Fraud Detection

Following are some minuses related to fraud detection that can be challenging for businesses or individuals:
- Cost Management
With the growing advancement in fraud techniques, businesses may require investing more in building a sound fraud detection mechanism. Relying completely on rule-based monitoring can be inadequate as deception techniques evolve over time.
- Remote Transactions
A majority of business entities transact remotely with their clients. Although this is convenient and economical, fraudsters can often pretend to be real customers and steal sensitive information from firms.
- Speed of Transactions
The prevailing transaction system focuses on speed and seamlessness. Smartphones can initiate applications for loans and even complex purchases simply by a few taps. However, fraudsters find this fast-paced system their ideal arena to commit illegal acts and disappear before getting caught.
- False Positives
A highly sensitive fraud detection system may yield a large number of false positives. This annoys customers, who might abandon their loyalty to the company. Also, it costs the organisation time and money to investigate the alerts raised by such systems.
- Wide Range of Digital Payment Options
Today, there are various tools and services for transferring money or making payments online. They include digital payment apps, mobile wallets, cryptocurrency platforms, credit cards, and digital savings accounts. This rise of digital financial services opens plenty of scopes for fraud.
- Evolution of Fraud Techniques
Since fraudsters keep developing their techniques, it becomes a tough challenge for fraud detection systems to counter them. As a result, it requires more effort, money, and time to employ enhanced detection techniques.
- Globalisation and Cross-Border Transactions
The global aspect of business makes any efforts to spot and prevent fraud very difficult. This is due to varying laws, jurisdiction issues, and security levels across different countries.
- Data Privacy and Compliance
Organisations face challenges in balancing fraud detection with compliance and data privacy rules. Although intended to protect customer data, stringent regulations may hinder access to vital information that may help determine fraud.
Simplifying Fraud Detection with Decentro’s APIs
Fraud detection plays a key role in protecting people and companies these days. Learning about common scams, adhering to smart practices, and using cutting-edge fraud-detecting tools can help merchants and businesses cut down their chances of becoming victims of such activities.
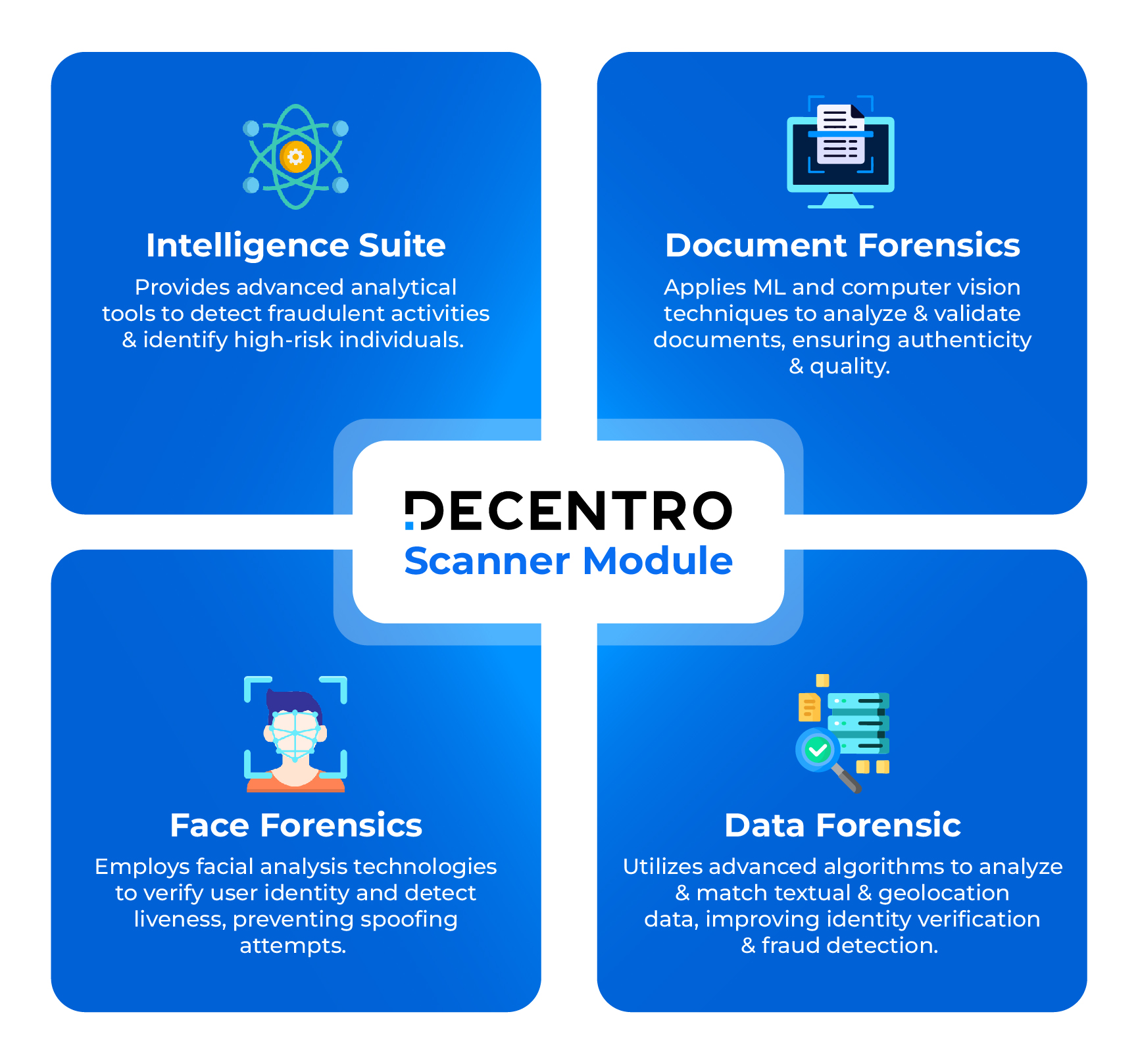
Decentro’s Scanner Module provides robust fraud detection APIs to help companies automate and simplify how they spot fraudulent activities. By integrating advanced machine learning (ML) and computer vision technologies, these APIs augment data from Decentro’s KYC & Onboarding and Bytes modules. This provides businesses with deeper intelligence and actionable insights.
This robust solution automates key fraud detection processes, such as customer authentication, transaction monitoring, and anomaly detection, helping firms stay ahead of potential fraud.
Wondering what else we provide that can streamline fraud detection for your business?


