Understand the top types of insurance fraud and how modern technology, behavioral analytics, and strong controls help insurers and fintechs reduce fraud effectively.
Types of Insurance Fraud in India (and How to Detect Them)
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents
India’s insurance sector is experiencing unprecedented growth. The market is projected to reach a market size (gross written premium) of US$246.93bn in 2026, which reflects the country’s economic momentum and expanding middle class.
But beneath this explosive growth lies a darker reality: fraud is scaling just as fast as the market itself.

According to Deloitte’s Insurance Fraud Survey 2023, fraud has surged dramatically across life and health insurance categories. The primary culprits? Increased digitisation (responsible for 34% of fraud incidents), remote working environments post-pandemic (22%), and weakened internal controls (22%). For an industry processing millions of new policies annually and also in a single day, a case in point, Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) has secured a Guinness World Record by selling 5,88,107 life insurance policies in a single day, January 20, 2025. These percentages translate into staggering losses.
For fintech founders and digital business builders, this isn’t just an insurance industry problem—it’s a problem for you too. If you’re building embedded insurance products, digital lending platforms, or any financial service that touches insurance, understanding these fraud patterns isn’t about compliance checkbox-ticking. It’s about survival.
The Fraud Landscape: Understanding What You’re Up Against
Insurance fraud in India isn’t limited to individual bad actors trying to game the system. It’s a sophisticated ecosystem involving organised crime rings, corrupt intermediaries, and increasingly tech-savvy criminals who’ve learned to exploit the very digital systems meant to improve customer experience.
The impact extends far beyond direct losses. Fraud inflates premiums for honest customers, erodes trust in the financial system, creates regulatory nightmares for businesses, and gives fraudsters the capital to fund even more sophisticated schemes. It’s a vicious cycle that threatens the entire ecosystem.
The Five Fraud Types Costing the Industry Billions
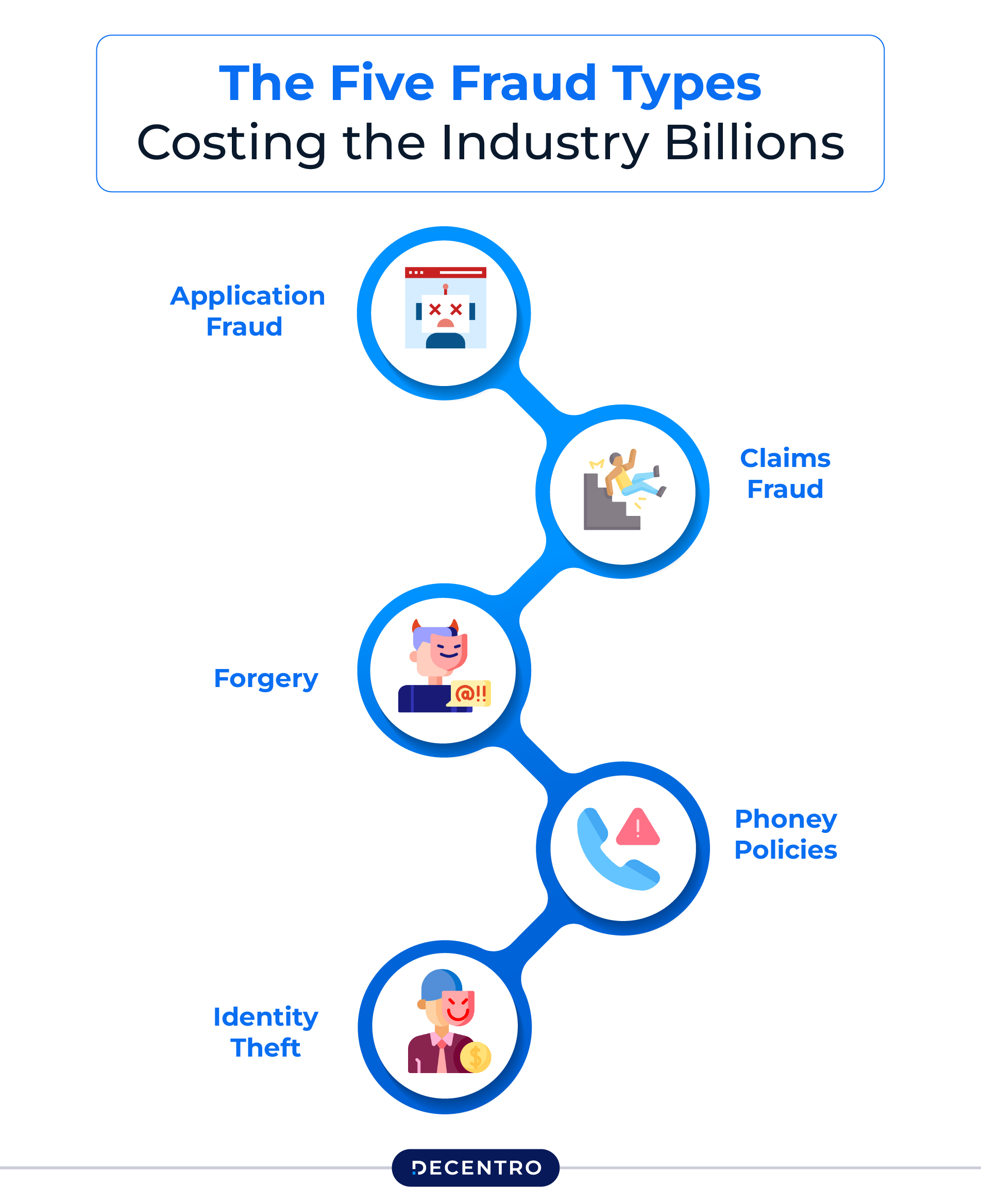
1. Application Fraud
Application fraud, also called material misrepresentation, occurs when policyholders intentionally lie during onboarding. This might seem like a victimless crime when someone conceals that they smoke or understates their age to get better rates. But when claims arise, these lies create massive problems.
Common schemes include concealing pre-existing medical conditions to secure health or life insurance, misrepresenting income levels to access higher coverage amounts, providing false information about risky occupations or lifestyle choices, and falsifying age to receive more favorable premium rates.
The challenge for digital platforms? Application fraud is nearly impossible to detect using traditional verification methods alone. A fraudster with basic document manipulation skills can create seemingly legitimate proof of income, fabricate employment letters, and present a clean medical history. By the time the fraud is discovered, years later, when a claim is filed, the losses have already compounded.
2. Claims Fraud
Claims fraud represents the most visible and financially devastating category. This is where fraudsters get creative, staging elaborate schemes to extract payouts they’re not entitled to.
The spectrum ranges from opportunistic to organised crime. On the lower end, you have individuals exaggerating minor vehicle damage on claims or inflating medical bills for treatments they did not receive. In the end, you have organised rings staging murders, faking deaths, kidnapping scenarios, or creating entirely fictitious accidents involving multiple “victims” and complicit medical providers.
Multi-claim fraud, the filing of multiple claims with different insurers for the same loss, has become increasingly common in the digital age. Without robust information sharing between insurers, a fraudster can submit the same vehicle damage claim to three different providers, tripling their payout while leaving each insurer unaware they’re being conned.
For fintech platforms offering embedded insurance or facilitating insurance distribution, claims fraud creates a particular challenge: how do you balance fraud prevention with the seamless, instant-gratification experiences that modern customers expect?
3. Forgery
Forgery fraud carries a particularly sinister edge because it typically involves family members or close associates betraying the trust of policyholders. These fraudsters alter policy documents without the owner’s knowledge, changing beneficiary names, increasing death benefit amounts, or modifying policy terms to redirect payouts to themselves.
This fraud type often surfaces only after the policyholder’s death, when legitimate beneficiaries attempt to claim benefits and discover they’ve been systematically written out. By then, the trail is cold, evidence is scarce, and the fraudster has often already collected the money and disappeared.
In digital platforms, fraud underscores the importance of multi-factor authentication, secure document management, and change-verification systems that alert policyholders to critical policy modifications.
4. Phoney Policies
The explosion of online insurance purchases has created fertile ground for phoney policy fraud. Scammers create convincing fake websites that mimic legitimate insurers, complete with professional design, customer testimonials, and official-looking documentation. They promise below-market premiums, special bonuses, or exclusive loan offers to lure victims.
The scammer pockets the premium payments, and victims discover too late, usually when they try to file a claim, that their “coverage” is worthless. By then, the fake website has disappeared, the phone numbers are disconnected, and the fraudster is running the same scam under a different name.
This fraud type poses a particular risk for fintech aggregators and comparison platforms. If your platform inadvertently promotes or partners with a phoney provider, the reputational damage and potential legal liability can be catastrophic, even if you were an unwitting accomplice.
5. Identity Theft
Identity theft in insurance has evolved from crude document forgery to sophisticated digital operations. Criminals harvest Aadhaar numbers, PAN cards, bank details, and other personal information through data breaches, phishing schemes, and social engineering. They then use this stolen information to purchase policies, file fraudulent claims, or collect benefits they’re not entitled to.
India’s rapid digitisation in the tryst of bringing financial services to millions has also created unprecedented opportunities for identity fraudsters. A single data breach can expose thousands of records, providing fraudsters with everything they need to create convincing fake identities at scale.
For fintech companies, identity theft represents an existential risk. If your platform becomes known as an easy target for identity fraudsters, you’ll face regulatory scrutiny, customer exodus, and potentially ruinous legal liability.
The Hidden Costs: Why Every FinTech Should Care
If you’re thinking, “I’m not an insurance company, why should this matter to me?” think again.
The Cost Spillover Effect
When fraud drives up claim ratios, insurers raise premiums across the board. If your fintech offers embedded insurance, partners with insurance providers, or integrates insurance into your product experience, those cost increases flow directly downstream to you. Your unit economics deteriorate, your product becomes less competitive, and your customers end up paying more, all because of fraud you didn’t commit.
Reputational Quicksand
Reputation is everything in fintech. Suppose your platform facilitates even a handful of fraudulent transactions, whether knowingly or unknowingly, you risk regulatory investigation, media exposure, and erosion of customer trust. In an industry where customers are entrusting you with their financial well-being, a fraud scandal can be fatal.
The Compliance Trap
IRDAI’s 2025 framework doesn’t just apply to insurance companies; it affects the entire ecosystem. If you’re in the distribution chain, you’re expected to implement fraud monitoring, maintain documentation, report suspicious activities, and demonstrate due diligence. The compliance burden is real, and non-compliance brings financial penalties and operational restrictions that can cripple a growing startup.
Competitive Erosion
Here’s the harsh reality: companies that can’t effectively detect and prevent fraud will suffer higher losses, slower onboarding, and poorer customer experiences than competitors with sophisticated fraud-prevention systems. In a market where customer acquisition costs are already high, you can’t afford to lose customers to friction or lose money to fraud.
The Regulatory Hammer: IRDAI 2025 Framework
Recognising the escalating threat, IRDAI released comprehensive Insurance Fraud Monitoring Framework Guidelines in 2025, replacing the outdated 2013 framework. The new regulations, effective April 1, 2026, represent the most significant regulatory tightening in over a decade.
Key provisions include:
- Zero-tolerance policy: All insurers and distribution channels must adopt an explicit zero-tolerance stance toward fraud.
- Dedicated oversight bodies: Establishment of Fraud Monitoring Committees and Fraud Monitoring Units with quarterly board reporting requirements.
- Board-approved Anti-Fraud Policy: Insurers must implement comprehensive, board-approved policies with annual fraud risk assessments.
- Five fraud categories: The framework explicitly covers internal fraud, claims fraud, distribution-related fraud, cyber fraud, and digital fraud.
- Industry-wide intelligence sharing: Insurers must contribute fraud data to the Insurance Information Bureau’s Fraud Monitoring Technology Framework, creating a collective “caution repository” of blacklisted entities.
- Compressed reporting timelines: Immediate notification to law enforcement when legally warranted and annual statutory returns within 30 days of fiscal year-end.
This regulatory tightening sends a clear message: India’s insurance industry is taking fraud seriously, and businesses operating in this space must invest in robust detection and prevention systems.
Beyond Basic KYC: The Behavioural Intelligence Revolution
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: traditional Know Your Customer processes and static credit scores can no longer catch sophisticated fraudsters.
Modern fraud rings have industrialised the process of creating fake identities. They know which documents to forge, which employment stories to tell, and which financial profiles pass basic verification. They’ve studied your onboarding process and identified exactly where the gaps are.
This is where behavioural intelligence fundamentally changes the game. Instead of asking “who does this user claim to be?”, behavioural analytics asks “how does this user actually behave?”
Key risk factors to monitor include:
- Transaction patterns and anomalies
- Geographic risks associated with specific jurisdictions
- Business type and industry susceptibility to fraud
- Source of wealth verification
- PEP involvement and association
- Digital identity consistency across touchpoints
- Employment stability and verification
- Device intelligence and behavioural biometrics
For businesses building insurance distribution platforms, digital lending products, or embedded financial services, integrating behavioural risk scoring is now almost a blueprint for sustainable growth in an increasingly fraud-prone digital environment.
How Modern Technology is Fighting Back
Leading fintech companies are deploying advanced fraud detection systems that go far beyond traditional approaches. These systems leverage document forensics for instant forgery detection, text and name forensics with phonetic and semantic analysis, behavioural biometrics to assess user interactions, and IP clustering and device intelligence to flag shared devices or location spoofing in real time.
Decentro’s Scanner and OmniScore represent this new generation of fraud prevention tools specifically designed for India’s digital financial ecosystem. Scanner provides real-time fraud detection and comprehensive user intelligence across banking, fintech, and e-commerce sectors.

At its core is OmniScore, a proprietary scoring system that analyses over 100 behavioural signals in real time to deliver a dynamic, 360-degree view of user trustworthiness. Unlike traditional credit scores that rely on historical data, OmniScore integrates three distinct intelligence layers: digital identity evaluatio,n examining mobile number usage and location patterns, financial credibility analysis of banking and credit-related data, and employment stability verification through multi-source validation.
Early results demonstrate significant impact:
- Leading NBFCs reduced application fraud by 22-25%.
- Fintech lenders achieved 30-45% better underwriting accuracy and reduced defaults
- E-commerce and gaming platforms saw checkout fraud drop by 15-18%.
Building Your Fraud Defence: Practical Steps
Layer Your Verification Defences
Single-point verification is dead. Modern fraud prevention requires combining document verification (checking that IDs are legitimate and unaltered), behavioural analytics (monitoring how users interact with your platform), device intelligence (tracking device reputation and detecting device farms), and database cross-referencing (comparing user information against industry fraud databases and public records).
Implement Real-Time Monitoring
Risk assessment can’t be a one-time event at onboarding. Deploy machine learning algorithms that monitor transactions continuously, flagging unusual patterns before losses occur. Watch for sudden changes in behaviour, location shifts, device switches, or changes in transaction patterns that might signal account takeover or fraud evolution.
Deploy Advanced Risk Scoring
Integrate behavioural risk scoring that analyses hundreds of signals in real-time. Modern systems examine digital identity consistency (mobile number usage patterns, email age and activity, social media footprints), financial credibility indicators (banking transaction patterns, credit utilisation, repayment histories), and employment stability markers (income consistency, employer verification, professional network validation).
Enable Rapid Response
When fraud is detected, speed matters. Implement systems that enable swift merchant-initiated refunds for confirmed fraudulent transactions, maintain flexible dispute-resolution processes, and establish clear escalation paths for high-risk scenarios. Quick response not only minimises losses but also demonstrates to customers that you take security seriously.
Share Intelligence Actively
Join industry fraud databases and information-sharing initiatives. The Insurance Information Bureau’s Fraud Monitoring Technology Framework creates a collective defence; a fraudster rejected by one platform will be flagged across the ecosystem. This network effect dramatically increases the cost of fraud and reduces criminals’ success rates.
Educate Your Users Continuously
Transparency builds trust. Clearly communicate what information you collect, why you need it, and how it protects users. Teach customers to recognise phishing attempts, explain why you’ll never ask for OTPs or passwords, and provide clear channels for reporting suspicious activity. An educated user base becomes your first line of defence.
Insurance-Specific Fraud Prevention Measures
For insurance providers, additional safeguards are essential given the unique vulnerabilities in the claims process:
Strengthen Claims Verification
Implement multi-stage claims authentication that includes cross-verification of medical records with healthcare providers, validation of treatment dates and costs against hospital databases, and photographic or video evidence requirements for damage claims. Use AI-powered image analysis to detect manipulated documents or staged damage photos.
Establish Medical Review Protocols
Deploy specialised medical fraud detection units that review high-value claims, unusual treatment patterns, or multiple claims from the same provider. Cross-reference diagnoses with treatment histories to identify inconsistencies, and maintain direct relationships with healthcare facilities for rapid verification of procedures and hospitalisation claims.
Monitor Agent and Intermediary Activity
Track agent behaviour patterns for red flags such as unusually high policy conversion rates, concentration of claims from specific agents, or patterns of policy churning. Implement mandatory training and certification renewal for intermediaries, and establish clear consequences for facilitating fraudulent applications.
Validate Policyholder Information
Go beyond basic KYC by verifying employment details directly with employers, cross-checking nominee relationships through official databases, and confirming address authenticity through utility bills or property records. For high-value policies, consider additional verification steps, such as in-person meetings or video KYC.
Deploy Pre-Authorisation Controls
For health insurance, implement robust pre-authorisation systems that require medical-necessity justification for expensive procedures. This prevents unnecessary treatments and catches fraudulent claims before costs are incurred. Maintain relationships with independent medical experts who can review complex cases.
Track Claim Frequency and Patterns
Use analytics to identify policyholders with suspiciously frequent claims, unusually high claim amounts relative to premiums paid, or claims that consistently occur near policy renewal dates. Flag policies where multiple family members make claims simultaneously or where claim timing suggests coordination.
Verify Beneficiary Authenticity
For life insurance claims, thoroughly verify death certificates against government records, confirm beneficiary identities through multiple documents, and investigate suspicious circumstances surrounding claims filed shortly after policy activation or premium increases.
Establish Fraud Reporting Mechanisms
Create confidential whistleblower hotlines for employees, agents, and customers to report suspected fraud. Protect reporters from retaliation and incentivise the provision of actionable information. Many fraud schemes are exposed by insiders who need safe channels to come forward.
Conduct Regular Fraud Audits
Perform periodic reviews of closed claims to identify fraud that slipped through initial screening. Use these findings to refine detection algorithms and training programs. Share anonymised fraud case studies across teams to build institutional awareness of evolving schemes.
Implement Cooling-Off Periods
For specific high-risk scenarios, establish waiting periods before claims can be filed on new policies. This deters fraudsters seeking immediate payouts and gives underwriting teams time to conduct thorough background checks on suspicious applications.
The Competitive Advantage of Fraud Prevention

As India’s insurance market surges over the next five years (2024‒28), the forecast that total insurance premiums will grow by 7.1% in real terms, well above the global (2.4%), emerging (5.1%) and advanced (1.7%) market averages, paints the cleat picture of the fact the winners won’t be the companies with the flashiest apps or the most significant marketing budgets. They’ll be the companies that can verify trust at scale, confidently onboard new customers, detect fraud before it happens, and build sustainable businesses that don’t bleed money to criminals.
The new IRDAI framework, combined with technological innovations in behavioural analytics and real-time risk scoring, creates an environment where fraud can be detected earlier, prevented more effectively, and prosecuted more rigorously. The tools exist. The regulatory framework is tightening. The question is whether your business will adapt fast enough.
The Bottom Line
Fraud will continue evolving. Criminals will develop new schemes, exploit new technologies, and find creative ways to game whatever systems we build. That’s guaranteed.
What’s not guaranteed is whether your business will evolve faster than the fraudsters targeting it.
For fintech founders looking to build on India’s massive insurance opportunity, the message is clear: fraud prevention is no longer a technical problem to be solved by your security team. It’s a strategic imperative that determines whether you’ll capture market share or become another cautionary tale of a promising startup that couldn’t manage its risk.
The future belongs to those who can verify trust at scale. In case you are looking to build such an infrastructure for your business, reach out to us at hello@decentro.tech
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common types of insurance fraud in India?
The five major types are: application fraud (lying during onboarding about health, income, or lifestyle), claims fraud (exaggerating or faking damages and losses), forgery (altering policy documents without the owner’s knowledge), phoney policies (fake insurance websites that collect premiums but provide no coverage), and identity theft (using stolen personal information to purchase policies or file fraudulent claims).
2. Why should fintech companies care about insurance fraud if they’re not insurers?
Fraud affects the entire financial ecosystem. When fraud drives up claim ratios, insurers raise premiums, which impacts any fintech offering embedded insurance or partnering with insurance providers. Additionally, if your platform facilitates fraudulent transactions, you face regulatory scrutiny, reputational damage, and potential legal liability. Under IRDAI’s 2025 framework, companies in the distribution chain must implement fraud monitoring and demonstrate due diligence.
3. What is the IRDAI 2025 Insurance Fraud Monitoring Framework?
Effective April 1, 2026, this comprehensive framework requires all insurers and distribution channels to adopt a zero-tolerance policy toward fraud. Key provisions include establishing dedicated Fraud Monitoring Committees, implementing board-approved anti-fraud policies, conducting annual fraud risk assessments, sharing fraud data through the Insurance Information Bureau, and maintaining compressed reporting timelines to law enforcement and regulators.
4. How does behavioral intelligence differ from traditional KYC in detecting fraud?
Traditional KYC asks “who does this user claim to be?” while behavioral analytics asks “how does this user actually behave?” Modern fraud rings can easily forge documents and create fake identities that pass basic verification. Behavioral intelligence monitors transaction patterns, geographic risks, device intelligence, digital identity consistency, and employment stability across multiple touchpoints in real-time, catching sophisticated fraud that traditional methods miss.
5. What practical steps can businesses take to prevent insurance fraud?
Implement layered verification combining document verification, behavioral analytics, device intelligence, and database cross-referencing. Deploy real-time monitoring with machine learning algorithms that flag unusual patterns. Use advanced risk scoring systems that analyze hundreds of signals simultaneously. Enable rapid response mechanisms for detected fraud. Participate in industry fraud databases and information-sharing initiatives. Finally, continuously educate users about recognizing phishing attempts and reporting suspicious activity.


