Learn why GST verification is essential for businesses. Discover methods, challenges, and best practices to stay compliant and avoid costly tax mistakes.

GST Verification 101: Everything Businesses Need to Know
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

Let’s face it – tax compliance is hardly the most exciting part of running a business. But in India’s evolving financial landscape, GST verification has become something you simply can’t afford to ignore. Whether you’re a startup founder or managing an established enterprise, understanding how to properly verify GST numbers can save you from major headaches down the road.
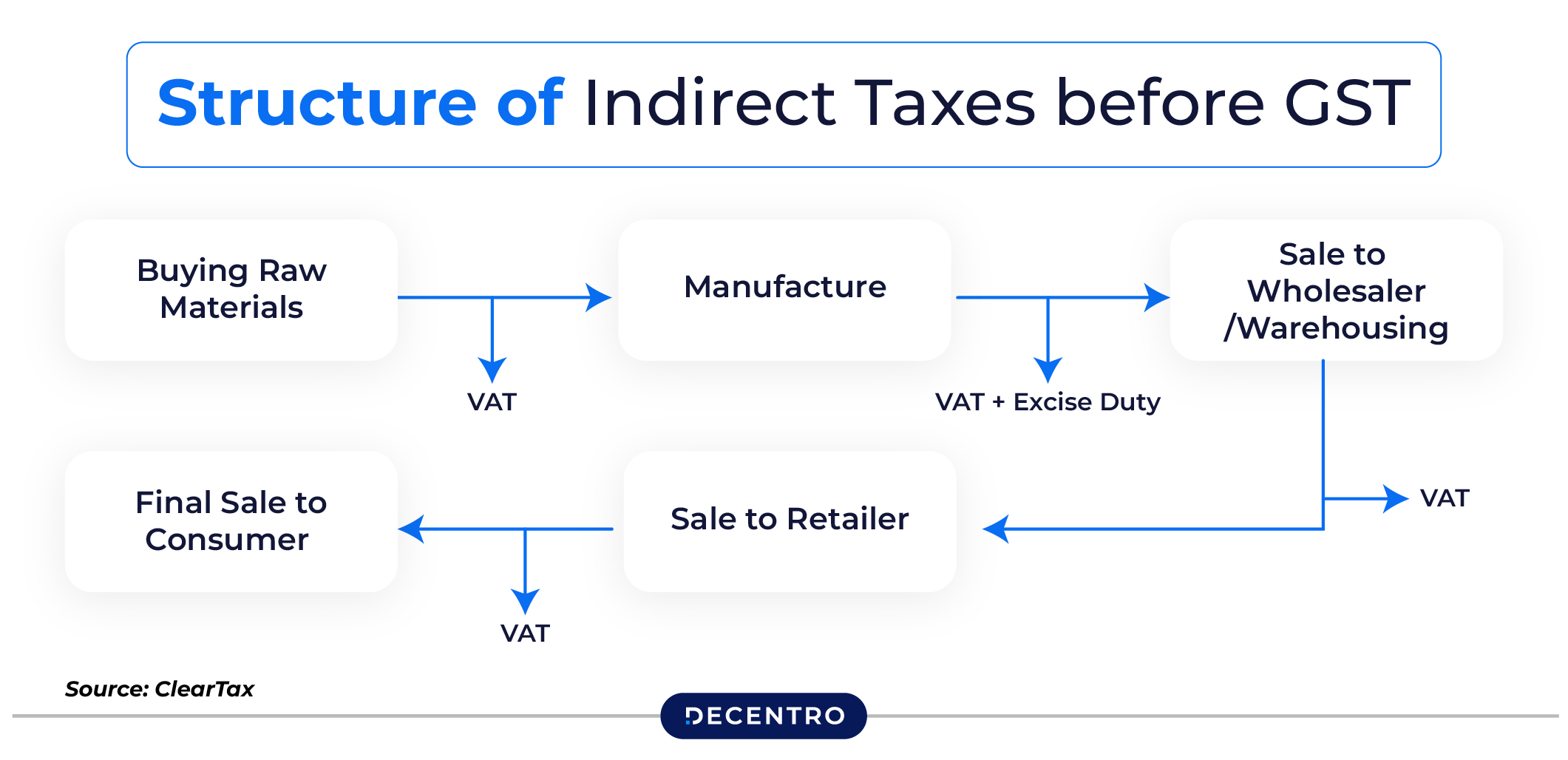
I’ve seen too many businesses learn this lesson the hard way – getting caught in fraud cases, losing input tax credits, or facing penalties. This guide aims to walk you through everything you need to know about GST verification, from the basics to best practices.
Understanding GST in India
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a comprehensive indirect tax system implemented in India on July 1, 2017, that replaced multiple taxes with a unified “One Nation, One Tax” framework. It’s a consumption-based tax applied at each stage of the value chain, from raw materials to the final product sold to consumers.
The key advantage of GST is its input tax credit mechanism, which eliminates the cascading effect (tax on tax) that existed in the previous tax regime. Under GST, businesses can claim credit for taxes paid on inputs, making the system more efficient.
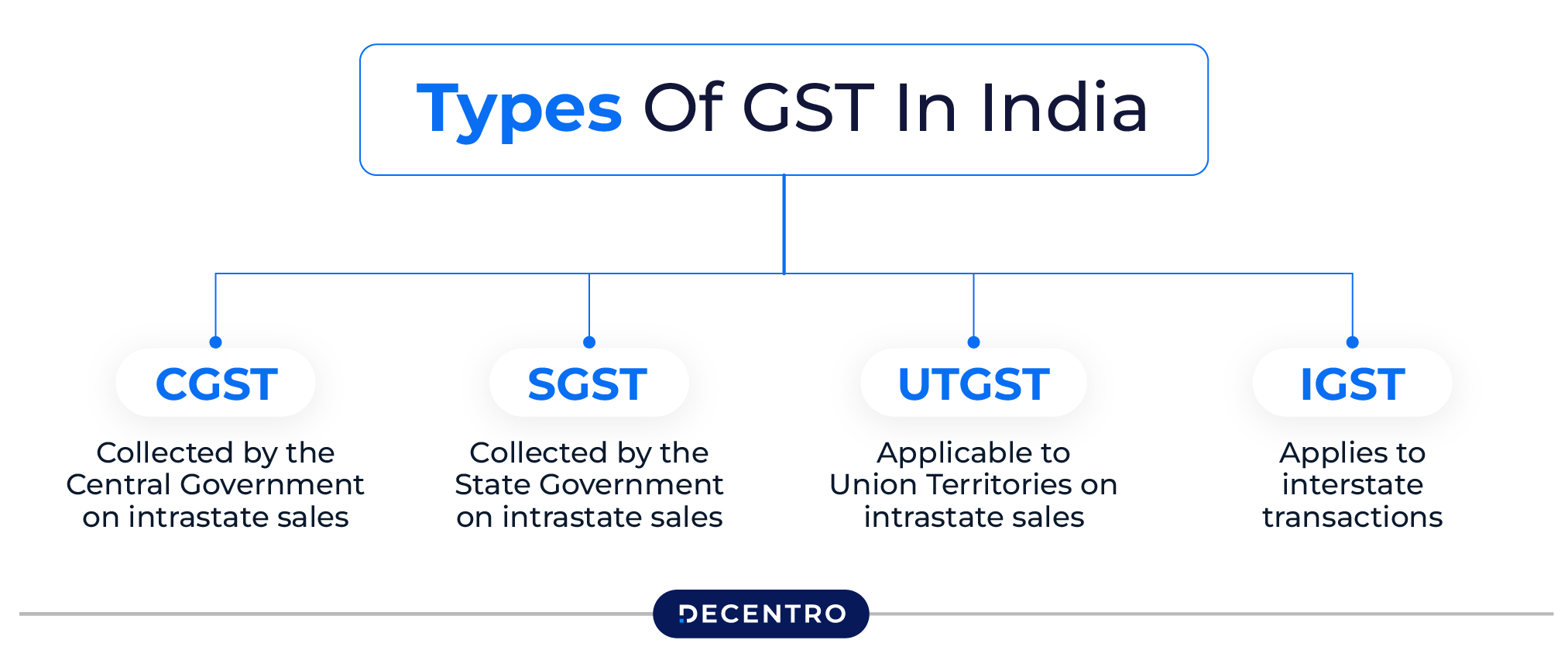
GST Structure
GST in India is divided into four components:
- CGST – Collected by the Central Government on intrastate sales
- SGST – Collected by the State Government on intrastate sales
- UTGST – Applicable to Union Territories on intrastate sales
- IGST – Applies to interstate transactions
For example, if a furniture retailer in Maharashtra sells within the state, both CGST and SGST apply. However, if they ship furniture from Maharashtra to Karnataka, IGST applies instead.
GST Returns: GSTR-1 and GSTR-2

The GST compliance framework requires businesses to file regular returns. Two critical components of this system are GSTR-1 and GSTR-2:
GSTR-1: This is a monthly or quarterly return (depending on turnover) that businesses must file detailing all outward supplies (sales). It includes information about taxable goods and services sold, including:
- Invoice details
- Tax rates applied
- Total value of supplies
- Tax amounts collected
GSTR-1 serves as the foundation for the GST ecosystem, as the government uses the information reported here to verify the input tax credits claimed by other businesses.
GSTR-2: This return was designed to capture details of all inward supplies (purchases). It would include:
- Purchase invoices
- Input tax credits available
- Amendments to previous returns
However, it’s important to note that while GSTR-2 was part of the original GST design, its implementation was suspended. Instead, the system now uses GSTR-3B (a summary return) and auto-populated GSTR-2A/2B (which shows purchase details based on suppliers’ GSTR-1 filings) to manage input tax credits.
This return system helps maintain transparency in the tax chain and ensures that businesses accurately report their tax liabilities and claim appropriate input tax credits.
How GST Components Work:
- For intra-state transactions: GST = CGST (50% of GST rate) + SGST/UTGST (50% of GST rate) Example: On a ₹1,000 item with 18% GST, you pay ₹90 as CGST and ₹90 as SGST = ₹180 total GST
- For inter-state transactions: GST = IGST (full GST rate) Example: On a ₹1,000 item with 18% GST, you pay ₹180 as IGST
GST Rates by Category:

- 0% (Nil rate): Essential items like fresh fruits, vegetables, milk, unbranded flour
- 5%: Essential commodities like packaged food items, sugar, tea, footwear below ₹1,000
- 12%: Processed food, mobile phones, computers, apparel above ₹1,000
- 18%: Most standard goods and services, cosmetics, refrigerators, washing machines
- 28%: Luxury items, premium cars, motorcycles, aerated drinks, tobacco products
The Long Road to GST Implementation
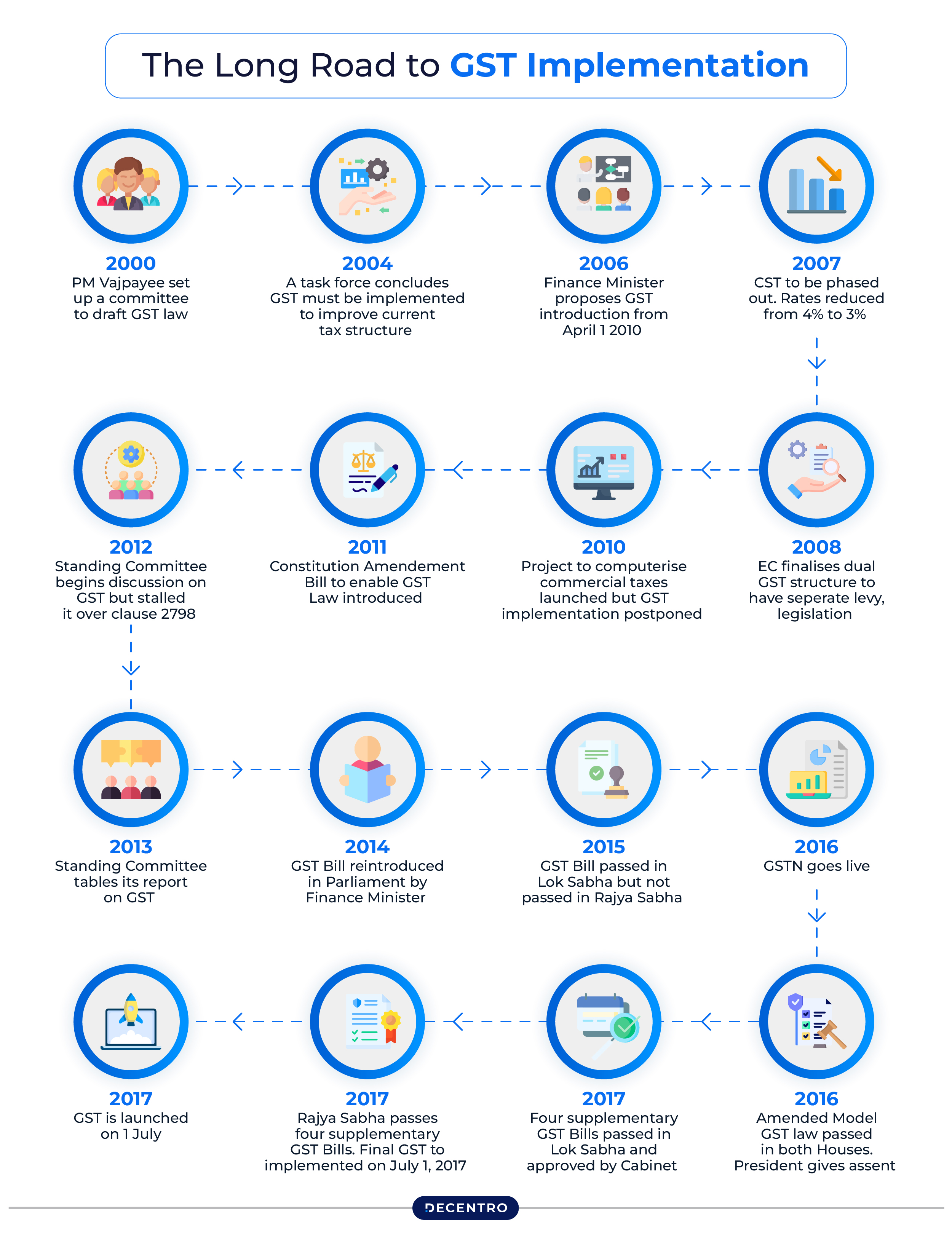
GST wasn’t built overnight. It took over 17 years from conception to implementation:
- 2000: The idea first emerged when a committee was formed to draft a new indirect tax law
- 2004: A task force highlighted the need for GST reform
- 2006: The Finance Minister announced plans to introduce GST by 2010
- 2007-2011: Various committees and discussions continued while CST rates were gradually reduced
- 2014: The GST Bill was reintroduced in Parliament
- 2015-2016: The bill cleared the Lok Sabha but faced hurdles in the Rajya Sabha
- 2017: Finally implemented on July 1st after passing both houses
This lengthy journey shows just how significant the reform was, completely transforming how businesses handle taxes across India.
Breaking Down the GSTIN
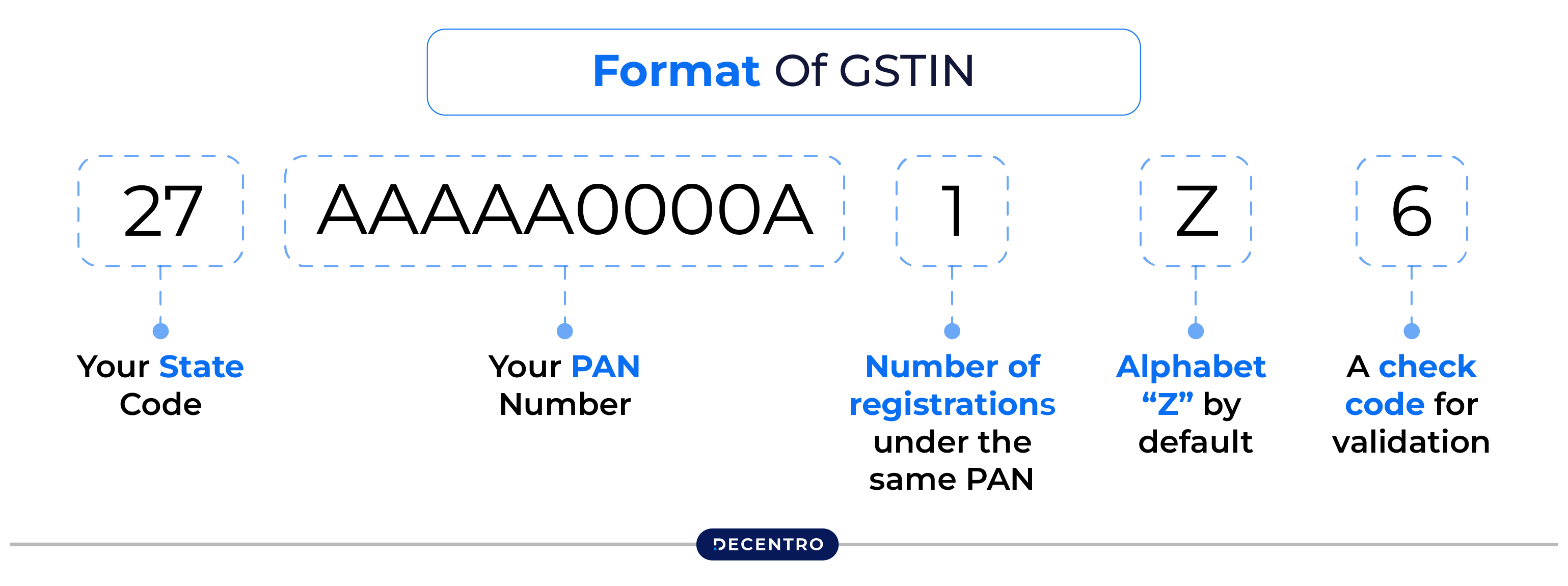
Think of the GSTIN (GST Identification Number) as your business’s tax ID card. This 15-character code is uniquely yours and tells a lot about your business at a glance.
Let’s decode a GSTIN:
- First 2 digits: Your state code (27 for Maharashtra, 29 for Karnataka, etc.)
- Next 10 characters: Your PAN number
- 13th digit: Number of registrations under the same PAN
- 14th digit: Currently always “Z”
- 15th digit: A check code for validation
For example, in the GSTIN “27AABCR1234A1Z7”:
- “27” indicates Maharashtra
- “AABCR1234A” is the PAN
- “1” indicates this is the first registration under this PAN
- “Z” is the default character
- “7” is the check digit
This structured format makes GSTIN verification possible and reliable.
Why Should You Care About GST Verification?

You might wonder if verifying GST numbers is worth your time. Trust me, it is. Here’s why:
Legal Protection
Imagine claiming input tax credits for transactions with a business that has a fake or cancelled GSTIN. When tax authorities catch this (and they will), you’re the one facing penalties and losing those credits. Verification is your first line of defence.
Real-World Fraud Prevention
The numbers are staggering. In Gujarat alone, fake GST billing schemes cost the government over ₹34,000 crores in just 4.5 years. In another case, authorities found more than 5,700 instances of fake invoicing amounting to nearly ₹40,000 crore.
These aren’t just government problems – businesses caught in these schemes face severe consequences, including:
- Denied input tax credits
- Financial penalties
- Legal proceedings
- Reputational damage
Building Trust
When you verify partners’ GSTINs, you’re signalling that you run a legitimate, compliant business. This builds trust with customers, suppliers, and financial institutions. A verified GSTIN means the business is likely filing regular returns like GSTR-1 and GSTR-2, which directly impacts credit claims and overall trustworthiness.
Many large corporations and MNCs now require GST verification before engaging with new vendors, making it essential for businesses looking to work with established companies.
Protecting Your Input Tax Credits
The whole point of GST was to eliminate cascading taxes through input tax credits. But these credits are only valid if your suppliers are GST-compliant. Regular verification ensures you can claim what you’re entitled to.
How to Verify GST Numbers: The Practical Guide
Let’s get into the nuts and bolts of how you can verify GST numbers:
Method 1: The DIY Approach via the GST Portal
The most straightforward method costs nothing but a few minutes of your time:
- Visit www.gst.gov.in
- Look for “Search Taxpayer” in the top menu
- Select “Search by GSTIN/UIN”
- Enter the 15-digit GSTIN
- Complete the captcha and hit “Search”
The portal will show you:
- Business name
- Status (Active/Inactive)
- Type of business
- Registration date
- Business address
- Nature of business activities
This method works well for occasional verification but becomes tedious when dealing with multiple suppliers.
Method 2: GST Verification APIs
For businesses that need to verify multiple GSTINs regularly, API integration is a game-changer:
- Subscribe to a verification service like Decentro
- Integrate the API with your existing systems
- Submit GSTINs directly through your software
- Receive instant verification results
The beauty of API integration is automation – you can verify GSTINs automatically during supplier onboarding or before processing payments.
Method 3: Bulk Verification
If you’re dealing with dozens or hundreds of suppliers, bulk verification saves precious time:
- Compile your GSTINs in the required format (usually CSV)
- Upload to your verification service
- Receive a comprehensive report for all numbers
This approach is particularly useful during annual compliance reviews or when onboarding multiple vendors simultaneously.
The Verification Process: What Happens Behind the Scenes?
When you verify a GSTIN, the system checks multiple databases to confirm:
- Whether the GSTIN format is valid
- If the business is registered
- The current status (active, canceled, suspended)
- Match between stated business name and official records
- Filing history and compliance status
Advanced verification services also check for red flags like:
- Recently registered GSTINs (potential fly-by-night operations)
- Inconsistent filing patterns
- Businesses registered in high-risk categories
Decentro’s Approach to GST Verification

At Decentro, we’ve built our GST verification solutions based on thousands of customer interactions and real-world business needs. Our approach focuses on three key elements:
1. Simple but Powerful Verification
Our basic GSTIN verification is straightforward but effective. Just send a simple API request. Within seconds, you get confirmation of the GSTIN’s validity and basic business details.
2. Deep-Dive Business Intelligence
Need more comprehensive information? Our GSTIN_DETAILED option provides everything from director details to filing history. This detailed verification gives you:
- Complete business contact information
- Registration date and jurisdiction details
- Constitution type (Pvt Ltd, Partnership, etc.)
- Current registration status
- Trade and legal names
- Director/partner details
- All business locations
- Nature of business activities
- Annual turnover information
- Complete filing history
- E-invoicing status
It’s like having a complete business profile at your fingertips.
3. Documentation Made Easy
One feature our customers particularly love is our downloadable PDF reports. By adding the generate_pdf parameter to your request, you get a professionally formatted report that you can:
- Store for compliance records
- Share with team members
- Present during audits
- Include in vendor documentation
The best part? They’re designed to be understood by both technical and non-technical team members.
Real-World Applications of GST Verification
Let’s look at some practical ways businesses are using GST verification:
Vendor Onboarding
Before adding new suppliers to your system, verify their GSTIN to ensure they’re legitimate and compliant.
Invoice Processing
Integrate verification into your accounts payable workflow to flag any invoices with invalid GSTINs before payment.
Credit Decisions
Financial institutions use GST verification to assess the legitimacy and stability of businesses before extending credit.
Marketplace Seller Verification
E-commerce platforms verify seller GSTINs to ensure compliance and build customer trust.
Regulatory Reporting
Maintain verified GSTIN records for regulatory reporting and audit requirements.
Common GST Verification Challenges (And How to Solve Them)

Despite its importance, GST verification comes with challenges:
Challenge 1: Handwritten or Poorly Scanned Documents
Problem: Extracting GSTINs from handwritten invoices or low-quality scans is error-prone.
Solution: OCR-powered document processing can accurately extract GSTINs from various documents, reducing manual errors.
Challenge 2: High Volume Verification
Problem: Verifying thousands of GSTINs manually is time-consuming and impractical.
Solution: Bulk verification APIs allow you to process multiple GSTINs simultaneously, saving hours of work.
Challenge 3: Keeping Up With Changes
Problem: Business statuses change – active GSTINs may become suspended or canceled.
Solution: Implement periodic re-verification of your vendor database to catch any status changes.
GST Verification Best Practices

To make the most of your GST verification efforts:
1. Make Verification Part of Your Business Onboarding Process
Don’t wait until there’s a problem. Verify GSTINs before you start doing business with new partners.
2. Document Everything
Keep records of all verification results, including screenshots or system-generated reports. These become invaluable during audits.
3. Set Regular Re-verification Schedules
Business statuses change. Set up quarterly or bi-annual reverification of your entire vendor database.
4. Train Your Team
Ensure that your finance, procurement, and compliance teams understand the importance of GST verification and know how to interpret results.
5. Integrate Verification With Your ERP
Connect your verification system with your ERP to automate the process and reduce manual work.
Conclusion: Why GST Verification Matters More Than Ever
As India’s tax landscape continues to evolve, GST verification has become a critical business function. It’s not just about compliance – it’s about protecting your business from fraud, securing your input tax credits, and building trust with partners and customers.
The good news is that verification doesn’t have to be complicated. With tools like Decentro’s verification API, businesses of all sizes can implement robust verification processes without significant investment or technical complexity.
Whether you’re verifying a single GSTIN or thousands, the peace of mind that comes from knowing you’re working with legitimate, compliant partners is well worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Not necessarily. Businesses with an annual turnover below ₹20 lakhs (₹10 lakhs in special category states) aren’t required to register, though they can opt for voluntary registration.
Portal verification takes a few minutes. API-based verification is nearly instantaneous, usually returning results in seconds
No. To claim Input Tax Credit (ITC), you need:
– Valid tax invoice from registered supplier
– Actual receipt of goods/services
– Tax paid to government by supplier
– Filed returns
– Verified supplier’s GSTIN
– Invoice appearing in your GSTR-2A/2B
Merely verifying a supplier’s GST registration doesn’t guarantee ITC eligibility. The transaction must be properly reported by your supplier in their GSTR-1.
GSTR-1:
– Records all your sales
– When filed, enables your customers to claim ITC
– Appears in your customers’ GSTR-2A/2B
GSTR-2 System:
– Original GSTR-2 implementation suspended
– Replaced by auto-generated GSTR-2A/2B
– Shows purchases based on your suppliers’ GSTR-1 filings
– Basis for your ITC claims
This creates a chain where your GSTR-1 affects your customers’ ITC, and your suppliers’ GSTR-1 affects your ITC, ensuring compliance throughout the supply chain.
You risk losing input tax credits, facing penalties, and potentially being implicated in tax fraud investigations.
Best practice is to verify during onboarding and then at least annually thereafter. For high-value or high-risk suppliers, quarterly verification is recommended.
Yes, you can verify your own GSTIN through the GST portal or verification services to ensure your information is correct and up-to-date.
You’ll get comprehensive information including business structure, director details, filing history, turnover information, and much more.
Yes, Decentro offers downloadable PDF reports for all verification results, making record-keeping simple and efficient.


