Learn how OPGSP helped Indian businesses accept global payments and why the move to PA-CB marks a major shift in cross-border trade.

From OPGSP to PA-CB: India’s Cross-Border Shift
Avi is a full-stack marketer on a mission to transform the Indian fintech landscape.
Table of Contents

Introduction: The Digital Payment Revolution
Remember when international payments meant endless paperwork, hefty bank charges, and days of waiting? For Indian businesses—especially the smaller ones—selling globally used to be a logistical nightmare. But over the past decade, we’ve witnessed a revolution in how cross-border payments work, largely thanks to Online Payment Gateway Service Providers (OPGSPs) and now Payment Aggregators – Cross Border (PA-CBs).
Let me walk you through this fascinating evolution and what it means for businesses today.
The OPGSP Era: How It All Started
How does OPGSP work?

Back in 2010, as e-commerce began booming in India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recognized the need for a structured framework to handle online export payments. They introduced the OPGSP guidelines, initially focused on “Processing and Settlement of Export Related Receipts.”
In simple terms, OPGSPs acted as digital middlemen. When a customer abroad paid for Indian goods or services, the OPGSP would:
- Receive the payment
- Convert it to INR
- Transfer it to the Indian seller’s bank account
By 2015, the RBI expanded these regulations to include import payments as well, creating a more comprehensive system for international trade.
Why OPGSPs Were Game-Changers
For over 300,000 MSMEs across India, OPGSPs became lifelines. Before their existence, these businesses had limited options:
- Use expensive foreign payment gateways like PayPal or Stripe (with transaction costs sometimes reaching 3-5%)
- Set up subsidiary offices abroad (expensive and complex)
- Incorporate in foreign countries (even more expensive and complex!)
OPGSPs changed the game by offering:
- Lower transaction fees than traditional wire transfers
- Support for multiple currencies
- Competitive exchange rates
- Real-time tracking capabilities
- Built-in fraud detection
- Chargeback management
Some innovative OPGSPs even offered virtual accounts, allowing Indian businesses to receive payments as if they had local bank accounts in countries like the US or UK without actually opening physical accounts there.
Understanding the Regulatory Framework: How OPGSPs Were Governed
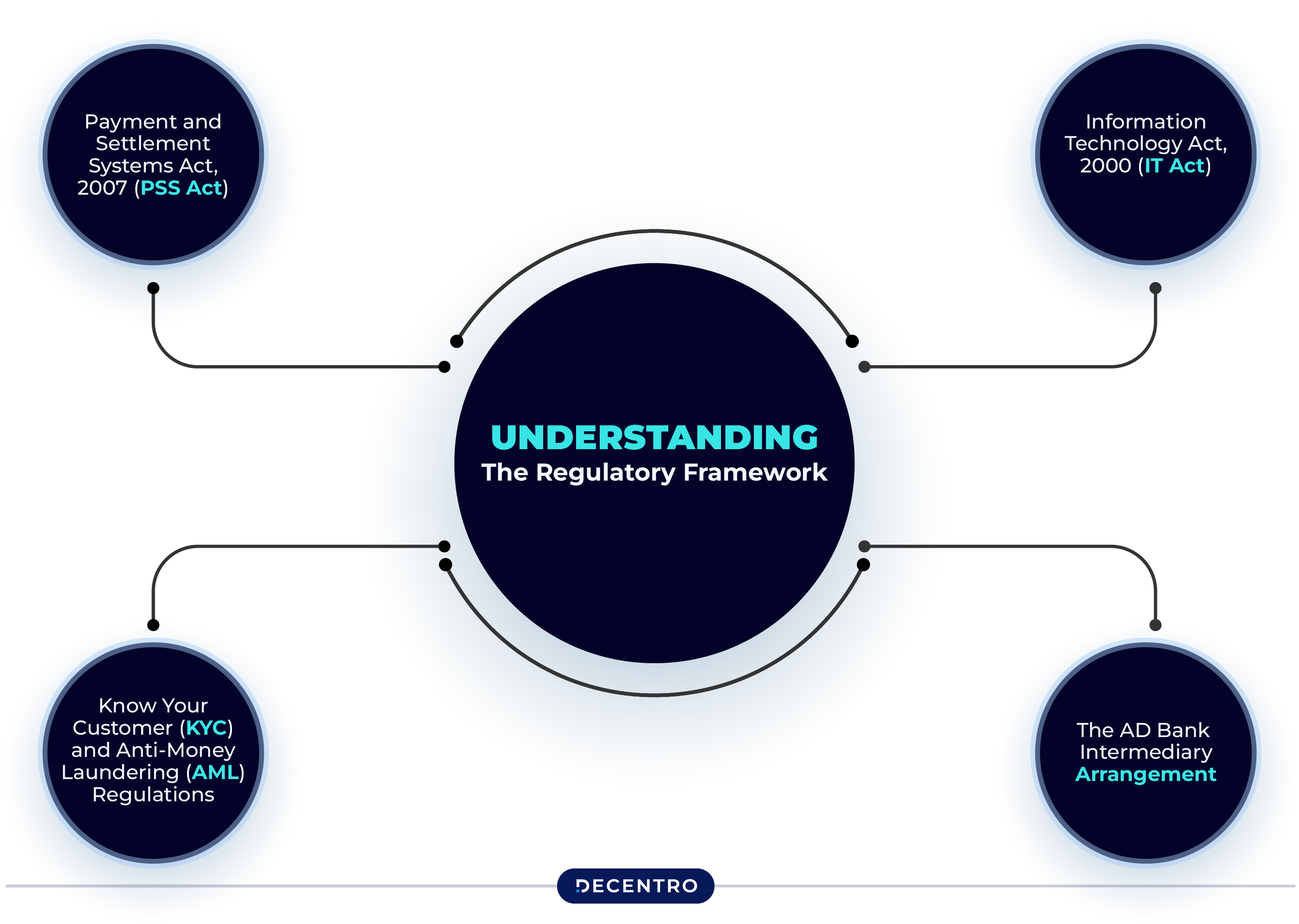
As OPGSPs grew in importance, so did the need for robust regulation. After all, we’re talking about billions of dollars flowing across borders—security and compliance couldn’t be afterthoughts.
The Reserve Bank of India stepped in as the primary watchdog, establishing a multi-layered regulatory framework that balanced innovation with protection. Let’s break down the key components that kept the OPGSP ecosystem in check:
Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (PSS Act)
Think of this as the constitution for payment systems in India. This foundational legislation gave the RBI legitimate authority to regulate payment gateways and ensured they operated within specific boundaries.
For OPGSPs, this meant accountability at every step of the transaction journey. Each international payment had to follow prescribed protocols, creating a standardized approach that helped build trust in the system.
Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act)
With cyber threats evolving daily, the IT Act provided crucial protection against digital vulnerabilities. It established:
- Legal validity for electronic transactions
- Framework for addressing cybercrime
- Penalties for payment fraud and data breaches
This legislation essentially assured international customers that “your payment information is legally protected in India”—a crucial reassurance for anyone sending money across borders.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations
Perhaps the most visible aspect of the regulatory framework was the KYC/AML requirements. These rules required OPGSPs to:
- Verify the identity of merchants before onboarding
- Implement suspicious transaction monitoring
- Report unusual patterns that might indicate money laundering
- Maintain detailed records of all cross-border transactions
While businesses sometimes found these requirements cumbersome, they served an essential purpose—keeping India’s international payment corridors clean and legitimate.
The AD Bank Intermediary Arrangement
One distinctive feature of the OPGSP model was how they operated through Authorized Dealer (AD) Category-I banks. These banks served as intermediaries between the OPGSPs and the RBI, exercising quasi-regulatory control.
This arrangement meant that OPGSPs weren’t directly regulated by the RBI but rather through their banking partners. While this added a layer of security, it also created operational challenges and sometimes limited the OPGSP’s innovation flexibility.
This regulatory framework shaped how OPGSPs operated daily. From implementing sophisticated encryption protocols to conducting thorough merchant due diligence, compliance wasn’t optional—it was essential for survival in the space.
What Is The Eligibility Criteria for Becoming an OPGSP?

Not just anyone could become an OPGSP—the RBI maintained strict criteria to ensure only legitimate, capable players entered this critical financial space. To qualify as an OPGSP, entities needed to meet several key requirements:
- Legal Entity Status: Only companies incorporated in India under the Companies Act were eligible to apply.
- Financial Stability: Applicants needed to demonstrate sound financial health, including:
- A minimum net worth of ₹10 crore at the time of application
- A positive net worth maintained throughout operations
- Banking Relationships: Prospective OPGSPs had to establish relationships with AD Category-I banks, who would ultimately be responsible for ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Technical Infrastructure: Entities needed robust, secure systems capable of:
- Processing international transactions
- Maintaining transaction records
- Implementing fraud prevention measures
- Ensuring data security compliance
- KYC/AML Capabilities: Applicants needed to demonstrate sound Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures.
- Operational Experience: While not explicitly stated, banks generally preferred partnering with entities that had a proven track record in payment processing.
These requirements created a careful balance—stringent enough to ensure security and stability, but still accessible enough to foster innovation in the cross-border payments space. This framework allowed trusted payment facilitators to emerge while keeping fly-by-night operators at bay.
Even after approval, OPGSPs operated under continuous oversight. They had to submit regular reports to their partner banks, who reported to the RBI. This indirect regulatory approach worked reasonably well but eventually evolved into the more direct PA-CB framework we see today.
The Challenges: Why Change Was Needed
Despite their benefits, the OPGSP framework had its share of challenges:
- Risk management issues, particularly with returns and chargebacks
- Hesitancy from banks to fully embrace the system
- Limited transaction thresholds (USD 10,000 for exports and USD 2,000 for imports)
- Indirect regulatory oversight (OPGSPs were regulated through AD Category-I banks rather than directly by RBI)
These limitations meant many tech exporters still felt compelled to use foreign payment solutions or establish overseas entities.
The Evolution: From OPGSP to PA-CB
In early 2023, the RBI proposed a new framework called Online Export-Import Facilitators (OEIF). While it suggested higher transaction limits, it also introduced potentially burdensome compliance requirements.
But the fundamental transformation came in October 2023, when the RBI unveiled the Regulations on Payment Aggregators—Cross-Border (PA-CB), effectively replacing both the OPGSP guidelines and the proposed OEIF framework.
RBI’s PA-CB Circular: OPGSP Update 2024

On October 31, 2023, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a master circular titled “Regulation of Payment Aggregator—Cross Border” to streamline the existing cross-border payment framework. Under this new regulatory regime, all Indian entities facilitating online cross-border payments for imports and exports will now collectively be termed Payment Aggregators Cross Border (PA-CB).
Key highlights of the circular include:
- All non-bank entities undertaking cross-border payment activities must apply for RBI approval by April 30, 2024
- PA-CBs must maintain a minimum net worth of ₹15 crore, increasing to ₹25 crore by March 31, 2026
- Transaction limits have been significantly increased to ₹25 lakhs per unit value for goods and services
- PA-CBs must follow KYC norms as per the Master Direction on KYC and perform additional due diligence for transactions exceeding ₹2.5 lakhs
- Based on their activities, PA-CBs can seek authorization under three categories: Export Only (PA-CB-E), Import Only (PA-CB-I), or both Export and Import (PA-CB-E&I)
This regulatory change represents a significant step toward formalising and standardising cross-border payment operations, with the RBI now directly overseeing all such transactions in India. The circular also indicates that no new OPGSPs can be established, marking a clear transition to the PA-CB framework.
What Are PA-CBs and How Are They Different?
Under the new regulations, entities facilitating cross-border payments are now called Payment Aggregators – Cross Border (PA-CBs). They come in three flavors:
- Import-only PA-CB (PA-CB-I)
- Export-only PA-CB (PA-CB-E)
- Both import and export PA-CB (PA-CB-E&I)

The key difference? These entities now fall directly under RBI regulation, moving beyond the previous arrangement where they operated primarily through agreements with AD Banks.
Navigating the New PA-CB Regulations: What Businesses Need to Know
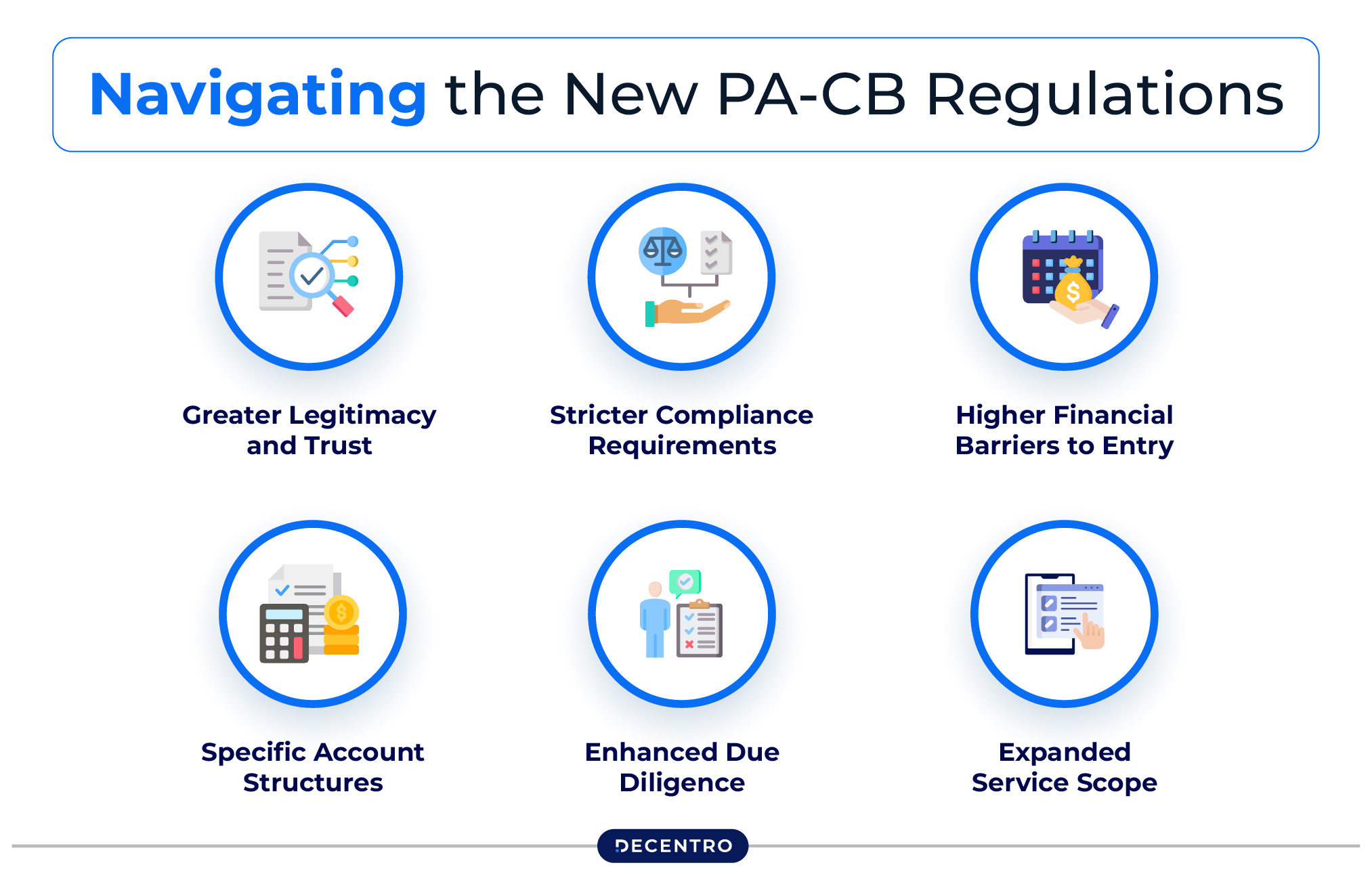
1. Greater Legitimacy and Trust
Direct RBI oversight means customers and partners can place more confidence in these payment systems.
2. Stricter Compliance Requirements
Non-bank PA-CBs must:
- Register with the Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND)
- Implement robust fraud prevention and risk management
- Follow baseline technology guidelines
- Establish effective customer grievance redressal mechanisms
3. Higher Financial Barriers to Entry
Existing providers needed ₹15 crore net worth at application time, rising to ₹25 crore by March 2026. New entrants face similar requirements.
4. Specific Account Structures
- Import-focused PA-CBs must maintain an Import Collection Account
- Export-focused PA-CBs need an Export Collection Account (which can be in INR or foreign currencies)
5. Enhanced Due Diligence
PA-CBs must conduct thorough checks on merchants and, for larger imports, on buyers too.
6. Expanded Service Scope
The regulations now allow for importing services beyond just software, opening new possibilities for businesses.
Decentro’s Global Product Suite: Your One-Stop Solution for Cross-Border Transactions

In this evolving landscape of cross-border payment regulations, Decentro stands out as a fully compliant comprehensive suite of global products designed to simplify international business operations. Let’s explore how Decentro’s four core global offerings can transform your cross-border transaction experience:
1. Global Payment Collection
Decentro’s Global Payment Collection solution enables businesses to receive payments from international customers seamlessly and cost-effectively:
- Local Collection Capabilities: Accept payments in USD, GBP, EUR, and other major currencies with local bank details
- Multiple Collection Methods: Support for international cards, bank transfers, and popular regional payment methods
- Instant Notifications: Real-time alerts when payments are received
- Automated Reconciliation: Smart matching of incoming payments with your invoices
- Customizable Payment Pages: Create branded payment experiences for your international customers
For SaaS companies, content creators, and service exporters, this means no more payment delays or hefty cross-border fees eating into your margins.
2. Global Payouts
Making payments to international vendors, suppliers, or partners is now as simple as domestic transfers with Decentro’s Global Payouts:
- Bulk Processing: Send multiple international payments with a single API call
- Competitive FX Rates: Save up to 2% on currency conversion compared to traditional banks
- Comprehensive Coverage: Send payments to over 100+ countries worldwide
- Compliance Automation: Built-in checks ensure all payouts meet regulatory requirements
- Detailed Payment Tracking: Monitor the status of each payment from initiation to receipt
Whether you’re paying overseas freelancers, refunding international customers, or settling supplier invoices, Global Payouts eliminates the complexity traditionally associated with sending money abroad.
3. Multi-Currency Accounts
Decentro’s Multi-Currency Accounts allow businesses to hold, manage, and transact in multiple currencies without the need for separate international bank accounts:
- Virtual Account Numbers: Get dedicated account details in major currencies (USD, EUR, GBP)
- Instant Currency Conversion: Convert between currencies when rates are favorable
- Simplified Treasury Operations: Manage your global cash flow from a single dashboard
- Reduced FX Exposure: Mitigate currency fluctuation risks by holding funds in the currency of your choice
This solution is particularly valuable for businesses with regular international transactions, allowing them to avoid unnecessary currency conversions and optimize their foreign exchange strategy.
4. Global Ledgers
Decentro’s Global Ledgers provide businesses with a powerful financial management system for their international operations:
- Multi-Currency Accounting: Track transactions across all currencies in real-time
- Automated Reconciliation: Eliminate manual matching of international payments
- Custom Reporting: Generate financial reports customized to your business needs
- API-First Approach: Integrate ledger functionality directly into your existing systems
- Audit Trail: Maintain comprehensive records for compliance and financial reporting
With Global Ledgers, businesses gain unprecedented visibility into their international money movements, simplifying compliance reporting and financial planning.
Why Choose Decentro?
As a fully compliant PA-CB, Decentro offers several unique advantages:
- Regulatory Expertise: Navigate complex RBI regulations with confidence
- Streamlined Onboarding: Get up and running quickly with a digital-first approach
- Developer-Friendly APIs: Integrate global payment capabilities with minimal code
- Dedicated Support: Access expert assistance for your cross-border payment needs
- Continuous Innovation: Benefit from regular updates and new features aligned with regulatory changes
By leveraging Decentro’s complete global product suite, businesses of all sizes can now access enterprise-grade cross-border payment capabilities without the complexity or cost traditionally associated with international expansion.
Ready to Go Global with Confidence?
The new PA-CB regulations bring opportunities and challenges—but you don’t have to navigate them alone. Decentro is fully compliant with the latest RBI guidelines and ready to grow your business internationally.
Start Your Global Journey Today
Sign up for Decentro’s Global Suite and experience:
- Seamless international collections and payouts
- Local account details in major markets
- Multi-currency management with competitive FX rates
- Real-time transaction visibility and reporting
- Full regulatory compliance without the headache
Special Offer for New Customers: Sign up now and receive your first month of transactions with zero platform fees, plus a complimentary consultation with our cross-border payments specialists to optimize your international payment strategy.
Don’t let regulatory complexity hold back your global expansion. With Decentro’s Global Suite, the world is just one API away.
What This Means For Your Business
If you’re an Indian business engaged in cross-border trade, these regulatory changes combined with Decentro’s solutions offer you:
- More Secure Transactions: Enhanced monitoring and compliance built into every service.
- Increased Transparency: Clear visibility into all your international money movements.
- Operational Efficiency: Automate manual processes and reduce the administrative burden of international transactions.
- Competitive Advantage: Enter new markets faster and serve international customers more effectively.
With Decentro’s comprehensive global product suite, even small businesses can now operate globally with the same capabilities as larger enterprises, all while maintaining full regulatory compliance.
Future of OPGSPs in India
The transition from OPGSP to PA-CB represents India’s growing sophistication in handling international payments. As these regulations create a more robust and secure cross-border payment ecosystem, businesses need partners who can help them navigate this new landscape.
Decentro’s Global Payment Collection, Global Payouts, Multi-Currency Accounts, and Global Ledgers provide the tools businesses need to thrive in this evolving regulatory environment. By combining technological innovation with regulatory compliance, Decentro is helping Indian businesses unlock global opportunities.
As we move forward, businesses that embrace these new solutions will gain a significant competitive advantage in the global marketplace. The world of cross-border payments continues to evolve, and staying ahead of these changes is now easier than ever with the right partner.
Have you started exploring how these new PA-CB regulations will impact your business? Are you ready to upgrade your cross-border payment capabilities with Decentro? Share your thoughts or questions in the comments below!