Learn about ATMs, their types, core functions, design elements, steps to withdraw and deposit money, history, and more in this comprehensive guide.

ATM: Full Form, Types, and How It Works – A Complete Guide
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

ATMs form the core of the present transactional world of finance. They simplify and automate cash withdrawals and deposits while providing 24/7 availability. This significantly reduces the time people spent at the bank for such tasks.

According to a report by CMS Infosystems, monthly average cash withdrawals from ATMs increased by 5.51% in FY-2024, reaching ₹1.43 crore. As digital banking grows, ATMs remain important in terms of access to finance for people living in remote areas who cannot reach traditional banks.
ATM: Full Form and Overview
ATM stands for “Automated Teller Machine.” The term ATM is made of “Automated,” which indicates that it functions on its own, “Teller,” which is a connection to a worker in a bank, and “Machine,” the description of the device.
It is an electronic machine that allows people to execute various banking-related activities without going to a teller in the bank. They include cash withdrawals, deposits, balance inquiries, fund transfers, and more.
Additionally, it ensures easy access and seamless handling of your bank accounts, which is even possible when banks remain closed.
Brief History of ATMs
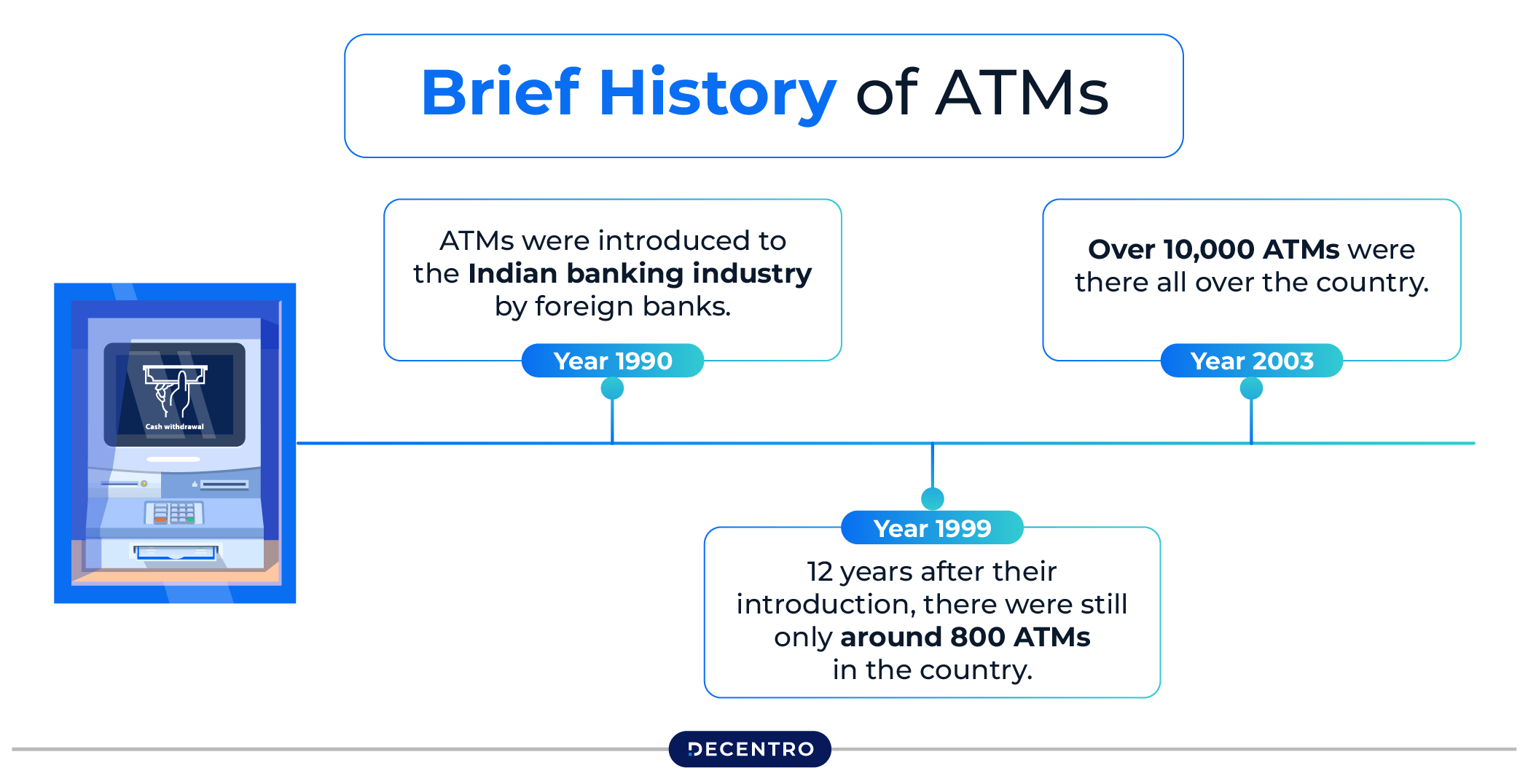
Here is a brief discussion about the historical background of ATMs and how they gained popularity among people:
- In the Beginning
The concept of ATM first came in the 1960s. In 1967, it was first introduced by the Barclays Bank in London. It was a simple machine that allowed customers to draw a certain amount of cash using a special paper voucher and a personal identification number (PIN). This new technology was intended to streamline banking operations and lessen the need for bank tellers.
- Introduction of Magnetic stripe
In the early 1970s, magnetic stripe technology revolutionised ATMs. Magnetic stripe cards meant customers could simply insert them into the machine to access their bank accounts.
It eliminated the use of traditional paper vouchers and thus improved the user experience. This technology also marked the beginning of what would come later with several advanced features.
- Connected ATMs and Shared Banking
During the late 1970s and early 1980s, banks started linking their ATMs. This new connection technology enabled ATMs to work across multiple banking systems, allowing customers to use any networked ATM. Individuals also gained access to withdraw money at multiple bank locations nationwide through this new system.
- Enhanced Features and User Experience
During the 1990s, after ATMs were upgraded, banks added enhanced features such as cash and cheque deposits, fund transfers, and bill payments. Due to these improvements, ATMs become an integral part of everyday life. The customer experience improved with large buttons, coloured and multi-touch displays, and user-friendly graphical interfaces.
What are the Functions and Uses of Automated Teller Machines?
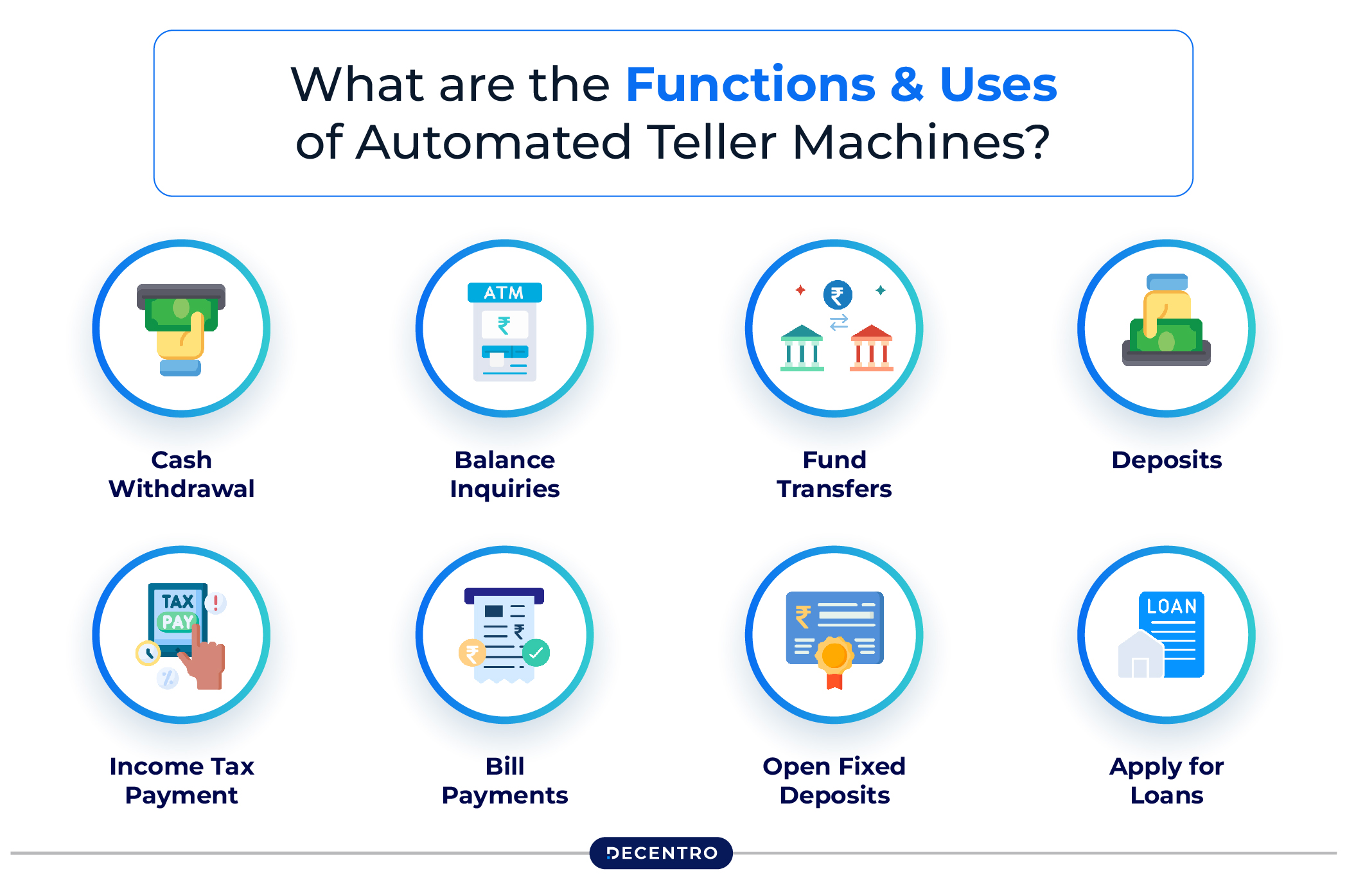
Here are the essential functions of ATMs:
- Cash Withdrawal: You can withdraw cash from an ATM using your debit or ATM card by inserting it, entering your PIN, and selecting the amount you want to withdraw.
- Balance Inquiries: ATMs allow you to check your account balance, enabling you to keep easy track of your finances.
- Fund Transfers: Many ATMs allow you to transfer funds between your accounts. This makes it easy to send money without having to go to a bank.
- Deposits: Some ATMs have deposit features so you can deposit cash or cheques directly into your account through the machine.
- Income Tax Payment: A few banking establishments help customers pay taxes using ATMs. They enable you to make payments for your advance tax, self-assessed tax, and taxes calculated by normal assessment processes.
- Bill Payments: Customers can use most ATMs to pay for utility bills, phone bills, and even mobile phone credit.
- Open Fixed Deposits: Users can open fixed deposit accounts directly from some of the ATMs. This allows them to invest their hard-earned funds at better interest rates.
- Apply for Loans: Some ATMs provide the option of applying for a loan. This function is designed to simplify the process of personal loan applications or other banking products much easier by eliminating the need to visit a bank.
Exploring the Various Types of ATMs
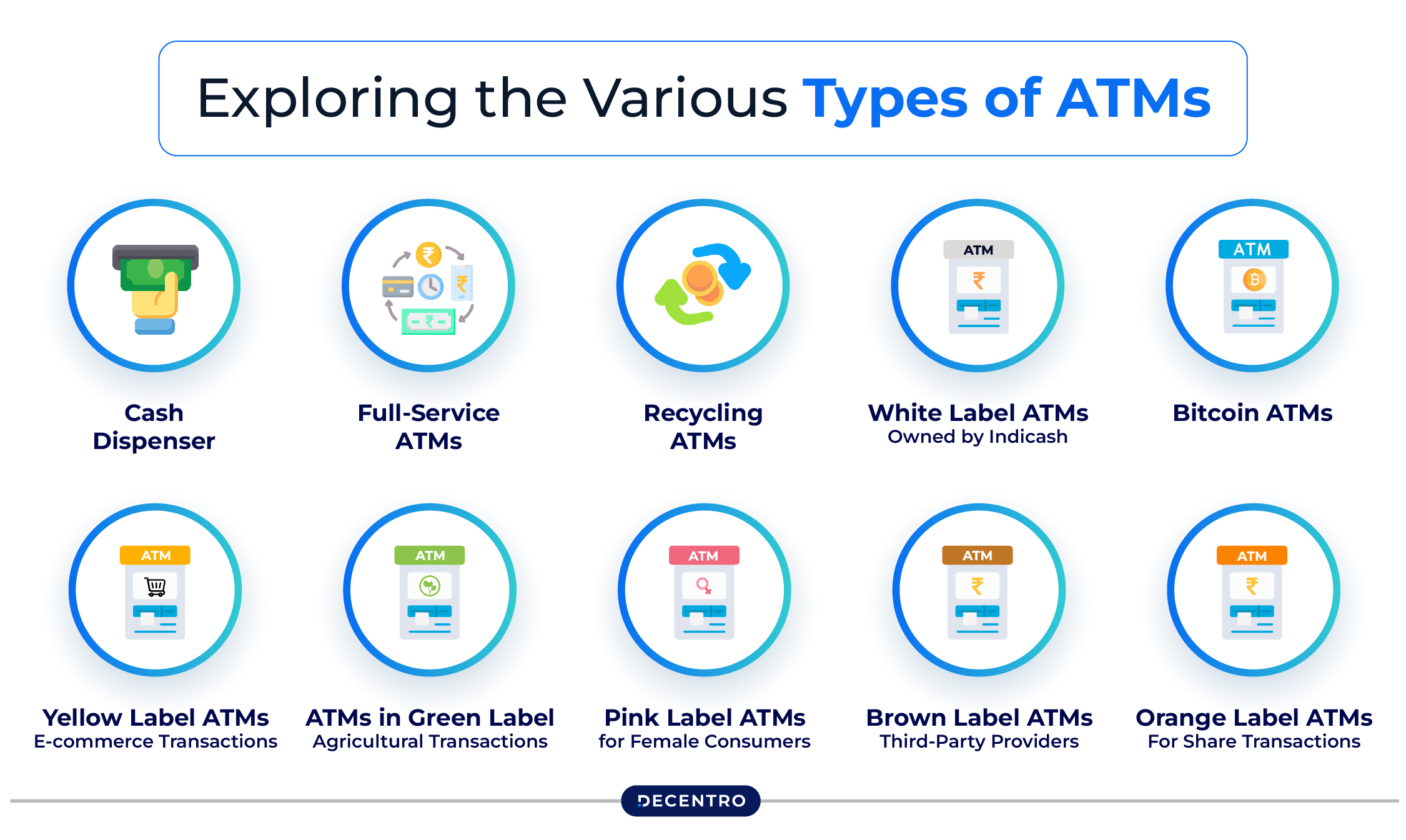
Below is an overview of the various commonly known types of ATMs in terms of their scope and technology:
- Cash Dispenser
Cash Dispenser is a type of ATM that is meant for instant cash withdrawals and balance inquiries. They are very user-friendly and are usually found in areas like shopping malls, airports, and railway stations other than roadsides. Such ATMs are ideal for customers who want easy access to money.
- Full-Service ATMs
Full-service ATMs provide a wider range of banking services, including cash and check deposits, bill payments, and fund transfers. These ATMs are similar to mini-branches, offering an extensive range of banking services.
Customers can even update passbooks and print mini-statements in these ATMs. They are convenient for individuals and businesses needing complete banking functionality.
- Recycling ATMs
Recycling ATMs accept deposits and recycle the deposited funds for further withdrawals. This drastically reduces the frequency of loading cash and optimises efficiency. Such ATMs are eco-friendly, cutting down on the need for physical cash transportation. They work well in areas where there is always a high demand for cash.
- White Label ATMs: Owned by Indicash
White Label ATMs are operated by third-party companies like Indicash (a brand by the Tata Group) under directions from the Reserve Bank of India. Such ATMs provide standard banking services such as cash withdrawal and balance inquiries but are not connected to any particular bank.
They serve considerable roles in the underserved or remote localities. These ATMs help expand banking where there are few traditional bank branches.
- Bitcoin ATMs
Bitcoin ATMs help customers buy or sell cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. These machines streamline crypto transactions through digital wallets. Many Bitcoin ATMs enable customers to convert their cryptocurrency into cash.
These ATMs cater to the needs of residents in towns or cities where digital currency is a commodity, and there is a high demand for cryptocurrency.
- Yellow Label ATMs: E-commerce Transactions
Yellow Label ATMs are specifically programmed to carry out online shopping and e-commerce transactions. They allow online purchases and payments for general digital financial transactions.
These ATMs are connected with digital payment platforms to provide a smooth user experience. They are ideal for customers who shop online or conduct many other digital payments.
- ATMs in Green Label – Agricultural Transactions
Green Label ATMs are exclusive for agriculture. They enable farmers and agricultural workers to access subsidies and other welfare benefits. These ATMs have a user-friendly interface targeted towards the rural populace. Additionally, they are necessary to advance financial inclusion on the agriculture front.
- Pink Label ATMs for Female Consumers
Pink Label ATMs are focused on safety and ease of use for women. They are in safe places with additional safety features such as cameras and bright lighting. These ATMs encourage women to bank independently, especially in areas where safety is a concern. The idea is to offer the female user a safe and comfortable banking experience.
- Brown Label ATMs: Third-Party Providers
Brown Label ATMs are bank-owned but are managed by third-party providers. The latter handles the machines’ installation, service, and technical support, while banks will supply the cash and provide branding. It enables banks to increase their ATM footprints with low costs. This serves as an excellent way for banks to expand their ATM access economically.
- Orange Label ATMs: For Share Transactions
Orange Label ATMs are made for share transactions wherein users can purchase and sell stocks or handle their investments. It eliminates the necessity of having brokers and makes trading stocks easy and more accessible. This is a convenient and safe way of managing investments for an active investor on the go.
Steps to Withdraw Money from an ATM
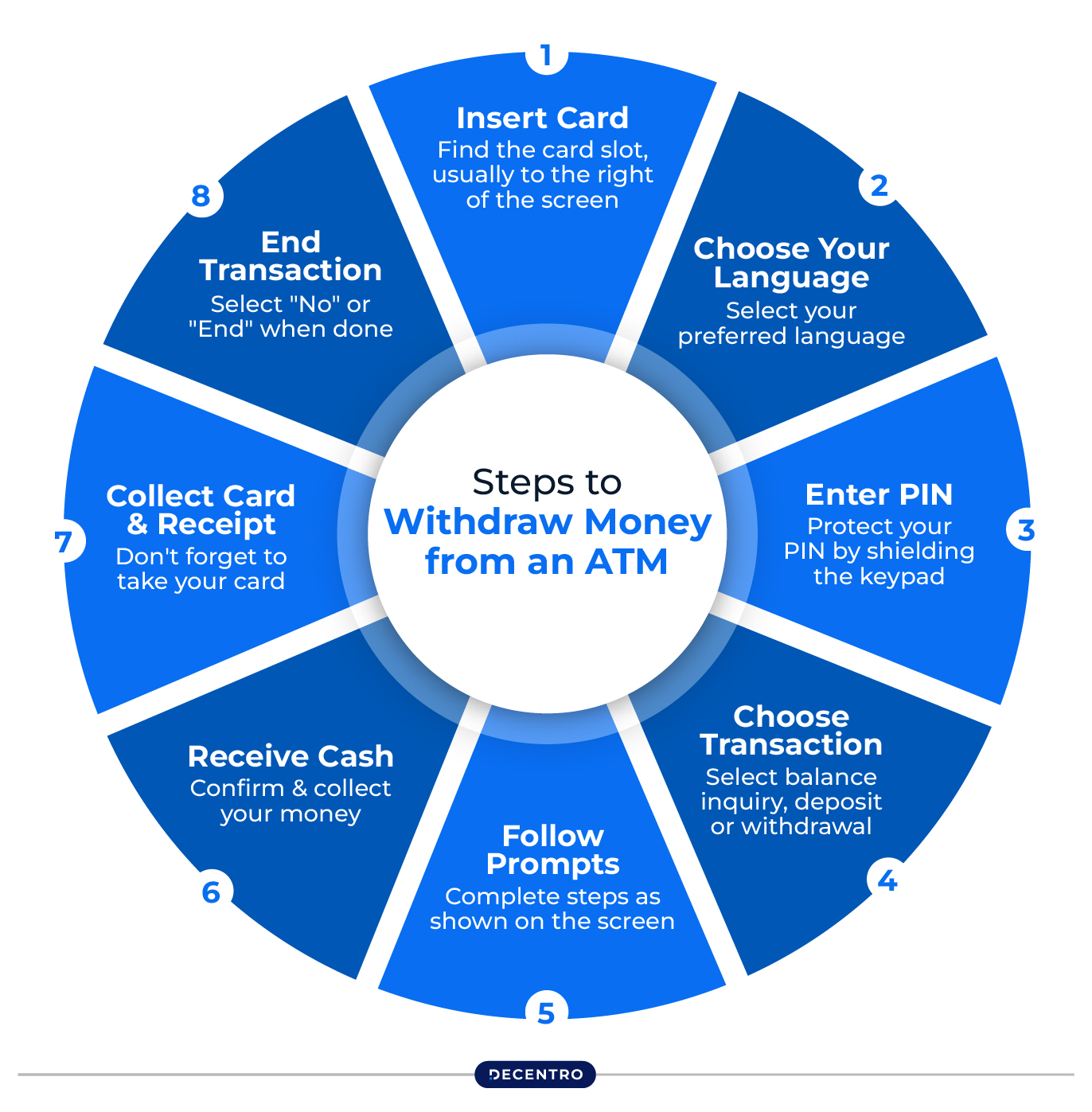
To withdraw money from an ATM, follow these steps:
Step 1: Insert Your Card
Find the card slot on the ATM and insert your card with the chip facing up or as shown by the machine.
Step 2: Choose Your Language
After the machine reads your card, select your preferred language for the transaction.
Step 3: Enter Your PIN
As the machine asks for the PIN, use the physical or on-screen keypad to enter the number securely.
Step 4: Choose Transaction Type
Once your PIN is entered, a menu will appear. Select “Withdraw Cash” from the options available.
Step 5: Select Account Type
Decide which account type (savings or current) you want to withdraw from.
Step 6: Input Withdrawal Amount
Type in the amount of cash you wish to withdraw.
Step 7: Collect Your Cash
After confirming the details on the screen, including the amount, press the “Enter” button. Your cash will be dispensed shortly, and you can take it from the machine.
Step 8: Print Receipt
If you want a receipt, some ATMs allow you to print one. Choose this option on the screen and wait for it to print.
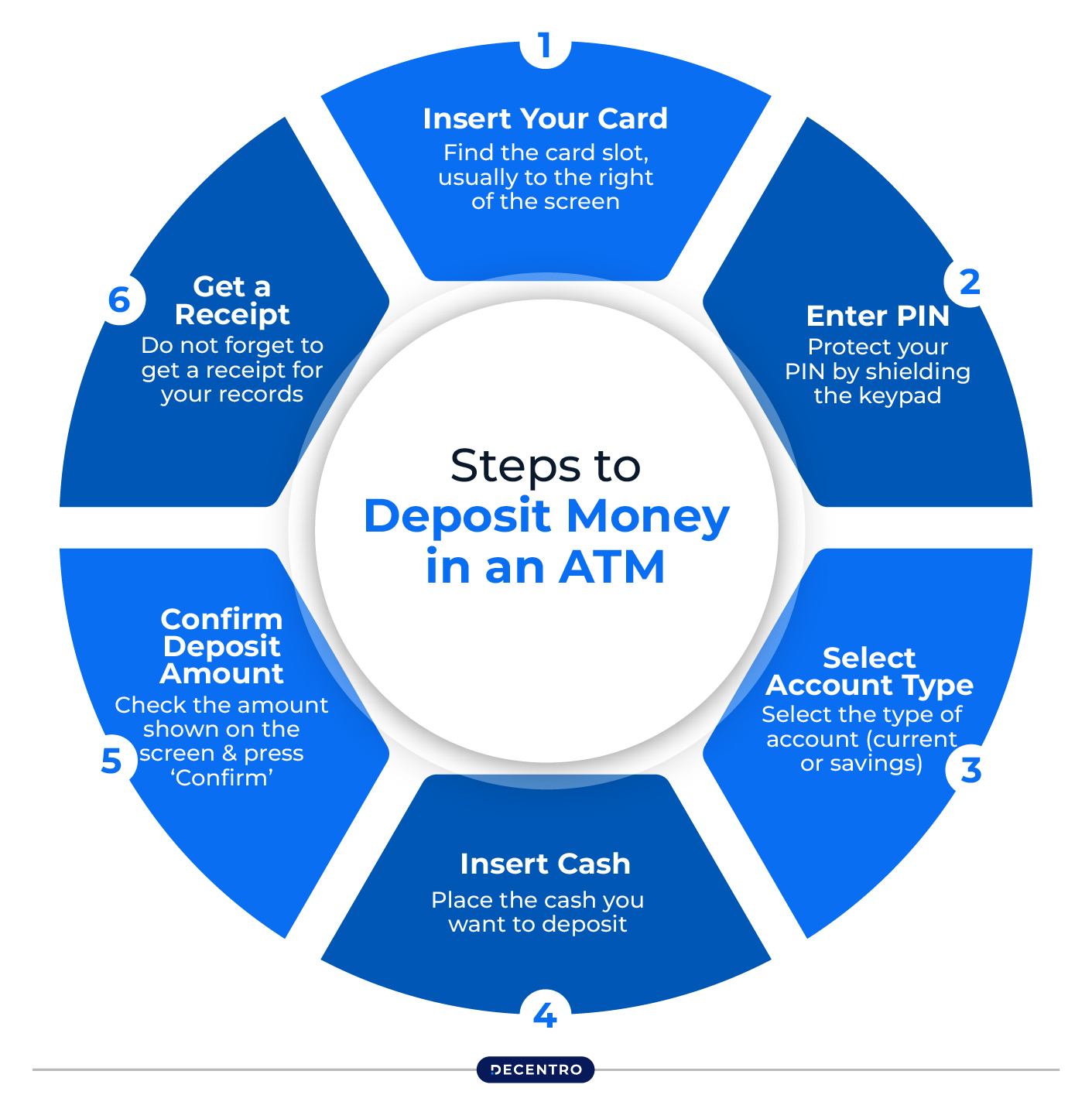
Steps to Deposit Money in an ATM
Following is the simple step-by-step process to deposit funds in an ATM:
Step 1: Insert Your Card
Start by putting your debit card into the ATM. Ensure it is facing the right way, as shown on the machine.
Step 2: Enter your PIN
Type in your PIN using the keypad.
Step 3: Select Account Type
Once you enter your PIN, select the type of account (current or savings) or input the account number where you want to deposit the cash.
Step 4: Insert Cash
Place the cash you want to deposit into the machine. Follow the on-screen instructions for proper cash insertion.
Step 5: Confirm Deposit Amount
After inserting the cash, check the amount shown on the screen and press ‘Confirm’. The deposited amount will appear in your account shortly.
Step 6: Get a Receipt
Do not forget to get a receipt for your records. The ATM will offer options to receive it printed, via email, or as a text message.
Knowing the Design Elements of an Automated Teller Machine
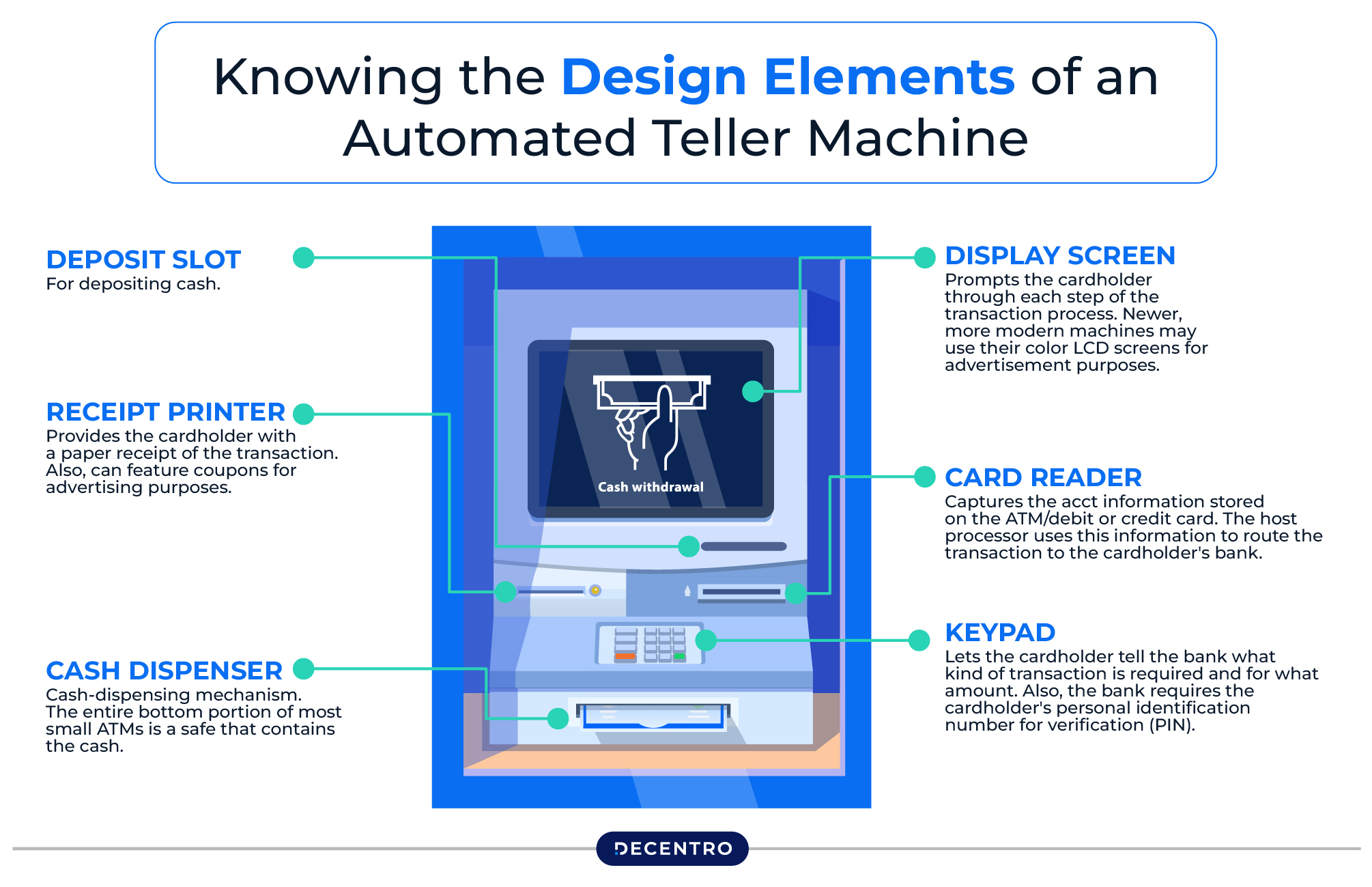
ATMs might differ in design from bank to bank or region to region, but one feature that is constant across all of them is their specific components. Following are the common design elements (input devices and output devices) that ensure the smooth functioning of ATMs and a seamless user experience:
Input Devices
- Card Reader
Customers insert their debit cards into a card reader slot present in the ATM machine. Once it is inserted, the reader scans the magnetic strip on the card or the chip embedded inside. The card details are retrieved and sent to the server for further processing, which takes place instantly.
- Keypad
Customers have to enter relevant data regarding the transaction using the keypad. These include the PIN, the amount of money they wish to withdraw, and other useful commands. It lets users operate the ATM quickly and seamlessly choose between various functions.
Output Devices
- Display Screen
A user-friendly electronic LCD or CRT monitor in the ATM displays transactions and guides the user throughout the process. It will include the transaction details, the options available (checking account balance, withdrawal, PIN change), and other actions that the user needs to take.
- Cash Dispenser
A cash dispenser is another crucial output device. It gives out the desired cash when the user confirms the withdrawal amount and finalises the transaction.
- Receipt Printer
After a transaction, users can get a receipt from the ATM’s printer. This offers a hard copy of the transaction details, including the transaction type, amount withdrawn, date and time, and the current account balance.
- Speaker Facility
Many ATMs come with built-in speakers providing audio instructions, allowing visually impaired customers to use them easily.
Benefits of Automated Teller Machines
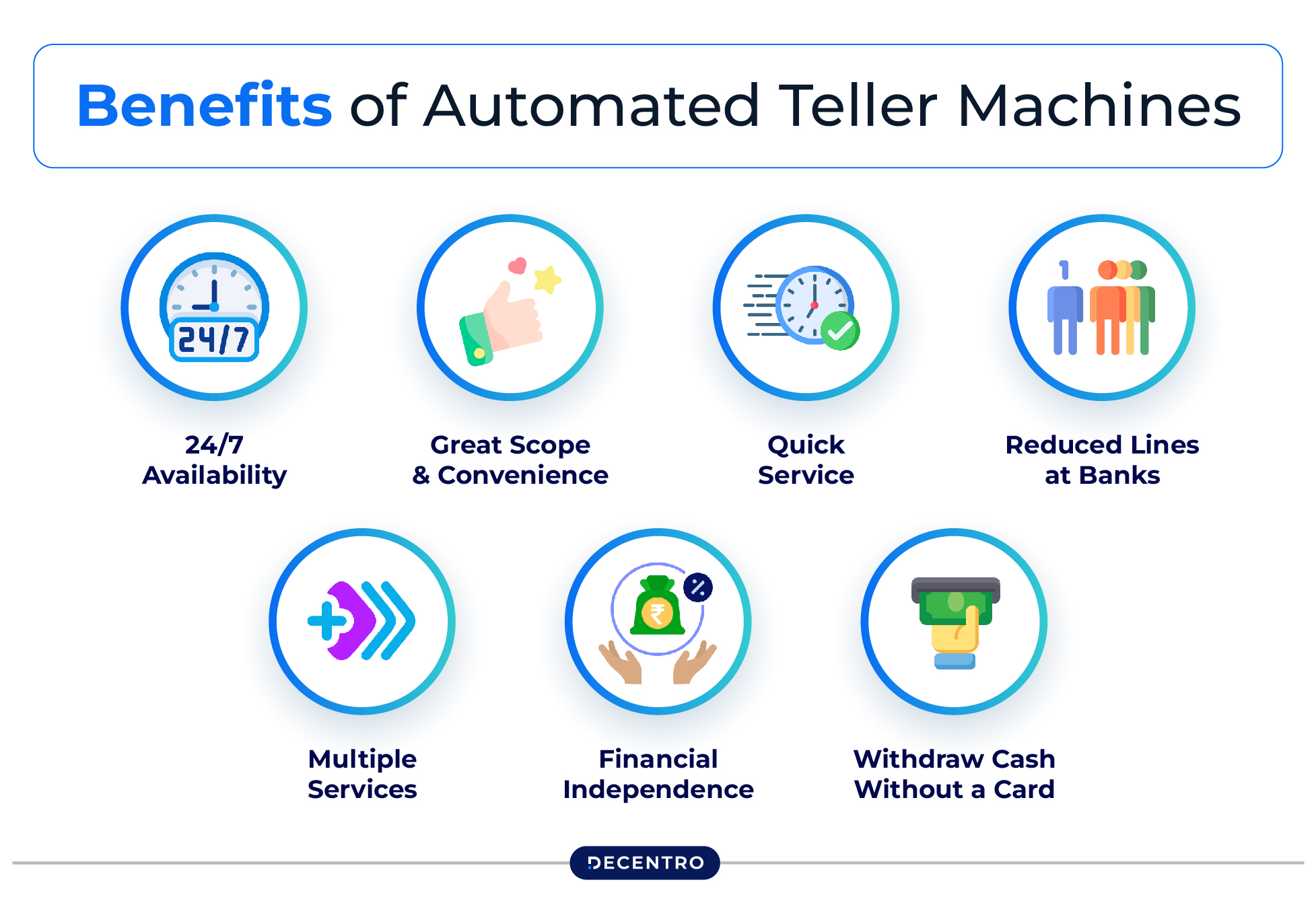
The following are the notable advantages of automated teller machines:
- 24/7 Availability
ATMs give you 24-hour access to banking services, which makes it ideal for urgent cash needs. This constant availability also enhances banking flexibility and ensures good customer service.
- Great Scope and Convenience
Using ATMs allows a customer to perform many financial tasks from anywhere, making banking simple and easy. This boosts the general customer experience.
- Quick Service
ATMs enable customers to quickly withdraw cash or check their account balances, which can be highly useful when one is in a rush. Such services are also highly useful during emergencies as one does not need to waste time by visiting the bank.
- Reduced Lines at Banks
Nowadays, banks are never over-crowded with customers because many people prefer using ATMs. This lessens the waiting time and enables bank employees to focus on complicated queries, making the process convenient for everyone.
- Multiple Services
ATMs provide a handful of services that include enabling deposit transfers, bill payments, cell phone recharges, and issuing mini statements.
- Financial Independence
Using ATMs provides the ability to manage your own transactions. This gives rise to a money management mindset that helps you in future finances.
- Withdraw Cash Without a Card
ATMs enable you to withdraw cash without using a physical card. However, this feature is only available at select ATMs and requires you to have a UPI app installed on your smartphone. This makes banking even easier and reduces the risk of losing your card.
Do You Need to Pay Any Fees for Using ATMs?
Often, ATMs can charge you some amount of fees for cash withdrawals or checking your balance. Those fees differ depending on the bank and account type, as well as the ATM network.
Based on your bank’s policy, ATM use may be free, or there might be an additional fee. Usually, if you opt to use an ATM that is not in your bank’s network, you may face extra charges. To avoid unwanted fees, check the limit for free transactions on your ATM card before completing your transaction.
Summing Up
ATMs have changed the face of banking by providing convenience and accessibility along with a wide-ranging service. Additionally, the increasing dependence of people on ATMs for their cash requirements shows their gradual shift towards digital finance.

Thus, businesses should also digitise their payment mechanisms to make customer transactions more seamless. In this regard, Decentro’s Multi-Collect APIs can be an ideal solution. They enable firms to seamlessly collect funds across a plethora of online payment methods like UPI, NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS.
Also, they offer features like auto-reconciliation, payment tracking, quick settlements, real-time notifications, and more.
Try Decentro’s Multi-Collect APIs today and handle digital payments like a pro!


