Get a comprehensive overview of IFSC codes, their components, how they work, role in transactions, how businesses can use them in the most prolific way, and more

IFSC Codes: How They Work and What Are Their Uses
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

With the advancement of modern banking, electronic transactions have become the backbone of financial operations. They enable the safe and quick transfer of funds, allowing individuals and businesses to transact without the hassles of issuing cheques or withdrawing cash.
In this regard, the Indian Financial System Code (IFSC) plays a major role. This unique code is instrumental in ensuring safe and smooth interbank transfers and paves the way for NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS transactions.
Let’s examine what an IFSC code means, how it works, and why it has gained importance in electronic transactions in India.
What is an IFSC Code? Understanding Its Significance
The IFSC code is an eleven-character alphanumeric code defined by the Reserve Bank of India to represent every bank branch in India. Providing this code is mandatory for electronic fund transfer systems like NEFT (National Electronic Funds Transfer), RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement), and IMPS (Immediate Payment Service).
IFSC codes enable a money transaction by indicating the bank branch to which the money is being transferred, facilitating a proper and efficient transaction. Each part of the code reflects valuable details for identification.
Components of IFSC Codes
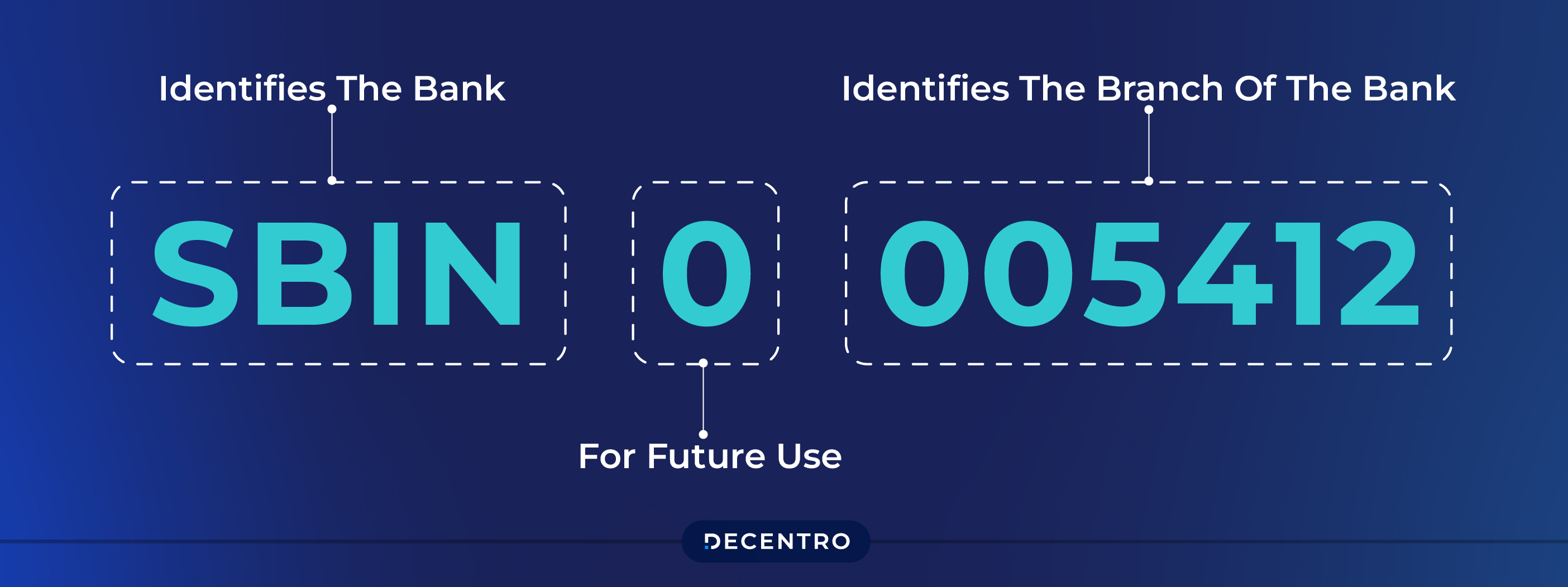
An IFSC code consists of an 11-character code made up of three parts. They are as follows:
- Bank Code: The first four letters show the bank, such as “SBIN” for the State Bank of India.
- Zero: The fifth character is always a ‘0’, used as a separator.
- Branch Code: The last six characters identify the specific branch.
For example, if the IFSC code for a particular branch is SBIN0054321, then “054321” uniquely identifies that branch of the State Bank of India.
IFSC Codes for Top Banks in India
The sample IFSC codes for some of the financial institutions are given in the table below:
| Bank Name | IFSC Codes |
| HDFC Bank | HDFC0000128 |
| HSBC Bank | HSBC0400002 |
| Yes Bank | YESB0CMSNOC |
| Citibank | CITI0000003 |
| Axis Bank | UTIB0000400 |
| IndusInd Bank | INDB0000018 |
| Punjab National Bank | PUNB0112000 |
| IDBI Bank | IBKL0NEFT01 |
| State Bank of India | SBIN0005943 |
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) provides these IFSC codes to help with smooth electronic fund transfers by clearly identifying each branch in India’s banking system.
Significance of IFSC Codes in The Indian Banking System
IFSC codes are important for domestic transactions and handling the extensive number of Indian banks spread throughout the country. Recent statistics state that there are 91 commercial banks present in India, with thousands of branches across the entire nation.
Now, to ensure that whenever an electronic payment is initiated, it reaches the right bank account, each one of these bank branches has a unique IFSC code. This significantly enhances the overall reliability of digital fund transfers, ensuring payments are quickly disbursed to the right individual without any hassles.
Thus, considering the diverse geographical reach of banks in India, ranging from major metropolitan to rural locations, the IFSC code system is crucial in facilitating hassle-free fund transfers. The importance of IFSC codes is particularly evident when we look at India’s digital payment systems, such as IMPS and RTGS, which rely heavily on accurate bank identification.
In fiscal year 2021, RTGS transactions totalled about 159 million across India, while IMPS saw a significant rise, with 534.63 million transactions in February 2024.
As of October 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) had assigned approximately 130,000 IFSC codes to different banks and their branches across India, highlighting the wide use of the IFSC system in enabling smooth and secure digital transactions.
How IFSC Codes Work: The Backbone of Electronic Transactions
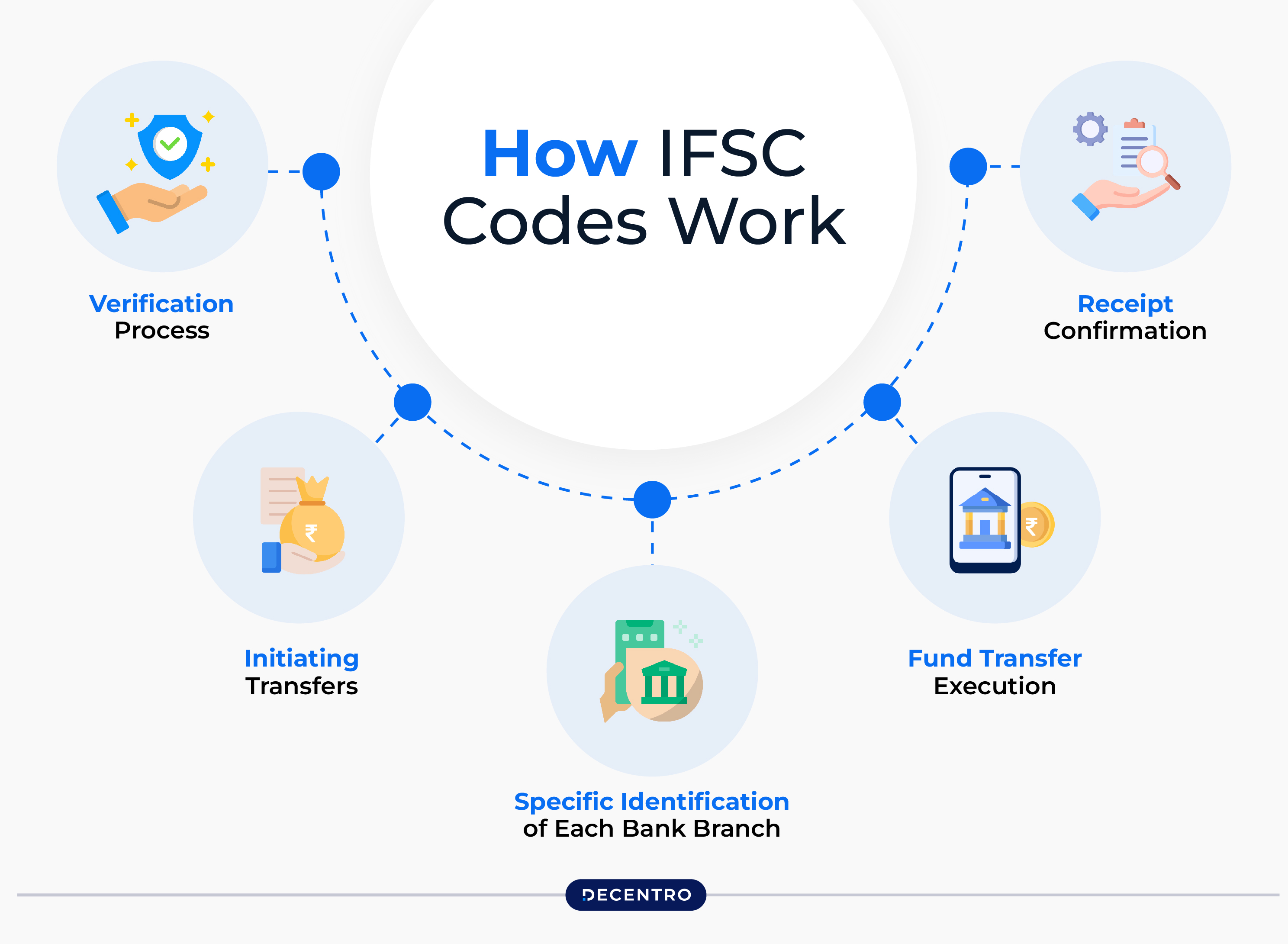
The IFSC code is vital in ensuring the security of electronic payment systems like NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS. Here is how it works:
- Specific Identification of Each Bank Branch
The Reserve Bank of India assigns a specific IFSC code to every bank branch associated with India’s National Electronic Funds Transfer system.
- Initiating Transfers
To identify the exact bank and branch and conduct a fund transfer, a customer must enter the IFSC code of the recipient’s bank branch.
- Verification Process
The bank checks the IFSC and the beneficiary’s account details to ensure the amount is transferred to the right account.
- Fund Transfer Execution
After the details are verified, the NEFT system enables the electronic transfer of funds from the originating bank to the recipient’s bank.
- Receipt Confirmation
The receiver’s bank acknowledges the receipt of funds, and the initiating bank updates the customer account that the money has been transferred successfully.
Thus, the IFSC code is pivotal in ensuring that the fund transfer is executed promptly, safely, and error-free.
Role of IFSC Code in Transactions – Step-by-Step Process
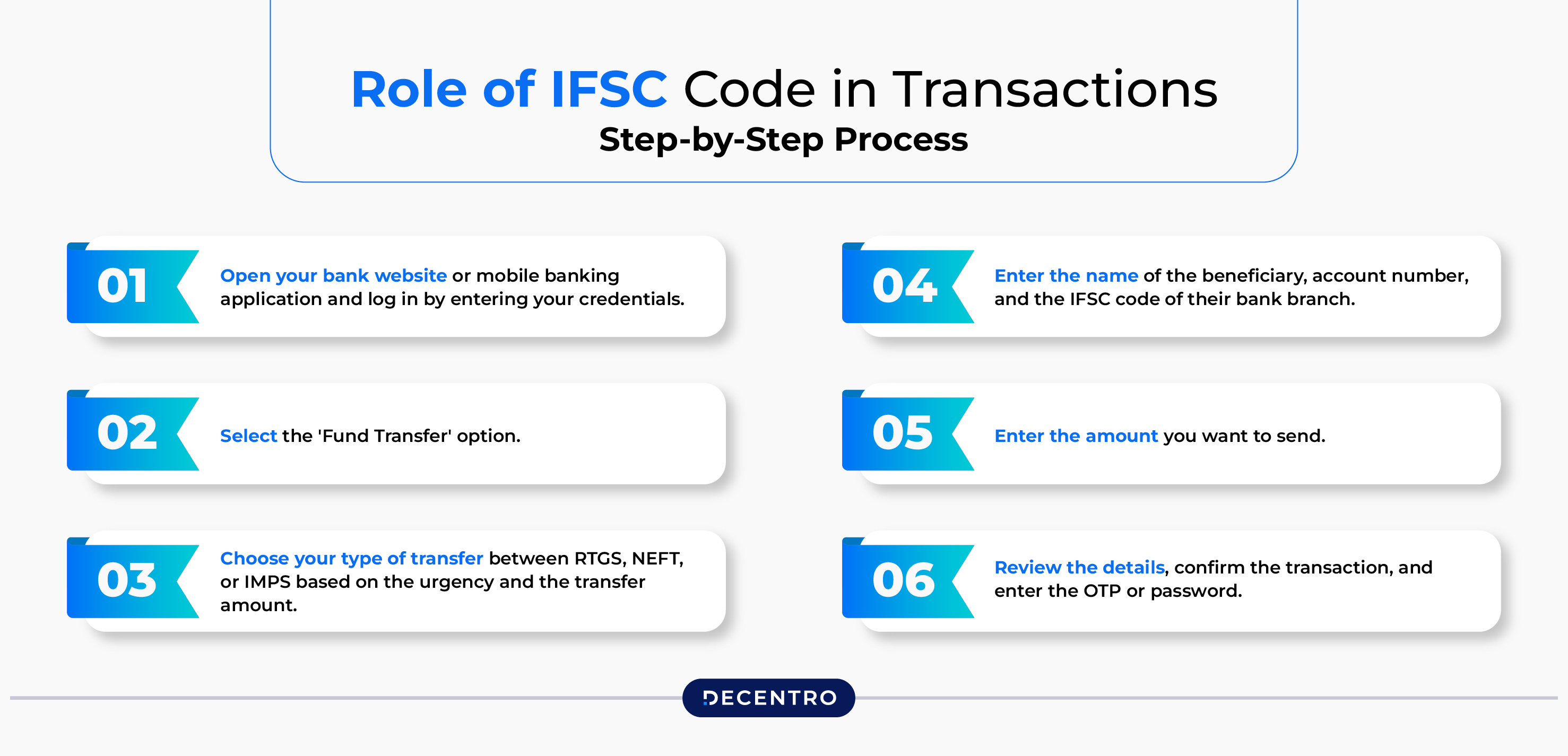
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how you can conduct an online bank transfer by using an IFSC code:
Step 1: Open your bank website or mobile banking application and log in by entering your credentials.
Step 2: Select the ‘Fund Transfer’ option.
Step 3: Choose your type of transfer between RTGS, NEFT, or IMPS based on the urgency and the transfer amount.
Step 4: Enter the name of the beneficiary, account number, and the IFSC code of their bank branch.
Step 5: Enter the amount you want to send.
Step 6: Review the details, confirm the transaction, and enter the OTP or password.
Uses of IFSC Codes: Unlocking Their Versatility
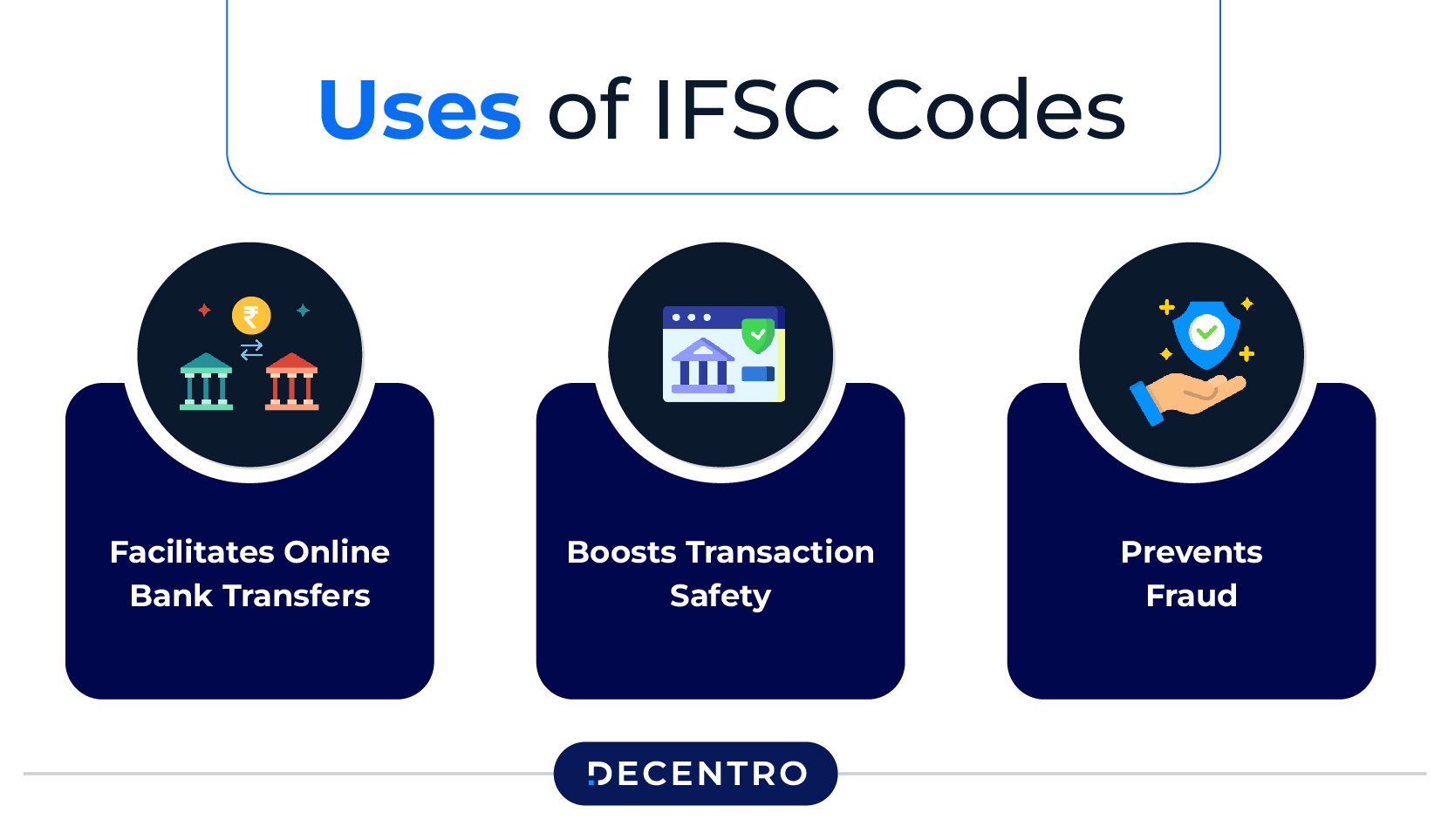
The primary function of an IFSC code is to help identify the proper branch and bank name for initiating an electronic transfer. Apart from this, it has a plethora of other uses like:
- Facilitates Online Bank Transfers
You can initiate an online bank transfer via your mobile phone, tablet, or laptop by providing the recipient’s bank account number and IFSC code in your mobile banking app or Internet banking account. What’s more, knowing just these two details allows you to conduct the transaction via NEFT, RTGS, or IMPS, as per your requirements.
- Boosts Transaction Safety
IFSC codes help pinpoint the exact bank branch when sending a large sum digitally. If you enter the wrong IFSC code, the bank may not process the transaction, preventing the funds from being deposited to the wrong bank account.
- Prevents Fraud
The IFSC code ensures the secure transfer of funds. Every bank branch has a unique IFSC code, so you can easily identify the bank and its branch. This mechanism significantly reduces the chances of fraudulent activities, boosting online transaction safety.
IFSC Code, MICR Code – Differences
The IFSC code only indicates the bank code and branch code. At the same time, the MICR code contains the PIN code, bank code, and branch code. The major differences between the IFSC code and the MICR code are discussed in the table below:
| Aspects | IFSC code | MICR code |
| Full-Form | Indian Financial System Code | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition Code |
| Primary Use | Electronic fund transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS) | Cheque processing and clearance |
| Geographical Scope | Domestic | Primarily Domestic, limited international use |
| Length | 11 characters | 9 characters |
| Application in Electronic Fund Transfers | Used for routing electronic payments such as NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS towards the right branch of the bank of the recipient | Not used for electronic transfers, but for cheque clearance within domestic banks |
| Relevance in Banking Services | This is very useful for establishing direct deposits, salary credits, bill payments, etc. | This is very important for cheque verification, processing, and clearing |
| Application in International Transfers | Not applicable (limited to domestic transfers) | Though mainly for cheque clearing in India, it can be used in international cheque processing |
Modes of Online Money Transfer Using IFSC Code (NEFT, RTGS & IMPS)
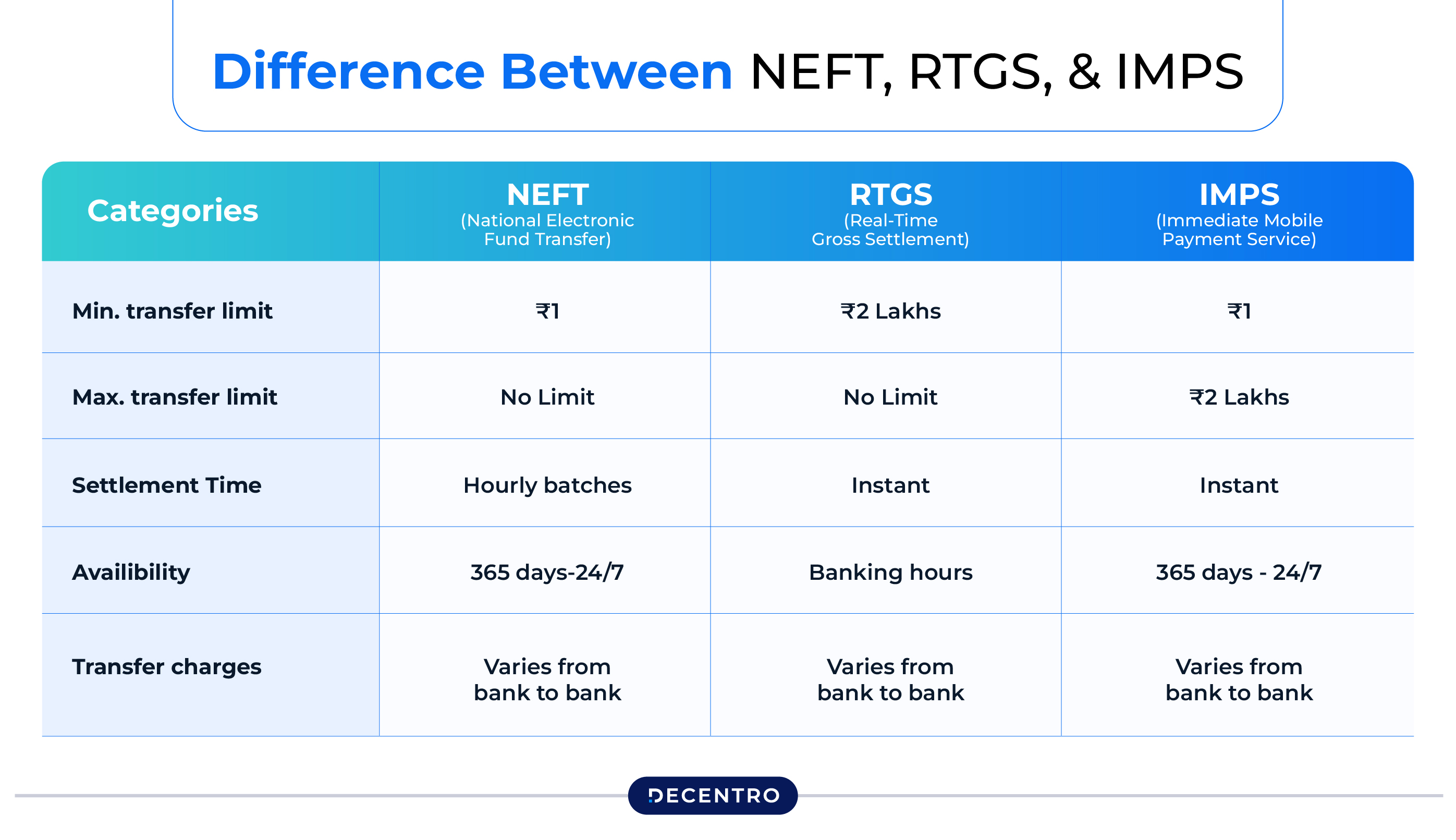
By using IFSC codes, you can send funds electronically to any bank account in India using the following payment methods:
- Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
RTGS is an electronic fund transfer system generally used for processing payments above ₹2 Lakh. It credits funds to the recipient’s bank account within a few minutes to up to 30 minutes and has no upper transaction limit.
RTGS payments are settled individually. Thus, they are processed almost immediately, making them ideal for urgent and high-value transfers. Moreover, this service can be availed 24/7 via Internet banking and by visiting the nearest bank branch.
- National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT)
NEFT is a nationwide electronic funds transfer payment system that allows people to send funds to any bank account or branch that offers this facility. The RBI monitors these transactions, which are processed in half-hourly batches 24/7.
The minimum transfer limit is ₹1, with the maximum threshold differing across banks. This service can be availed online and offline and funds are credited to the recipient’s bank account within 30 minutes to up to a few hours.
- Immediate Payment Service (IMPS)
IMPS payments enable instant fund transfers to bank accounts 24/7 (even on holidays). All transactions are handled by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and are processed immediately, facilitating real-time fund credits to the recipient’s bank account.
This facility can be used online via a mobile banking app or Internet banking. To initiate the transfer, the person sending the funds needs to provide either the beneficiary’s mobile number and Mobile Money Identifier (MMID) or account number and IFSC code. The minimum transfer limit is ₹1, while the maximum threshold is ₹5 Lakh.
How are NEFT and IFSC Codes Related?
NEFT stands for National Electronic Funds Transfer. It facilitates the electronic transfer of funds, enabling individuals and businesses to send money to any bank account within the system.
The IFSC Code (Indian Financial System Code) is an alphanumeric code that specifies the different branches of banks across India. This code is very important for NEFT because it provides the transaction route for the correct branch location.
To perform an NEFT transfer, the sender needs to input the sender’s bank account number along with the IFSC code of the bank branch where the recipient has their account. This ensures that the payments move through the NEFT system correctly.
How are RTGS and IFSC Codes Related?
RTGS refers to Real-Time Gross Settlement. It is a system designed to facilitate real-time transfers of high-value transactions. Likewise, in the case of NEFT, an IFSC code identifies the branch that has to receive the money. However, transactions are individually processed and thus settle within a few minutes to up to 30 minutes.
When making an RTGS transaction, a person or entity enters the recipient’s account number along with the IFSC code of their bank branch to allow the routing of the funds in real time.
Importance of the IFSC Code in IMPS Transfer
IMPS, which stands for Immediate Payment Service, is an essential tool for immediate fund transfers that require instant settlements to the recipient’s bank account. It can facilitate high-value transactions up to ₹5 Lakh and send funds to any bank account within India.
In case of an IMPS transfer, the recipient’s IFSC code and bank account number, helps the sender’s bank pinpoint the correct bank branch and account to credit the funds.
Importance of IFSC Codes in Banking: Why They Matter

IFSC codes are crucial in banking for the following reasons:
- Error Reduction
IFSC codes play a key role in eliminating routing mistakes during electronic fund transfers. They are like an identity code for every bank branch, allowing money to be routed directly to the right branch.
If a sender fills out the IFSC code properly, routing errors can be avoided to a significant extent. Thus, the funds can reach the intended recipient without delays or credits to the wrong bank accounts.
- Maintaining Regulatory Compliance
Banks and other financial institutions in the country must comply with the basic requirements per the regulation laid down by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). In this regard, using the proper IFSC codes for any electronic transfer of funds is a legal mandate.
It promotes transactional safety and enables banks to avoid the penalties and legal complications that come with non-adherence.
How to Find Your Bank’s IFSC Code?
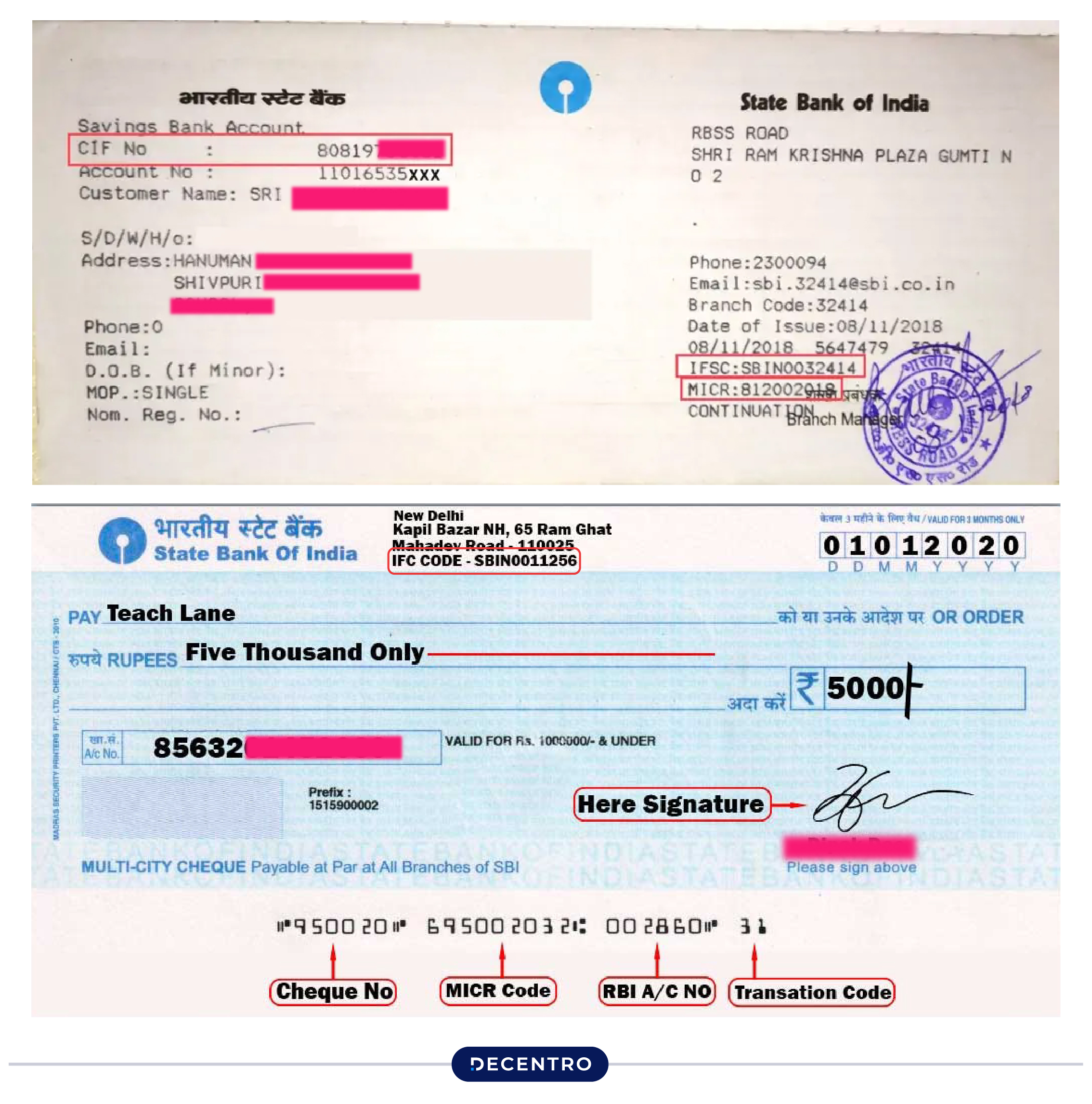
Following are the simple ways to find the IFSC code of your bank branch:
- IFSC code can be found in a bank’s chequebook very easily. It is generally written on the top left-hand side of the cheque.
- Almost all the banks mention the IFSC code on the first page of the passbook.
- IFSC codes may also be found on the respective official banks’ websites.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has a complete list of IFSC codes assigned to all banks.
- Many websites and applications help find or look up IFSC codes.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Making IFSC Transactions

Here are some of the common mistakes you should avoid when using IFSC codes to initiate transactions:
- Using the Incorrect IFSC Code
Always double-check the IFSC code before initiating a transfer. A wrong IFSC code can delay the transaction and cause the funds to be transferred to the wrong bank or account, causing unnecessary complications.
- Entering the Wrong Account Number
Ensure that you have the correct beneficiary account number. Even a small mistake in the account number can send funds to the wrong account, which can be difficult to recover.
- Misunderstanding Transfer Limits
Each transaction method (RTGS, NEFT, and IMPS) has its own set of limits. To avoid failed transactions, it’s essential to understand the maximum amount that can be transferred under each method. For example, RTGS is typically used for high-value transactions above ₹2 Lakh, while IMPS allows instant payments up to ₹5 Lakh.
- Overlooking Transfer Fees
Different transaction methods might incur varying fees depending on the bank and transaction amount. Failing to check for these fees in advance can lead to unexpected charges and potentially affect the transfer amount.
- Wrong Transaction Timing
If you plan to initiate an offline NEFT or RTGS payment, the transaction timings will differ based on the banking hours, weekends and holidays.
Decentro’s Payment APIs: Streamlining Transactions with IFSC Codes
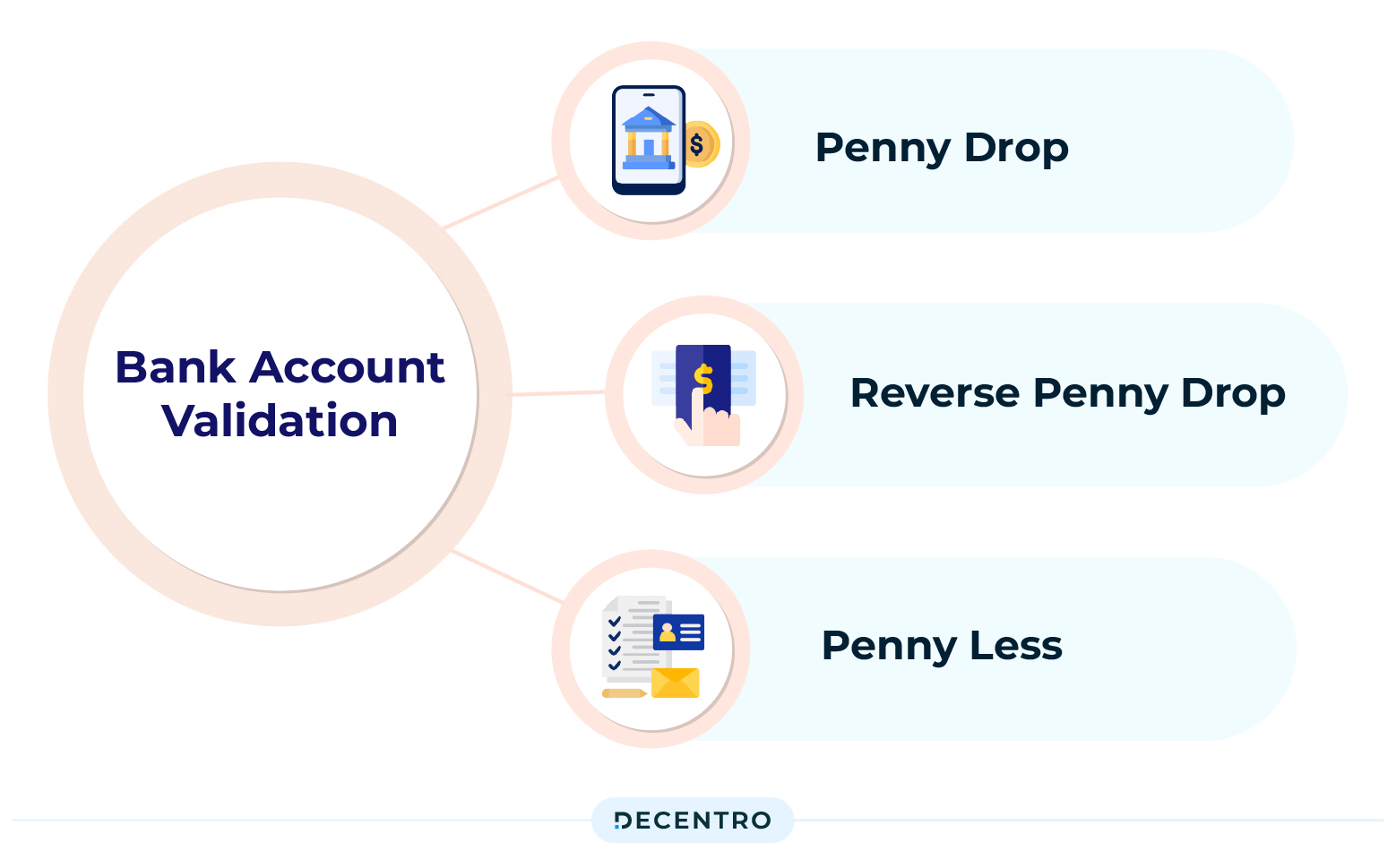
Now that you’re familiar with IFSC codes and their crucial role in banking transactions, it’s time to take your payment processes to the next level. This is where Decentro makes complex IFSC-based transactions easy and secure for businesses.
Using our Bank Account Validation API, you can instantly identify and authenticate a legitimate bank account by providing the customer’s bank account number and IFSC code. This can also be used for bulk account verifications, identifying fraudulent accounts and removing manual errors when initiating payments.
Moreover, you can perform penny drop verification to identify whether a bank account is active before initiating a transfer. Our APIs are easy to integrate into your existing workflow and even enable you to set up automated workflows to help ramp up customer experience.
What else can we do to enhance your business transactions?
Frequently Asked Question
The first four characters of the code represent the name of the bank, the fifth is always 0, and the last six characters indicate the branch code. For example, the first four characters of the IFSC for the State Bank of India are SBIN.
The IFSC code comprises 11 characters consisting of alphabets and numbers. The first four refer to the bank, the fifth will always be 0, and the last six refer to a particular branch.
No, to initiate an NEFT transfer, providing the IFSC code is a mandatory requirement.


