Discover CKYC’s role in secure customer identification, differences from KYC, and how Hyperstreams can enhance your Fintech compliance with our comprehensive guide.

The Complete Guide to CKYC – Features, Benefits and How It Works
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

Knowledge is power. And in the banking and payments industry, knowledge is essential to operating the system securely and efficiently.
Your knowledge is the industry’s Know Your Customer.
Almost a prerequisite, KYC has become the most convenient and secure way to avail of business services in the BFSI sector. KYC aims to assess the level of risk a person poses to the financial institution serving them. Ideally, if done once correctly, this KYC should suffice across all financial institutions in India.
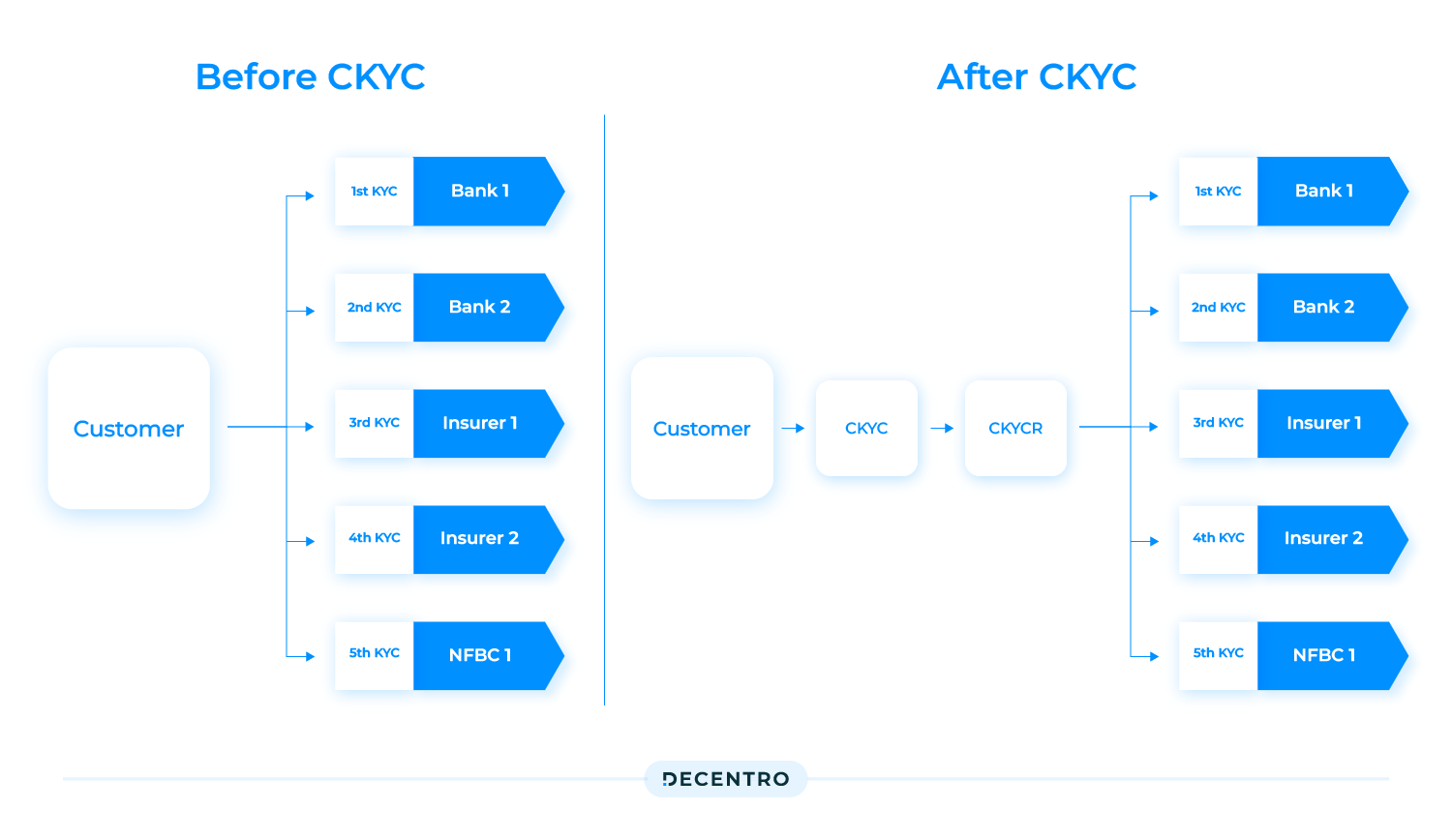
However, the periodic nature of executing the entire end-to-end verification and validation presented itself as an opportunity to have a one-stop repository for all the KYC documentation needs.
The Government of India announced a centralised repository in the form of CKYC in the 2012-13 Union Budget and went live in July 2016. So, with cKYC, once your KYC is done, it does not need to be done again.
While efficiency was the payoff, the intent always stayed rooted in preventing financial fraud, including money laundering and illicit usage of funds. With banks having witnessed the maximum number of frauds in the digital payments category during the fiscal year 2023-24, the need to centralise this process is now more pertinent than ever.
So what is CKYC?
Central Know Your Customer is abbreviated as CKYC. It is a centralised repository that holds customers’ personal information established by the Government of India. Previously, each financial firm had its own KYC procedure. The CKYC contributes to centralising all KYC processes on a single platform.
What is the difference between KYC, eKYC and CKYC?
KYC
Know Your Customer (KYC) is an umbrella term for the identification, due diligence and monitoring protocols put in place for financial institutions to prevent the occurrence of financial crimes.
KYC is done to identify a customer. Through this process, the identity of a consumer is verified. The customer has to fill in the details on a form provided by the financial institution. The customer then submits the filled form. This process is further supplemented by an In-Person Verification (IPV). Once the verification is complete, the relevant customer data is stored with the KYC Registration Agency (KRA).
eKYC
eKYC or Electronic KYC is an enhanced version of the regular KYC process. In eKYC, verification is done with the help of a customer’s Aadhaar Card number. While completing the eKYC process, the authentication of the investor’s identity can be done:
- Via One-Time Password
- Via Biometrics
KRA then stores the data digitally in its record.
CKYC
CKYC was the centralisation of KYC documents of customers availing various services in the financial sector. So, in essence, CKYC is a subset of KYC, just like eKYC. KYC is the traditional manual process of verifying customer identity using physical documents; eKYC is the digital version of KYC that allows remote verification. CKYC is a centralised repository in India that standardises the KYC process and enables interoperability among financial institutions.
Features of CKYC
- CKYC is a 14-digit number associated with the customer’s identification
- The information is securely saved in electronic form. The supplied document is then validated with the issuer
- If the KYC information changes, all relevant institutions are notified
Types of CKYC Accounts
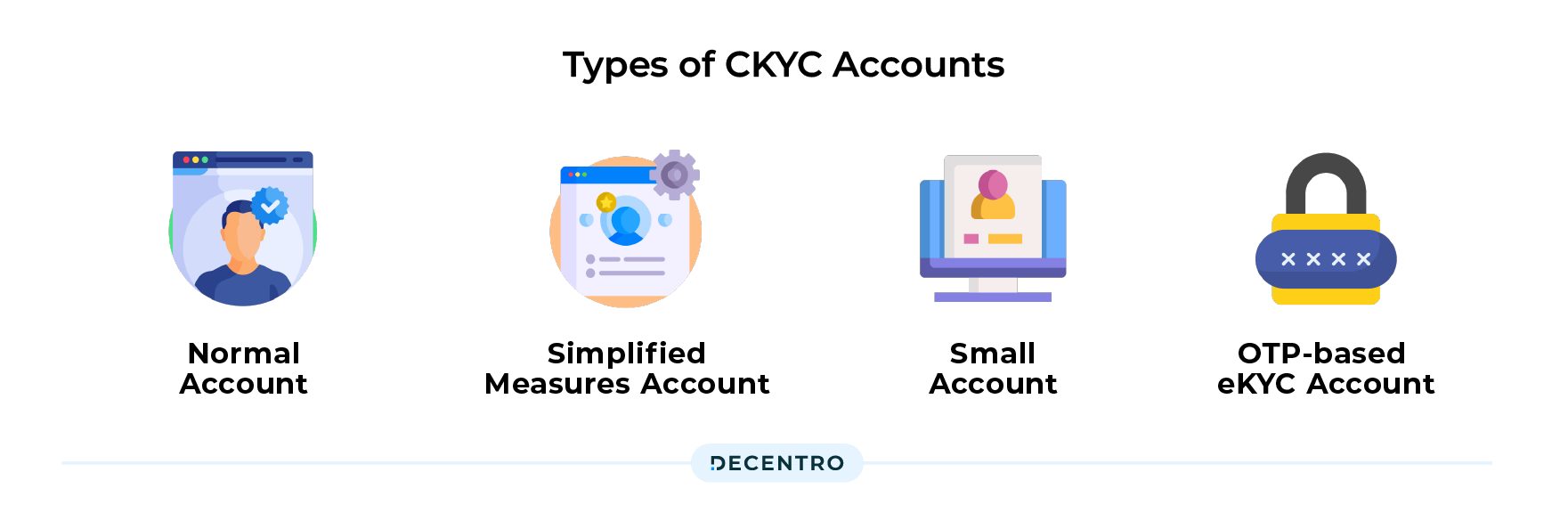
cKYC accounts also vary based on the documents submitted for cKYC verification. There are 4 types of cKYC accounts –
- Normal Account: A normal cKYC account is created if the customer submits PAN, Aadhaar, Voter ID, Passport, Driving License or NREGA job card as proof of identity.
- Simplified measures account: This account is created when the customer submits any other Officially Valid Document (OVD) as proof of identity. Simplified measures accounts possess a cKYC identifier prefixed with an ‘L’.
- Small account: This account is opened when customers submit their identifying details and a photograph. The cKYC identifier for these accounts is prefixed with an ‘S’.
- OTP-based eKYC account: This sort of account is opened for a customer when they perform OTP-based eKYC for customer identification and provide a photograph. The cKYC identifier in this case is prefixed with an ‘O’.
So what is the Process?
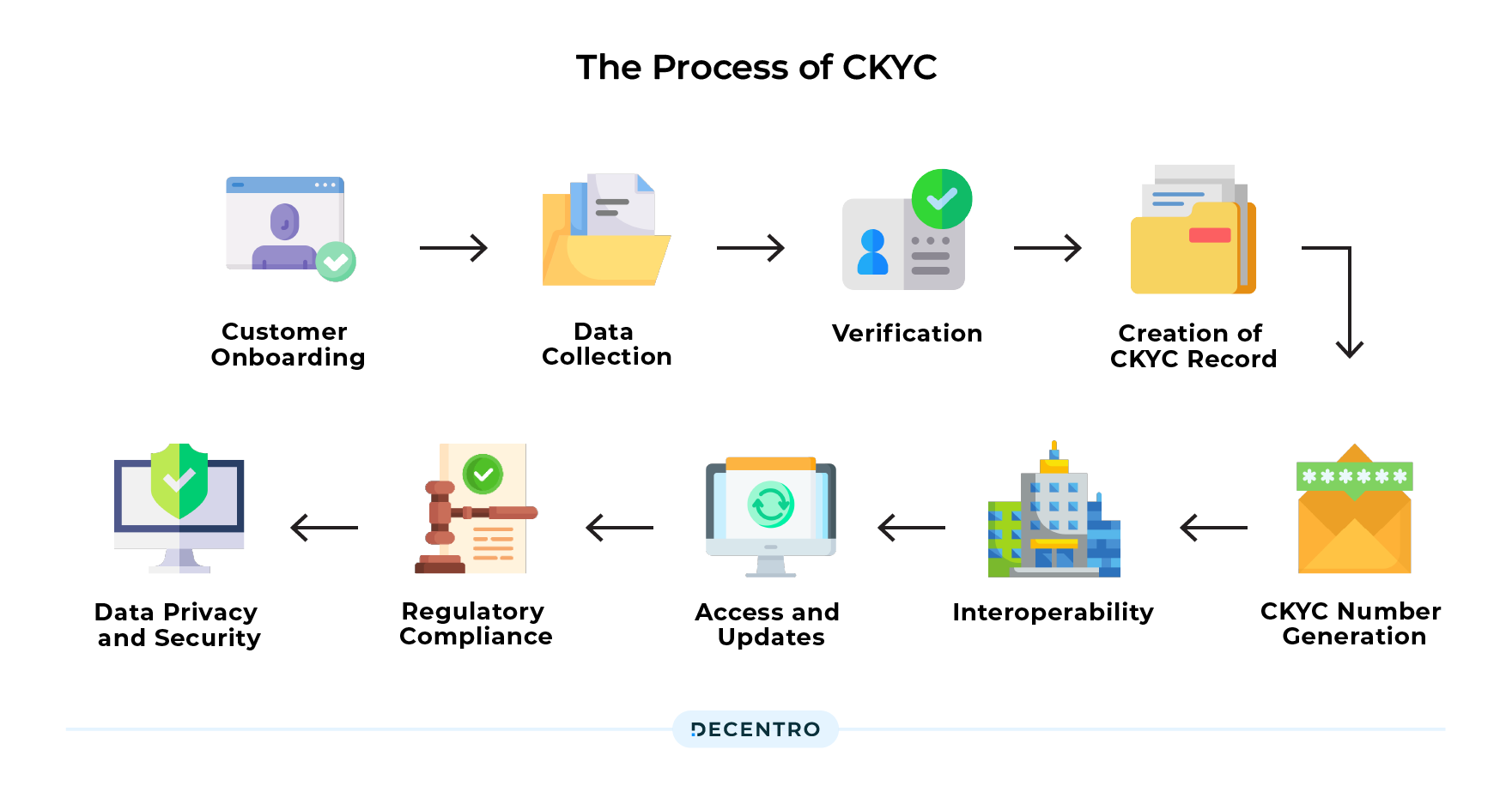
The CKYC (Central Know Your Customer) process in India involves collecting, verifying, and storing KYC information of individuals and legal entities in a centralised repository. The objective is to create a unique identifier for each customer and facilitate seamless and standardised KYC compliance across various financial institutions. Here’s how the CKYC process works:
- Customer Onboarding: When an individual or legal entity wishes to open an account or avail of financial services from a bank, mutual fund, insurance company, or any other regulated financial institution in India, they must undergo the KYC process.
- Data Collection: The customer is asked to submit the necessary identification and address proof documents and other information required for KYC compliance. Commonly accepted documents include Aadhaar, passport, voter ID, driving licence, PAN card, utility bills, etc.
- Verification: The financial institution then verifies the submitted documents and information. This may involve physical verification of original documents or electronic verification through authorised agencies like UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India) for Aadhaar verification.
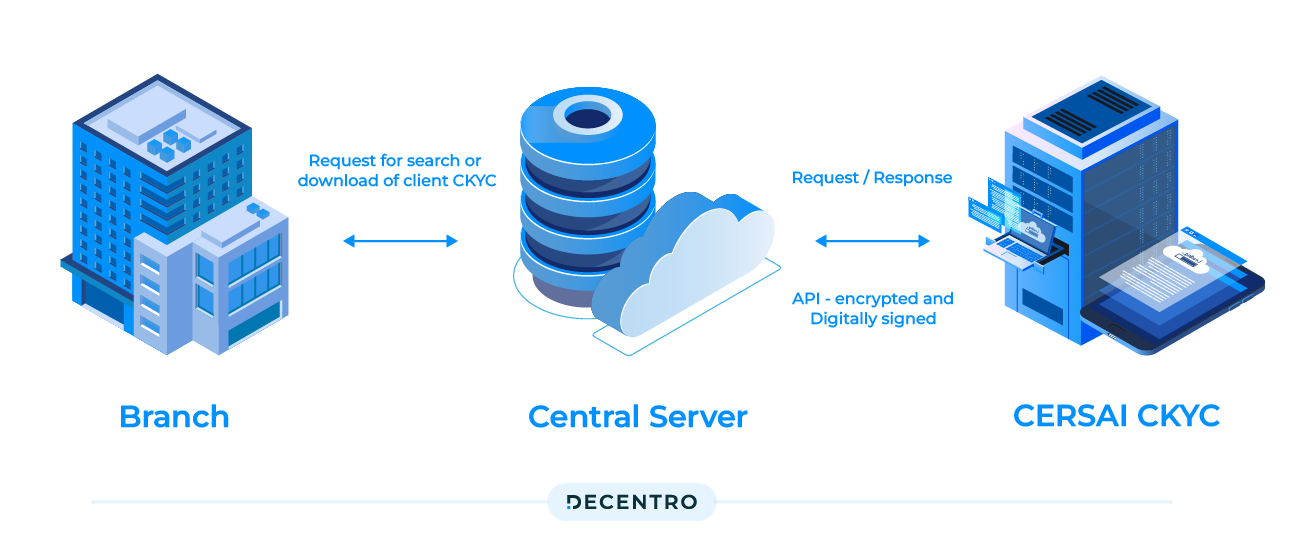
- Creation of CKYC Record: Once the verification process is completed and the KYC details are validated, the financial institution uploads the customer’s KYC data to the Central KYC Registry (CKYCR). The CKYCR is a centralised repository managed by CERSAI (Central Registry of Securitization and Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest of India).
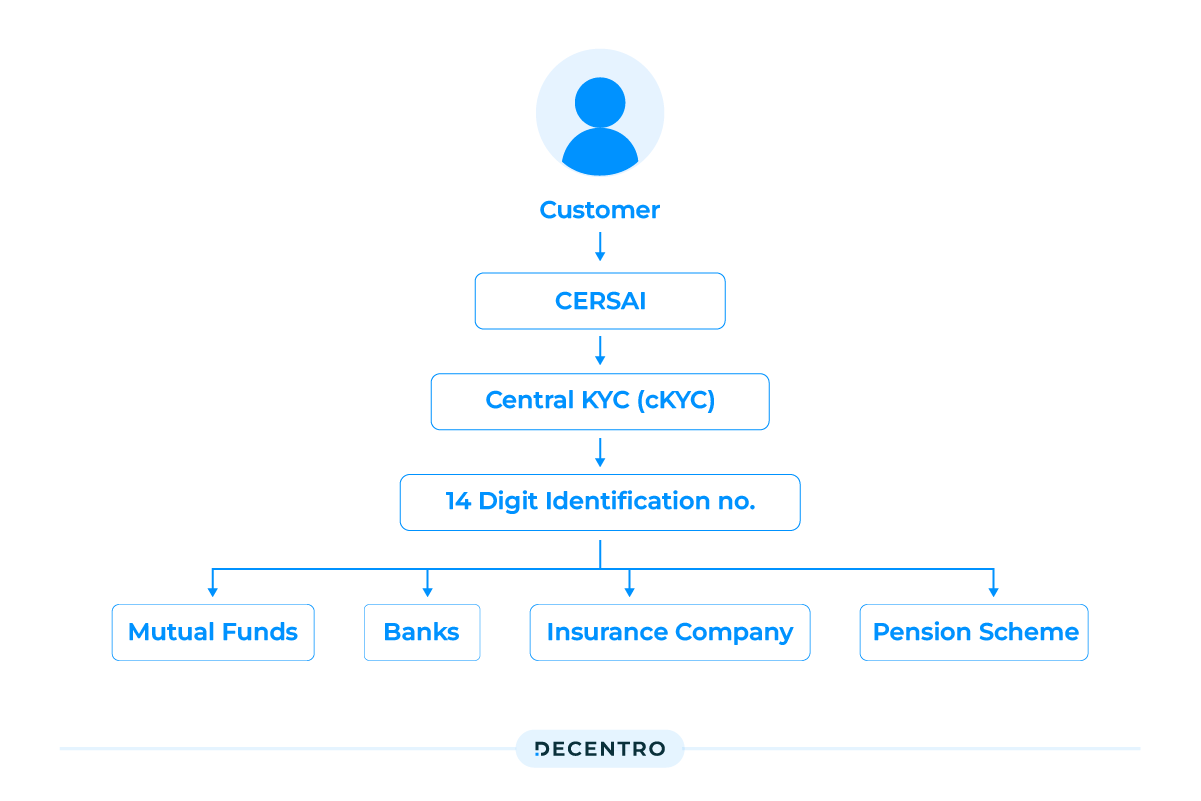
- CKYC Number Generation: After the customer’s information is successfully uploaded to the CKYCR, a unique 14-digit CKYC Number is generated. This number references the customer’s KYC information in the central repository.
- Interoperability: The CKYC Number is shared with the customer and can be used across all financial institutions and intermediaries in India. This allows the customer to open accounts or avail of services from different institutions without repeatedly undergoing the KYC process.
- Access and Updates: Authorised personnel from financial institutions can access the CKYCR in real-time through secure online channels to verify the KYC status of a customer. If there are any changes or updates to the customer’s KYC information, the financial institution is responsible for updating the details in the CKYCR.
- Regulatory Compliance: CKYC helps financial institutions comply with KYC regulations set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulatory authorities. It ensures consistency, accuracy, and standardisation in the KYC process, reducing the risk of fraud and money laundering.
- Data Privacy and Security: The CKYC follows strict privacy and security guidelines to protect customers’ sensitive information. Access to the CKYCR is restricted to authorised personnel only, and customer consent is obtained before sharing their information with other financial institutions.
Where does CKYC fit your Fintech journey?
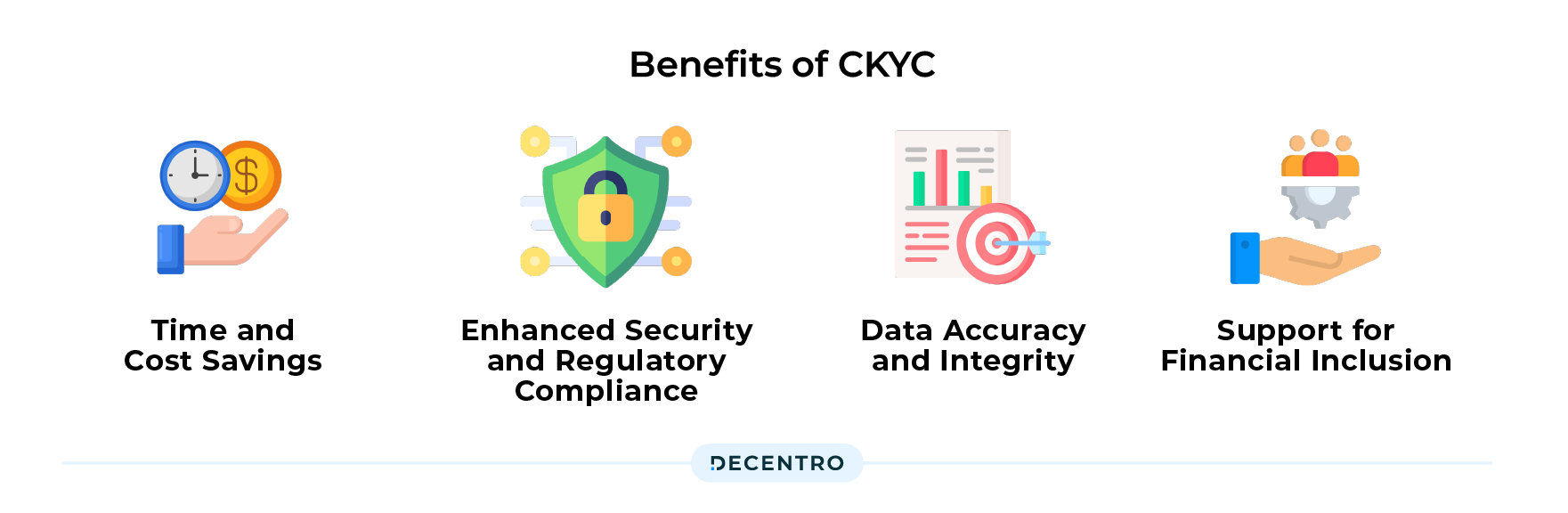
Deploying CKYC (Central Know Your Customer) for your Fintech business is a no-brainer for enhancing both operational efficiency and customer experience. This coupled with
Time and Cost Savings: By leveraging CKYC, Fintech companies can save time and resources for conducting their own KYC verifications. The centralised repository eliminates the need for duplicate KYC checks and physical document verification, thus reducing costs associated with customer acquisition considerably.
Enhanced Security and Regulatory Compliance: CKYC ensures that Fintech companies stay compliant with the KYC regulations set by regulatory authorities such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Additionally, CKYC follows strict data security and privacy guidelines, ensuring customer information is protected and accessed only by authorised personnel. This helps in preventing data breaches and unauthorised access to sensitive customer data.
Data Accuracy and Integrity: Centralized KYC data in the CKYCR reduces the chances of data discrepancies and errors. This ensures that customer information is up-to-date and accurate, leading to better decision-making processes for fintech companies and financial institutions
Support for Financial Inclusion: With the ease of access, financial inclusion discourse takes the front seat every time. More individuals and businesses can join the formal financial ecosystem by simplifying the onboarding process for underbanked and underserved populations. MSMEs and SMEs stand to benefit significantly from a CKYC deployment, and with the target audience sitting in the underbanked segment, there is an efficient trickle-down effect of inclusivity.
Where is the catch?
On the one hand, CKYC APIs and SDKs offer numerous advantages, including faster onboarding, enhanced compliance, improved data security, and a better overall customer experience. We have actively enabled players like CreditWise to connect with various financial institutions such as CERSAI, NSDL, UIDAI, and more.
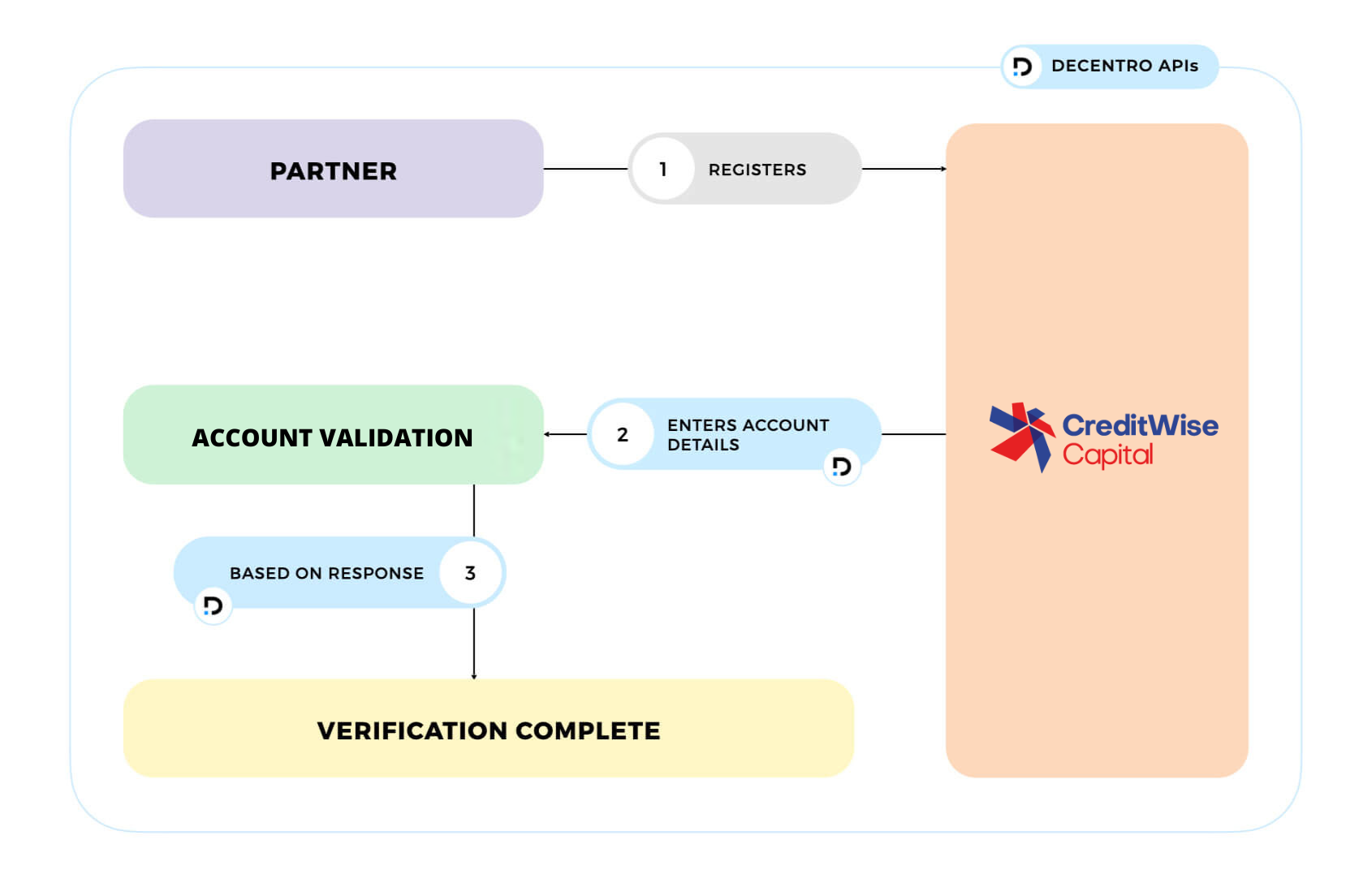
CreditWise was looking for a partner who could absorb the complexity of these integrations and offer a simple API with faster response times. Fortunately, we did see some fantastic transactions on the platform executed end-to-end via Decentro’s integrated APIs. CreditWise saw a 92% hit rate with respect to successful CKYC downloads so far. We could also verify the bank accounts of these verified users.
As rewarding as such partnerships are, there is always scope to do more from a technology perspective. And this scope was recognised by us at Decentro in the form of HYPERSTREAMS.
So what is HYPERSTREAMS?
Hyperstreams are a robust new offering of the Decentro stack that empowers developers to quickly build custom financial products and services. Hyperstreams, designed with the utmost attention to detail, provide seamless integration of APIs and SDKs, enabling you to create exceptional user experiences and drive financial innovation.
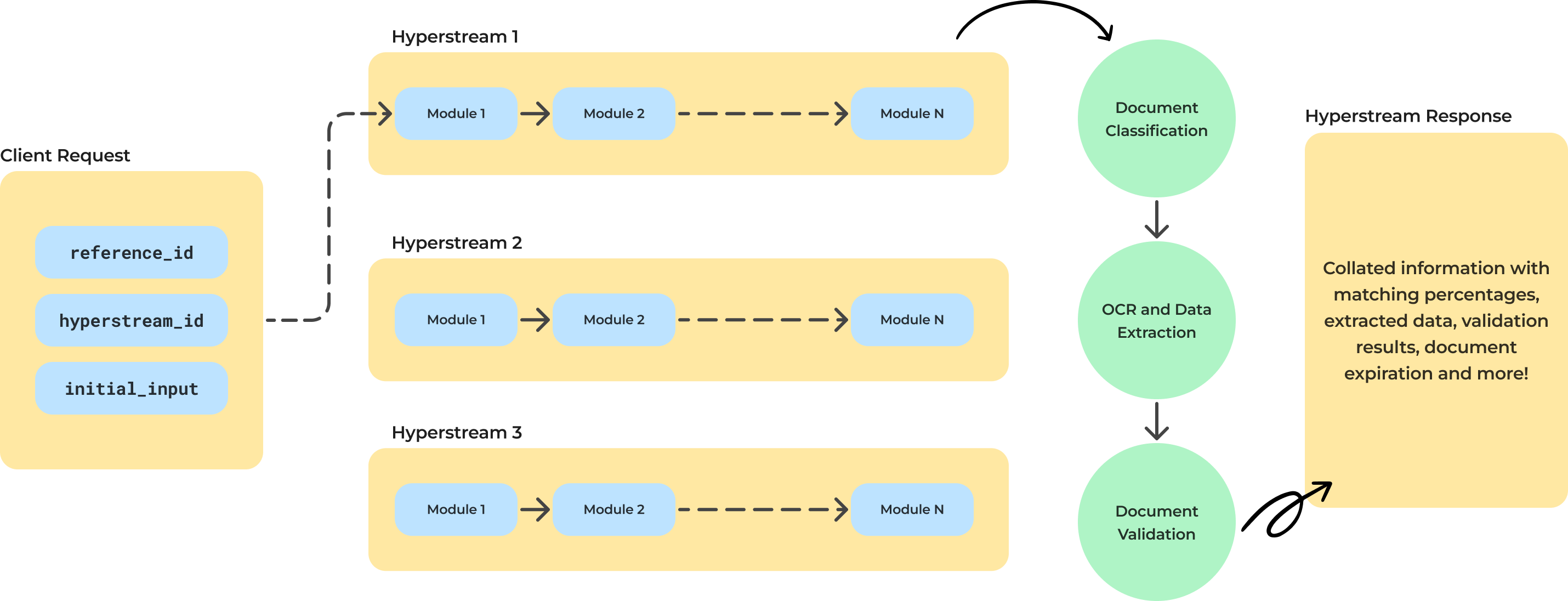
But how is it relevant for CYKC?
Since the changes in Central KYC Registry APIs after v1.2 significantly reduced the occurrences of additional helpful information in CKYC records, using CKYC Download alone for your onboarding might not be a seamless process or, in some cases, fully compliant.
The documents in the CKYC registry need to be classified correctly, and according to RBI’s directions, expired documents in the CKYC registry can no longer be used as valid KYC for onboarding a customer. The Advanced CKYC Download Hyperstream solves all these problems for you.

Furthermore, a CKYC Prefill Hyperstream would be very effective in this particular use case. It would take the minimum possible input from the user, i.e., the name and the phone number. Following this, the Hyperstream fetches all the user documents present in the CKYC Registry.
Whether it is operating on the back of an enhanced technology like Hyperstreams or operating on its own accord, one thing is clear, as the financial landscape evolves, CKYC will play a crucial role in ensuring efficient and secure customer identification and compliance processes. It is for you as a business to decide whether an enhanced offering in the form of Hyperstream is your preferred solution.
Curious to know how this new offering will fit into your roadmap?
Do you have a platform requiring verification of customers or businesses that you’re looking to make live?


