Explore how Decentro’s Ledgers module simplifies revenue recognition, ensuring accurate, real-time financial tracking and reporting.

Revenue Recognition: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
Avi is a full-stack marketer on a mission to transform the Indian fintech landscape.
Table of Contents

Revenue is the most important metric for any organisation in any given industry. Whether it’s a functional leader, an investor, or the strategy department, revenue remains critical to the overall growth of any business.
This blog delves into every facet of revenue recognition, demonstrating how a robust revenue recognition process can accelerate business growth. It offers practical tips for effective revenue recognition, explores future trends and best practices, and showcases how Decentro’s Ledgers module can streamline your revenue management framework.
What is Revenue Recognition?
Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that outlines the conditions under which Let us consider an example to understand revenue recognition better. Imagine a company where revenue is recognised or earned. Depending on the nature, certainty, and timing of the revenue, this can become extremely critical to maintaining the accuracy of a company’s financial statements.
Revenue recognition looks to answer when a business has actually earned its money. Typically, revenue is recognised when the product or service has been provided to the customer, irrespective of when the customer receives the payment. The same is recorded to the company’s financial statements.
Tech Solutions sells a software subscription to a customer for $1,200 per year. According to the revenue recognition principle, Tech Solutions cannot immediately recognize the entire $1,200 as revenue when receiving the payment. Instead, they must recognize the revenue over the period the service is provided.
Here’s how the method works:
- The customer pays $1,200 for the annual subscription.
- The entire $1,200 is allocated to the one-year subscription service.
- Recognize Revenue: Tech Solutions will recognize $100 as monthly revenue for 12 months ($1,200 / 12 months = $100 per month).
So, instead of recording $1,200 as revenue upfront, Tech Solutions recognizes $100 of revenue on their financial statement as the service is delivered.
Why Revenue Recognition Matters?

Revenue recognition helps solve common issues businesses face in several key ways:
1. Accuracy in Financial Reporting: By recognizing revenue when it is earned, businesses ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect their true financial position. This prevents the overstatement or understatement of revenue and profits, providing a more realistic picture of the company’s performance.
2. Compliance with Standards: Revenue recognition principles ensure compliance with accounting standards such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). In the US, two major revenue recognition standards need to be followed: ASC 606 and IFRS 15.
3. Enhanced Investor Confidence: Transparent and accurate revenue reporting builds trust with investors, stakeholders, and financial analysts. Consistent revenue recognition practices demonstrate that the company follows sound financial management practices, which can attract and retain investors.
4. Improved Cash Flow Management: By recognizing revenue appropriately, businesses can better align their revenue with expenses. This helps manage cash flow more effectively, ensuring the company has sufficient funds to cover its operational needs and invest in growth opportunities.
5. Informed Decision-Making: Accurate revenue recognition provides management with reliable data to make informed decisions regarding budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning. It helps identify trends and assess the financial health of different business segments.
Revenue recognition is crucial for maintaining financial integrity, building stakeholder trust, and supporting sustainable business growth.
Revenue Recognition Methods
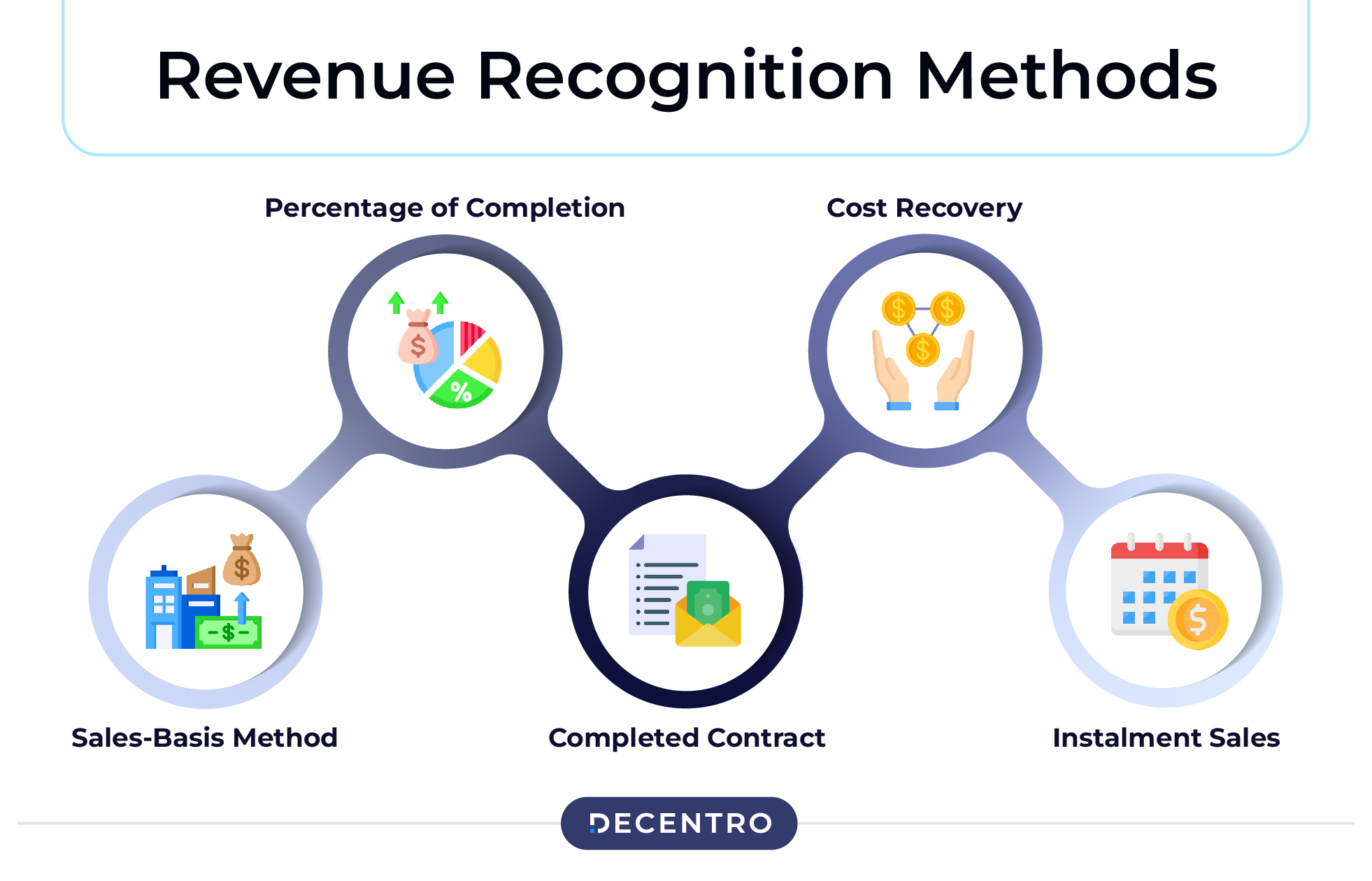
ASC 606 remains the fundamental principle when it comes to revenue recognition. However, different companies use different methods to recognise revenue. These are:
Sales-Basis Method
– Immediate Recognition: Revenue recognized at the point of sale.
– Retail Example: Recognize revenue when a customer makes a purchase.
– Subscription Example: For a £2,400 annual plan, recognize £200 monthly.
– Delivery Focus: Revenue recognized upon delivery, not payment.
Percentage of Completion
– Long-Term Contracts: Recognize revenue as project milestones are completed.
– Consistent Revenue: Provides steady financial reporting.
– Cost-Based Example: For a £30,000 project, recognize 50% completion at £15,000 incurred costs.
Completed Contract
– Upon Fulfillment: Revenue is recognized only when contract obligations are fully met.
– Example: Recognize revenue upon the final delivery of all goods.
– Ideal for Short-Term: Used for projects without interim progress indicators.
Cost Recovery
– Expense Recovery: Revenue recognized after contract expenses are covered.
– Conservative Method: Suitable for uncertain expenses or payment delays.
– Post-Expense Income: Only remaining revenue is marked as income.
Instalment
– Payment-Based: Revenue is recognized as payments are received.
– Example: For a £1,200 item paid in £100 monthly instalments, recognize £100 monthly.
– Risk Mitigation: Accounts for potential non-payment.
Common terms you need to know to understand Revenue Recognition
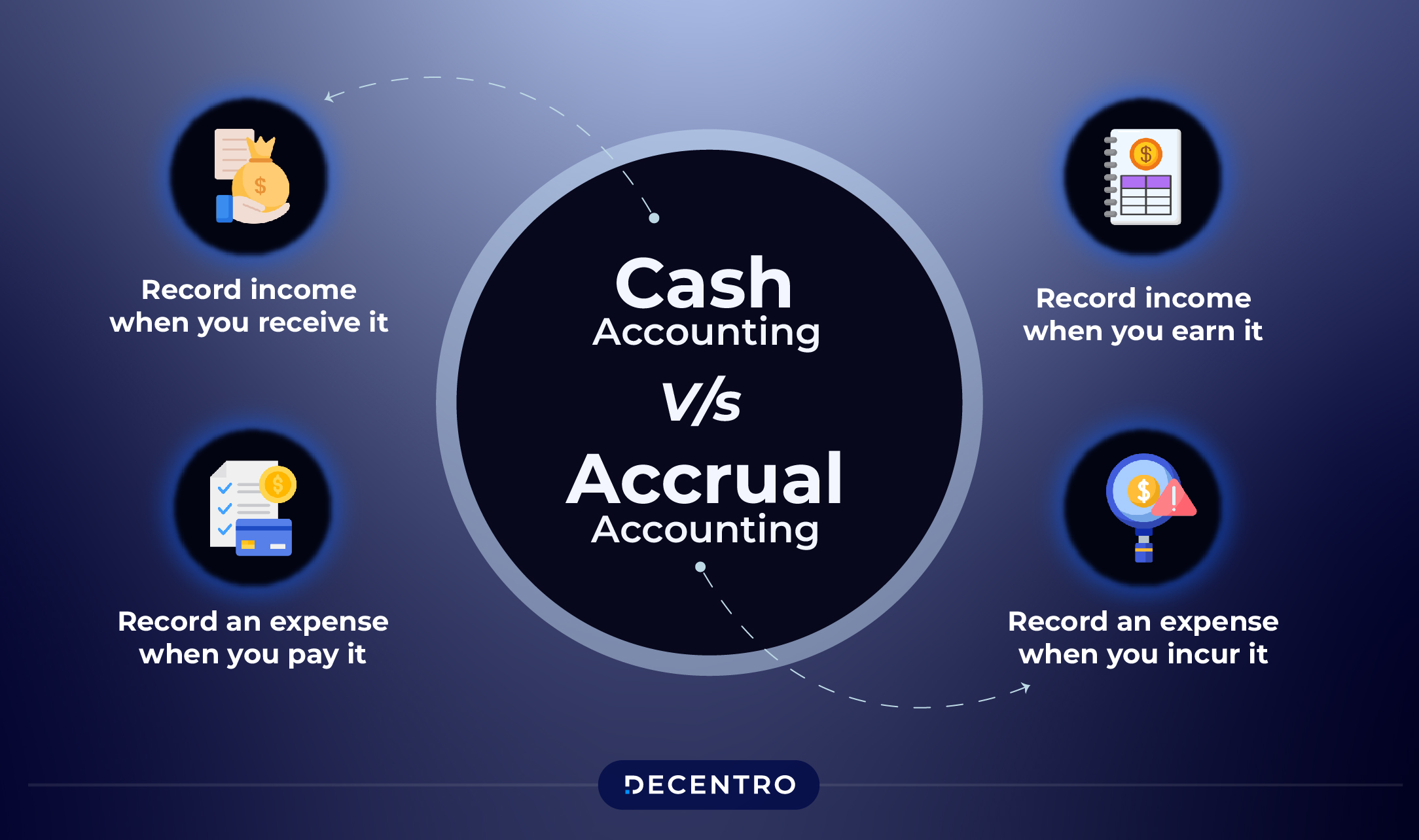
- Cash Accounting: Revenue and expenses are recorded only when cash is received or paid out. This provides a clear view of cash flow but does not necessarily reflect the actual financial position over time.
- Accrual Accounting: Revenue and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash is exchanged, providing a more accurate picture of a company’s financial health over time.
- Matching Principle: Record expenses in the same period as the related revenues to accurately reflect company performance, a key aspect of accrual accounting.
- Revenue Recognition Principle: GAAP dictates when and how businesses record revenue in their financial statements.
- International Accounting Standards Board (IASB): An independent board that sets accounting standards for publicly listed companies in 144 countries, though some countries like the US, India, and China may not follow them.
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): Standards and principles developed by the IASB to ensure consistency across markets, economies, industries, and businesses, and are less specific than GAAP.
- IFRS 15: International guidelines by the IASB for a unified revenue recognition process, enhancing comparability across markets, industries, and business models.
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): The nonprofit organization that sets and maintains US GAAP rules for both for-profit and nonprofit organizations.
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP): Standard accounting rules required by the FASB for businesses that don’t meet the IRS definition of a small business in the US.
- ASC 606: US guidelines by the FASB for a unified revenue recognition process to enhance comparability across markets, industries, and business models.
- Performance Obligation: A distinct product or service the seller agrees to deliver as part of a commercial contract.
- Transaction Price: The amount of a performance obligation, including discounts and consumer rights for returns and refunds.
Core Principles of Revenue Recognition
The revenue standard for public companies took effect for annual reporting periods starting after December 15, 2017, for most calendar year-end public business entities, and in 2019 for many non-public business entities. However, in June 2020, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) deferred the effective date for non-public entities that still needed to issue or make available their financial statements reflecting the adoption of the standard. These entities can now adopt the standard for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019, and for interim reporting periods within annual reporting periods starting after December 15, 2020. The IASB made its standards listed in IFRS 15 effective for financial statements issued on or after January 1, 2018.
As mentioned earlier, revenue recognition is part of accrual accounting, determining when and how businesses recognise revenue. Generally, revenue recognition is fairly straightforward. However, it can get extremely complicated when a company needs more product production time. As a result, there are several situations in which the revenue recognition principle can be exceptions. Therefore, financial analysts prefer having a standard revenue recognition guideline to ensure an apples-to-apples comparison between companies when reviewing line items on any company’s income statement.
Accounting Standards Codification 606
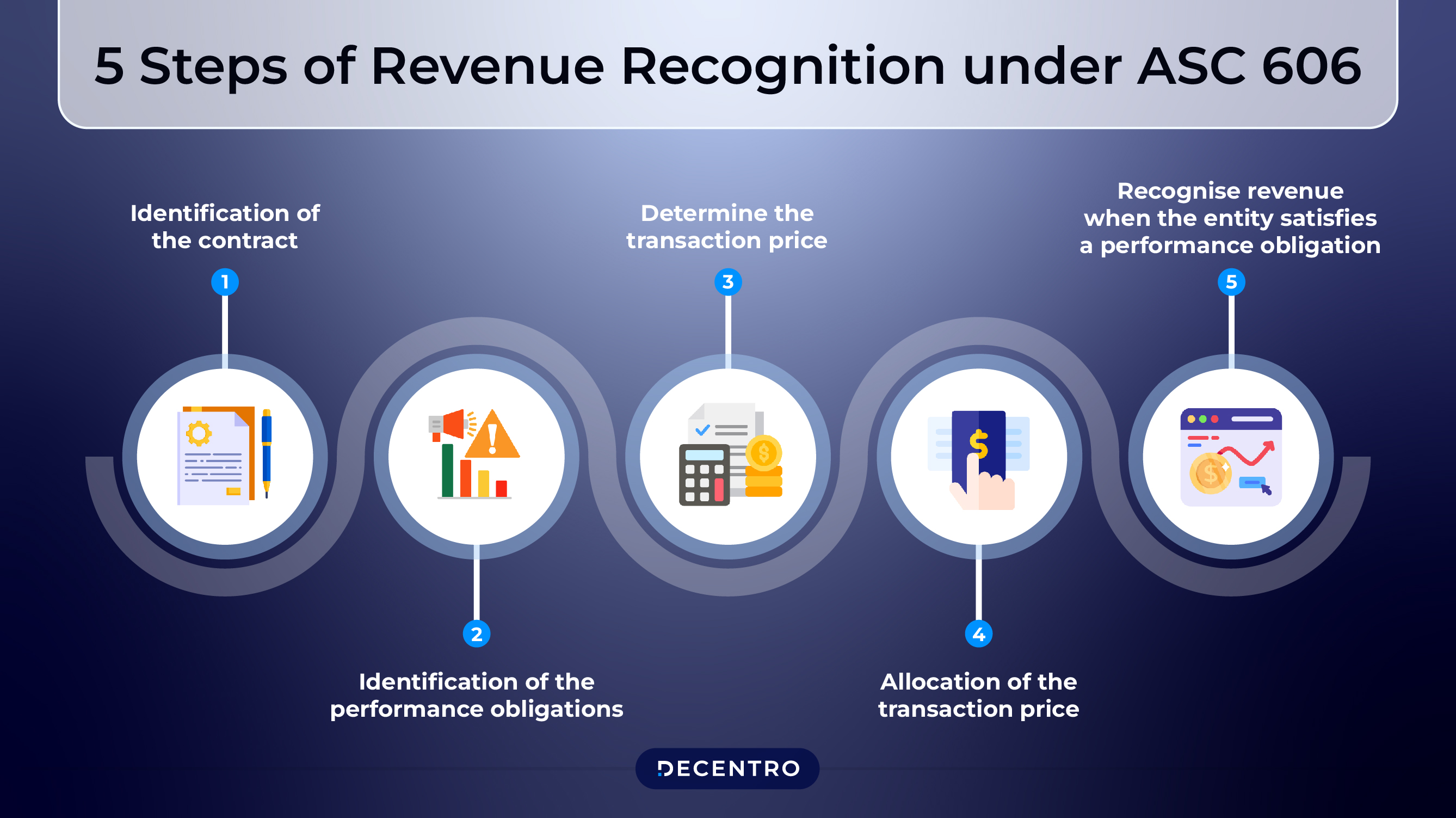
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) jointly issued Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, providing a uniform set of guidelines for revenue recognition.
5 Steps of Revenue Recognition under ASC 606:
- Identification of the contract
- Identification of the performance obligations
- Determine the transaction price
- Allocation of the transaction price
- Recognise revenue when the entity satisfies a performance obligation
IFRS Reporting Criteria
Businesses must meet certain conditions as per IFRS requirements. The table below highlights the three different categories for the requirements:
| Performance | Collectability | Measurability |
| Transferring the risk and reward from the seller to the buyer | A reasonable assurance about the collection of payment. | Easy measurement of the amount of revenue. |
| Loss of control over the goods sold by the seller. | Easy measurement of the cost of revenue. |
- Performance: The seller has mostly completed what they promised to do to get paid.
- Collectability: The seller expects to receive payment.
- Measurability: The seller can match the expenses with the revenue earned from the transaction, following the matching principle.
Implementing Revenue Recognition in Your Business

Implementing revenue recognition in your business is essential for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. Follow these steps based on ASC 606 to ensure a smooth and effective implementation:
1. Identify Contracts with Customers:
– Clearly document all agreements and contracts with your customers.
– Ensure each contract specifies the terms and conditions, including the goods or services to be provided.
2. Define Performance Obligations:
– Break down the contract into distinct performance obligations or promises to deliver goods or services.
– Identify what you need to fulfil to meet your contractual commitments.
3. Determine the Transaction Price:
– Establish the total amount of consideration you expect to receive from the customer.
– Consider any variable elements such as discounts, rebates, or performance bonuses.
4. Allocate the Transaction Price:
– Assign the transaction price to each performance obligation based on their relative standalone selling prices.
– Ensure the allocation reflects the value delivered to the customer.
5. Recognize Revenue as Performance Obligations are Fulfilled:
– Record revenue as you satisfy each performance obligation.
– This may be at a point in time (e.g., product delivery) or over time (e.g., providing a service over a period).
6. Ensure Compliance with Accounting Standards:
– To maintain consistency and transparency, adhere to relevant accounting principles, such as GAAP or IFRS.
– Regularly review and update your revenue recognition policies to stay compliant with any regulation changes.
7. Enhance Financial Reporting:
– Accurate revenue recognition leads to more reliable financial statements, reflecting your true financial performance.
– Provide stakeholders and investors with a clear, honest view of your earnings and financial health.
8. Improve Decision-Making:
– With precise revenue data, you can make better-informed business decisions.
– Use the insights gained from accurate revenue recognition to plan and strategize effectively.
9. Manage Cash Flow More Effectively:
– Align your revenue recognition with your expenses to better manage cash flow.
– Ensure that your financial planning accounts for the timing of both revenue and expenses.
10. Build Trust with Stakeholders:
– Transparent and consistent revenue recognition practices build trust with investors, customers, and other stakeholders.
– Demonstrate your commitment to financial integrity and sound business practices.
Following these steps, you can implement a robust revenue recognition process that will support your business’s long-term financial stability and growth.
Common Types of Revenue Recognition
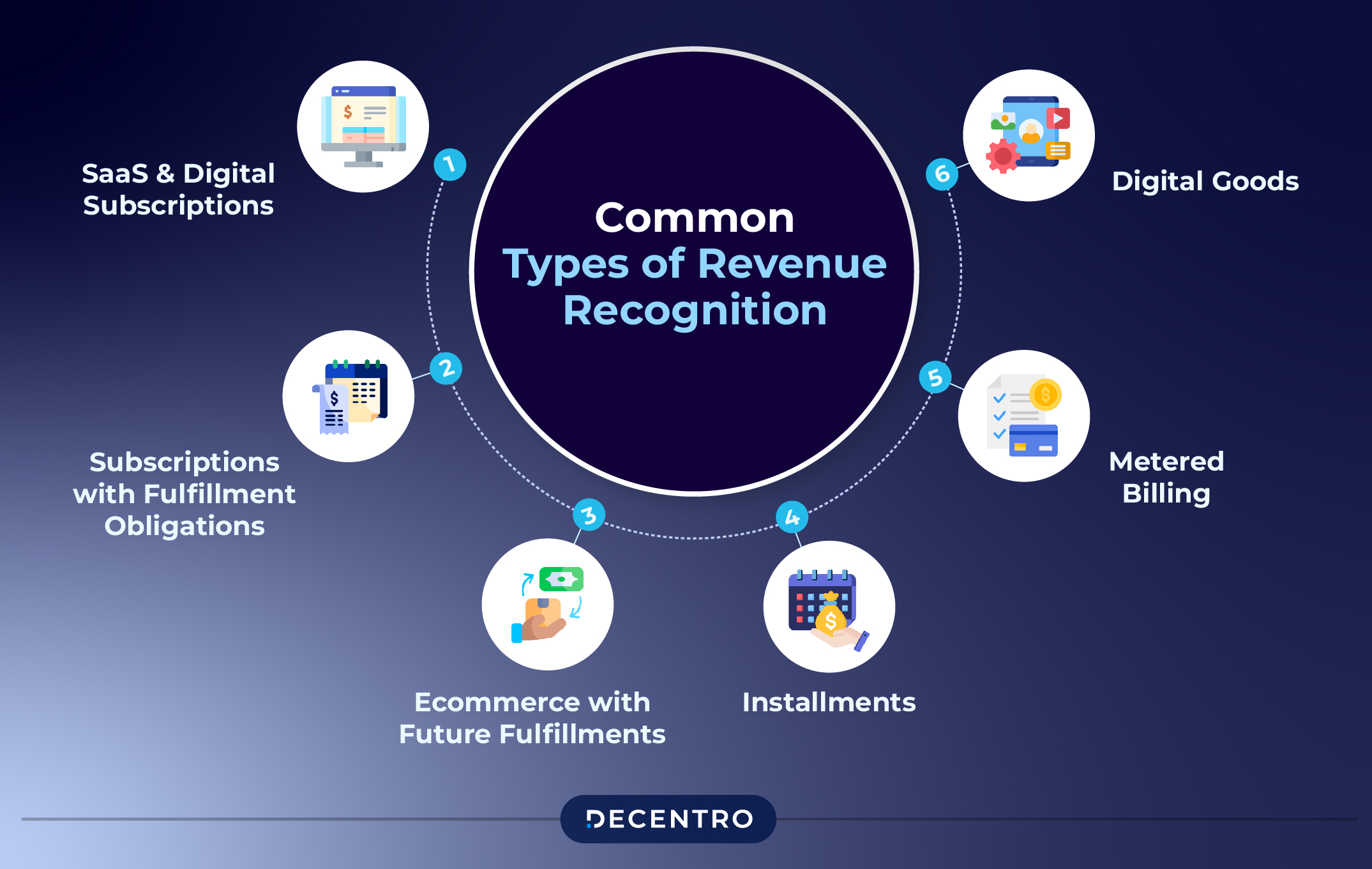
- SaaS and Digital Subscriptions:
- Recognize revenue linearly over the service period (e.g., Netflix, Slack).
- Account for upgrades, downgrades, prorations, and cancellations.
- Subscriptions with Fulfillment Obligations:
- Recognize revenue when performance obligations are fulfilled (e.g., weekly snack box delivery).
- Assess setup or consulting fees separately from recurring fees.
- E-commerce with Future Fulfillments:
- Recognize revenue when controlling transfers at shipment or delivery.
- Payment may be received before delivery, but revenue is recorded upon fulfilment.
- Installments:
- Recognize revenue when the product/service is provided, not when payment is received.
- Record revenue upfront for instalment payment plans (e.g., buy now, pay later).
- Metered Billing:
- Pre-paid: Recognize revenue as customers use prepaid credits (e.g., exercise classes).
- Post-paid: Recognize revenue according to usage and bill in arrears (e.g., cloud storage).
- Digital Goods:
- Recognize revenue immediately upon delivery (e.g., e-books, music, movies).
- Differ from subscription services by allowing immediate possession and usage of digital products.
How Decentro’s Ledgers Facilitates Revenue Recognition
Decentro’s Ledgers module is a powerful, scalable system of record for all transactions and balances for all your business requirements. Decentro’s Ledgers API offers a powerful solution for businesses seeking to enhance their revenue recognition process.

Decentro’s Ledgers API provides a seamless and automated way to manage financial transactions, ensuring accurate and timely revenue recording. This advanced tool helps businesses track performance obligations, match expenses with revenue, and maintain compliance with accounting standards.
Decentro’s Ledgers API can help businesses with:
1. Automated Revenue Tracking: Decentro’s Ledgers module automates revenue tracking, ensuring precise and real-time recording of all financial transactions, reducing manual errors and saving time.
2. Compliance with Standards: The module aligns with GAAP and IFRS requirements, guaranteeing that businesses maintain compliance with regulatory standards and avoid potential legal complications.
3. Real-time Updates: It enables businesses to efficiently track payments in real time, ensuring revenue is recognized accurately as soon as obligations are fulfilled.
4. Expense Matching: The module facilitates the matching of expenses with corresponding revenue, adhering to the matching principle and providing a clear view of financial health.
5. Enhanced Financial Reporting: Decentro’s Ledgers module improves the accuracy and reliability of financial reports by providing detailed and organized ledger data, supporting better strategic decision-making.
Decentro x Automa8e – Building Revenue Recognition for Growth
Automa8e, a company known for its innovative dashboard product that helps customers record and visualize purchase and sales transactions, is taking a significant step forward in enhancing its revenue recognition process by integrating with Decentro’s Ledgers API module. The Ledgers module is a part of our cross-border stack and can help businesses streamline financial operations, improve accuracy, and ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Purchase Flow Enhancement (Buyer Side)
Automa8e’s customers currently manage their purchases through the dashboard by uploading purchase orders or invoices, which are then reflected as pending payments. Automa8e will integrate with Decentro’s Create Beneficiary and Initiate Payout APIs to further streamline this process. Here’s how the enhanced flow works:
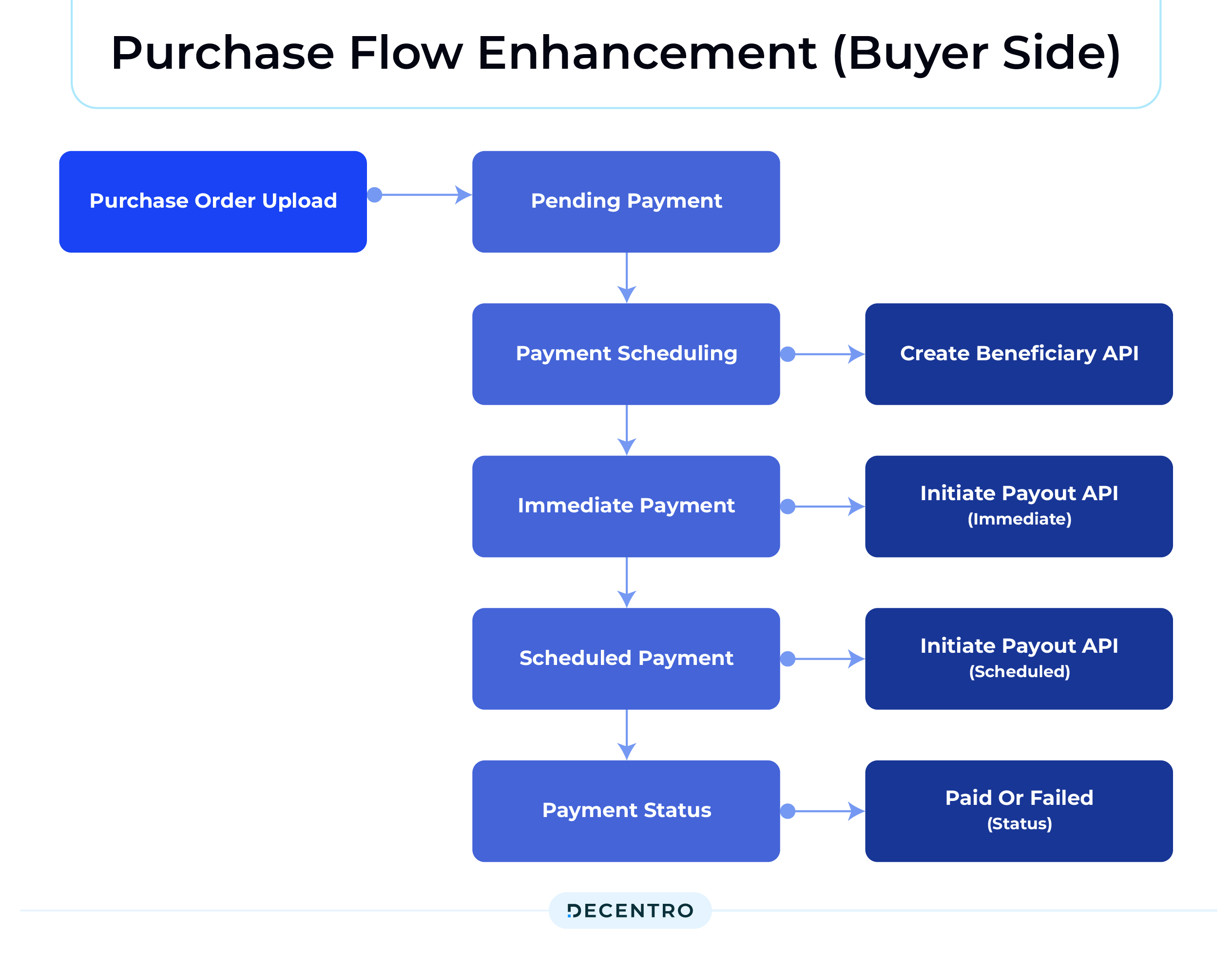
1. Purchase Order Upload: The purchase order is uploaded to the Automa8e dashboard. This invoice then appears as a pending payment.
2. Payment Scheduling: Customers can make the payment immediately or schedule it for a future date. They provide beneficiary details on the dashboard, which triggers Decentro’s Create Beneficiary API.
3. Immediate or Scheduled Payments:
– Immediate Payment: If the customer chooses to pay right away, Automa8e executes Decentro’s Initiate Payout API instantly.
– Scheduled Payment: Automa8e builds a scheduling logic to execute the Initiate Payout API at the designated time for future payments.
4. Status Updates: The invoice status changes from Pending to In Transit after initiating the payout. Depending on the outcome, the invoice status is updated to Paid or Failed.
Sales Flow Enhancement (Seller Side)
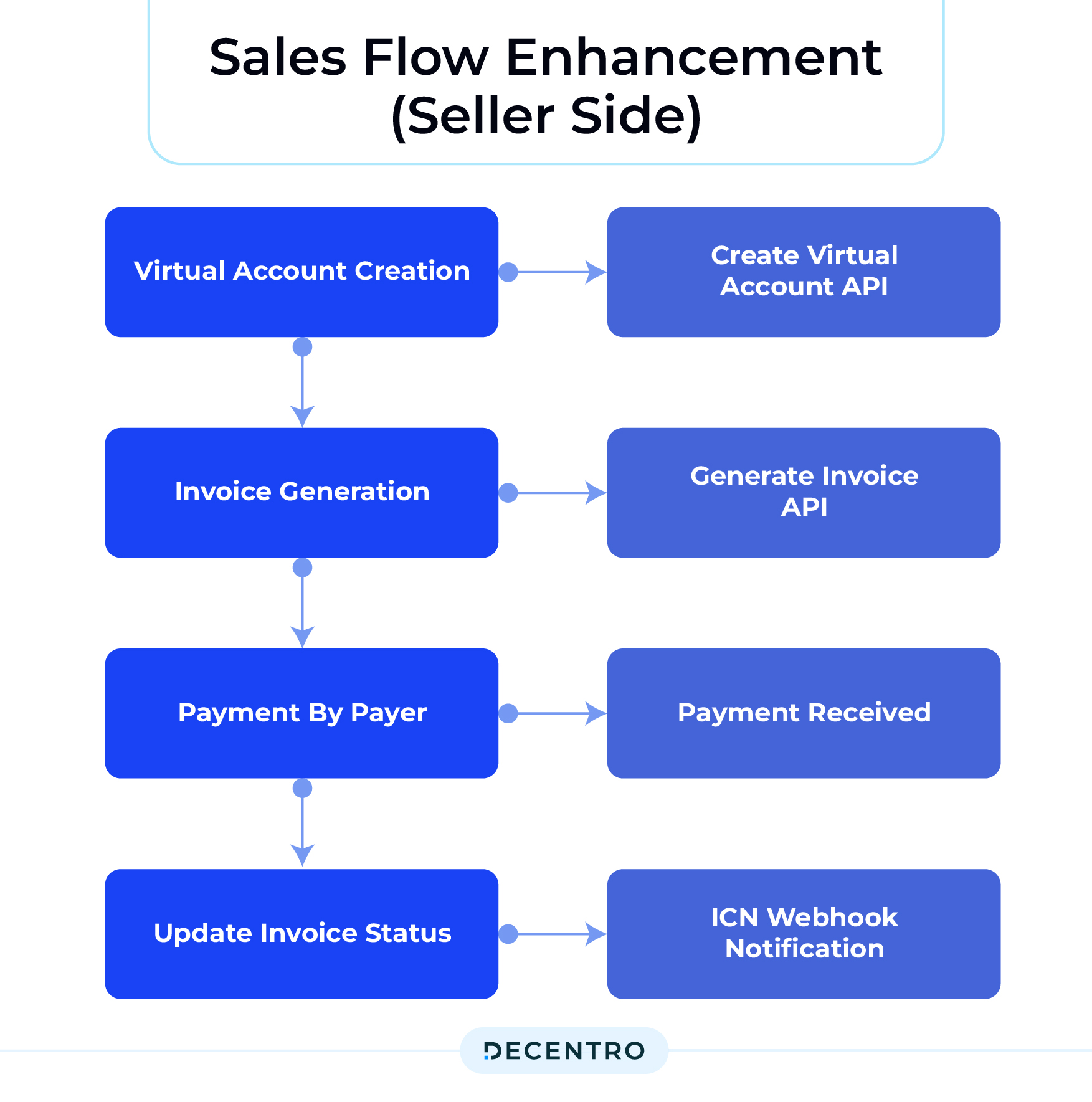
On the seller side, Automa8e will integrate with Decentro’s Virtual Account and Invoice Generation APIs, along with the ICN webhook, to automate and enhance their revenue collection process:
1. Virtual Account Creation: Automa8e’s customers create a virtual account using Decentro’s Create Virtual Account API for each payer. This step is crucial for segregating and managing payments efficiently.
2. Invoice Generation: Customers then generate an invoice using Decentro’s Generate Invoice API, including the virtual account details. The invoice is shared with the payer, who pays via their mobile or net banking app.
3. Payment Notification and Status Update: Once the payment is received in the virtual account, Decentro sends an ICN webhook notification to Automa8e. The dashboard updates the sales invoice status from Pending to Success, providing real-time visibility into payment statuses.
By integrating with Decentro’s robust API suite, Automa8e is poised to enhance its revenue recognition process significantly. This collaboration ensures that Automa8e can offer its customers an automated, accurate, and efficient way to manage financial transactions, from purchase orders to sales invoices. By leveraging Decentro’s technology, Automa8e improves operational efficiency and strengthens its financial reporting and compliance, paving the way for sustained business growth.
Best Practices for Effective Revenue Recognition

An organisation of any scale should follow some best practices associated with revenue recognition. These are:
1. Adopt Standardized Processes: Implement standardized revenue recognition procedures in compliance with GAAP or IFRS. This ensures consistency and accuracy in financial reporting across all transactions.
2. Document Performance Obligations: Clearly define and document performance obligations in contracts. This helps accurately determine when revenue should be recognized as each obligation is fulfilled.
3. Allocate Transaction Prices Appropriately: Allocate the transaction price to each performance obligation based on their relative standalone selling prices. This ensures that revenue is recognized in proportion to the value delivered.
4. Regularly Review and Update Policies: Continuously review and update revenue recognition policies to reflect changes in business models, market conditions, and regulatory requirements. This keeps the practices relevant and compliant.
5. Utilize Technology for Automation: Leverage accounting software and APIs to automate revenue recognition processes. Automation reduces the risk of errors, enhances efficiency, and provides real-time insights into revenue streams.
Future Trends
The future of revenue recognition is set to be transformed by automation, advanced analytics, and real-time financial reporting. Emphasizing compliance and cross-department collaboration, these trends will help businesses achieve greater accuracy and efficiency in their financial processes.
- Increased Automation: Adopting advanced automation tools and artificial intelligence (AI) is set to revolutionize revenue recognition. Automated systems will streamline processes, reduce manual errors, and provide real-time updates, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
- Greater Emphasis on Compliance: With evolving regulatory landscapes, there will be a stronger focus on compliance with accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS. Companies must stay updated with changes and implement robust compliance frameworks to avoid penalties and ensure transparency.
- Real-time Financial Reporting: The demand for real-time financial reporting is expected to grow. Companies will adopt technologies that enable instant access to financial data, allowing for timely decision-making and improved financial management.
- Focus on Customer-centric Metrics: Revenue recognition will increasingly incorporate customer-centric metrics such as customer lifetime value (CLV) and recurring revenue. This shift will help businesses better understand and manage their revenue streams based on customer behaviour and engagement.
- Customization for Diverse Business Models: As business models become more diverse and complex, revenue recognition practices must be more flexible and customizable. Solutions tailored to specific industries and business structures will become increasingly important.
By embracing these trends, companies can stay ahead of the curve, ensuring their revenue recognition practices are efficient, compliant, and aligned with the latest technological advancements.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, effective revenue recognition is critical for maintaining financial integrity and supporting sustainable business growth. Businesses can streamline their financial operations and enhance accuracy by understanding and implementing best practices, leveraging advanced technologies like Decentro’s Ledgers module, and staying compliant with evolving standards.
As revenue recognition practices continue to evolve with increased automation, real-time reporting, and customer-centric metrics, companies like Automa8e, through their integration with Decentro, are well-positioned to navigate these changes and achieve greater efficiency and transparency in their financial processes.
Transform Your Revenue Management
Frequently Asked Questions
ASC 606 offers a comprehensive and impartial method for acknowledging revenue. This model mandates businesses to acknowledge their revenue when they have rendered a service to the client.
Revenue recognition is more than just compliance; it benefits your business by ensuring consistent financial reporting. This consistency allows you to compare current financials with past ones accurately. It also makes comparing your performance with competitors easier, helping you gauge your standing in the market.
Yes, small businesses should understand revenue recognition. Even if they aren’t required to follow GAAP, doing so can boost credibility with lenders and investors. GAAP-compliant financial statements make it easier to secure financing, often at a lower cost, helping businesses grow and expand.
When a customer pays for a subscription upfront, we generally consider it deferred revenue. The company receives the money immediately, but the service is distributed over a period of time. Therefore, we count this payment as deferred revenue.
Under ASC 606 and IFRS 15, SaaS companies must provide specific business operations details. These disclosures include:
Pricing Methods: How they price software licenses when sold individually.
Performance Obligations: Identification of performance obligations in deals involving both on-site and cloud services.
Contract Terms: Assessment of varying considerations and terms for terminating contracts.
Contract Acquisition Costs: Inclusion of certain contract acquisition costs in their capital accounts.
Backlog Disclosures: Details about any backlog disclosure requirements.
These steps ensure transparency and clarity in the company’s revenue recognition practices.


