Unlock seamless billing cycles with secure eNACH mandates. Here’s an in-depth guide to getting started with eNACH Mandates & Recurring Payments with Decentro.

ENACH Mandates: A Guide to Effortless Recurring Payments
Heading Product for Decentro, an API banking platform. Built and scaled teams across Product, Data, and Partnerships in the Fintech space.
Table of Contents

A Quick Glance
| The recurring payment mandates, or Mandates, space has been ripe for disruption, across use cases, such as SIP instalments, loan EMIs, insurance premiums, and subscriptions. | The NACH (National Automated Clearing House) platform, a mature and standardised infrastructure by NPCI, stands out for its security and flexibility. | The secure and reliable PAN India acceptance ensures a seamless payment experience for customers. |
| Mandates can be established through different methods like ECS, NACH, UPI, and card mandates, each catering to specific requirements. | ENACH, an enhanced version of NACH, eliminates the need for repeated manual payments, providing a convenient and automated payment solution. | Decentro’s Banking APIs for ENACH mandates present a valuable opportunity for businesses to streamline recurring payments and enhance the overall payment experience for their customers. |
Remember the time when you signed a document mentioning your EMI amount when you bought a car? I guess you missed it, considering the tons of documents you signed.
How about the time you invested on a wealth-tech platform or directly with an AMC for a monthly SIP? Maybe – you remember adding your debit card information.
How about the time when you had to set up your 4K Full HD subscription on Netflix using UPI? Now – you get it. You did it for the first time on Netflix of late.
And what about the time when all your active bill payments on your credit cards failed for insurance premiums? Yikes – that was one heck of a frustrating experience.
So, what’s common about all these scenarios? It’s not cards or UPI; it’s payments, right? Obviously, but what’s different?
It’s recurring payments, also known in the Fintech jargon as Mandates.
What is a Recurring Payment Mandate?
Simply put, an instruction.
A mandate is a consent by an individual or business to consent to debits at a predefined frequency to a specific business entity, like a Lender or an Insurer, for example.
Mandates can be taken in various fashions electronically using ENACH or physically using a physical NACH to a specific corporate, backed by a relevant authorization mechanism to be audited or approved by the customer’s sponsor bank (the account where the payer holds the bank account).
What is the Objective of Recurring Payments?
It’s pretty simple. To ensure payments, primarily to merchants or business entities, happen promptly without minimal hassles to the payer but with a level of authentication. Let’s dive deep into the basics.
Recurring payments came into existence primarily to facilitate use cases that required individuals or businesses to repeatedly pay other companies, thus creating a certain element of friction in user experience. Some important use-cases include SIP installments, Loan EMIs, Insurance premiums, and subscriptions.
What are the Types of Recurring Payments?
Recurring payments exist across the board on other payment infrastructures, each designed to power specific use-cases. Let’s look at some of them.
ECS Mandates
ECS Mandates are primarily payer-initiated, where the payer adds a biller to the payer’s bank account.
NACH Mandates
NACH Mandates are primarily payee initiated where the payee creates a directive authorized by the payer through specific modes
ENACH Mandates
ENACH mandates are e-mandates that use ENACH for recurring payments. ENACH mandates are entirely digital and can be created, registered, and managed online via an ENACH service provider like us, Decentro.
UPI Mandates
These are primarily payee-initiated mandates where the payee creates a directive authorized by the payer through UPI.
Card Mandates
The mandates are primarily payee initiated, where the payee creates a declaration authorized by the payer through a debit or credit card.
Typically, once the payee is authorized to debit by the payee at a specified date or frequency, transactions are debited if there are sufficient funds in the linked account of the payer.
What are NACH Mandates?
As mentioned above, NACH mandates are a recurring payment method where the mandate is linked to an underlying bank account of the payer, which in most cases is a savings or a current account.
The NACH infrastructure processed 2.46B transactions in the current financial year, according to NPCI.
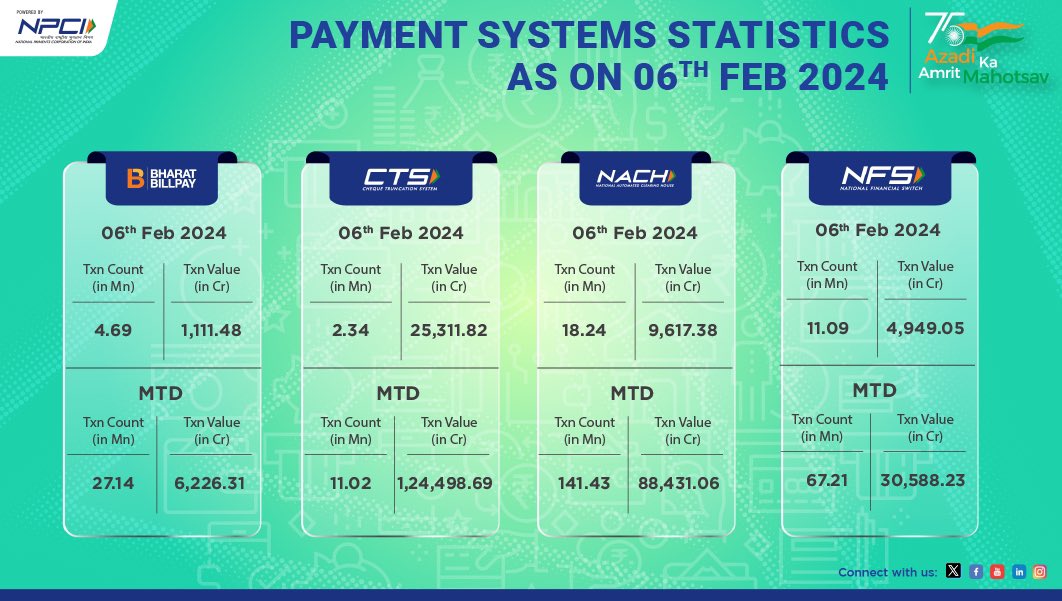
NACH stands for National Automated Clearing House, a framework established by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI). NACH was introduced to replace the legacy ECS-based mandates, which varied across banks to simplify the payment infrastructure.
NACH is a payments infrastructure that can be implemented by any regulated bank in the country as a sponsor or destination bank and adopted by any Indian business entity looking to facilitate payments.
Your business can use the NACH platform to debit accounts for specific use-cases or credit beneficiary accounts like refunds, dividend payments, etc.
What are the Types of NACH?

Two types of NACH can be activated to transfer funds electronically.
- NACH Debit
NACH Debit collects various payments such as insurance premiums, loan EMI, bill payments, etc. Large institutions like insurance companies and banks receive periodic payments from a large group of customers through this facility.
- NACH Credit
Large corporations use this type of NACH facility to send money to a pool of beneficiaries. For example, a corporate entity uses NACH Credit to pay salary or dividends to every employee each month.
What are the Benefits of NACH Mandates?
A lot, as a payee and payer. Due to its security and flexibility, NACH facilitates recurring payments of high value or frequency but not high time sensitivity.
From a payee’s perspective, NACH ensures that a payer cannot cancel a mandate without requesting the payer. This is a critical risk mitigant for various industries like Lending & Insurance, where there’s a risk of default.
From a payer’s perspective, NACH requires full customer authorization by using account information like Netbanking login credentials or Debit card information. It also eliminates the hassles of repeated manual payments.
How is NACH Different from Other Mandates?
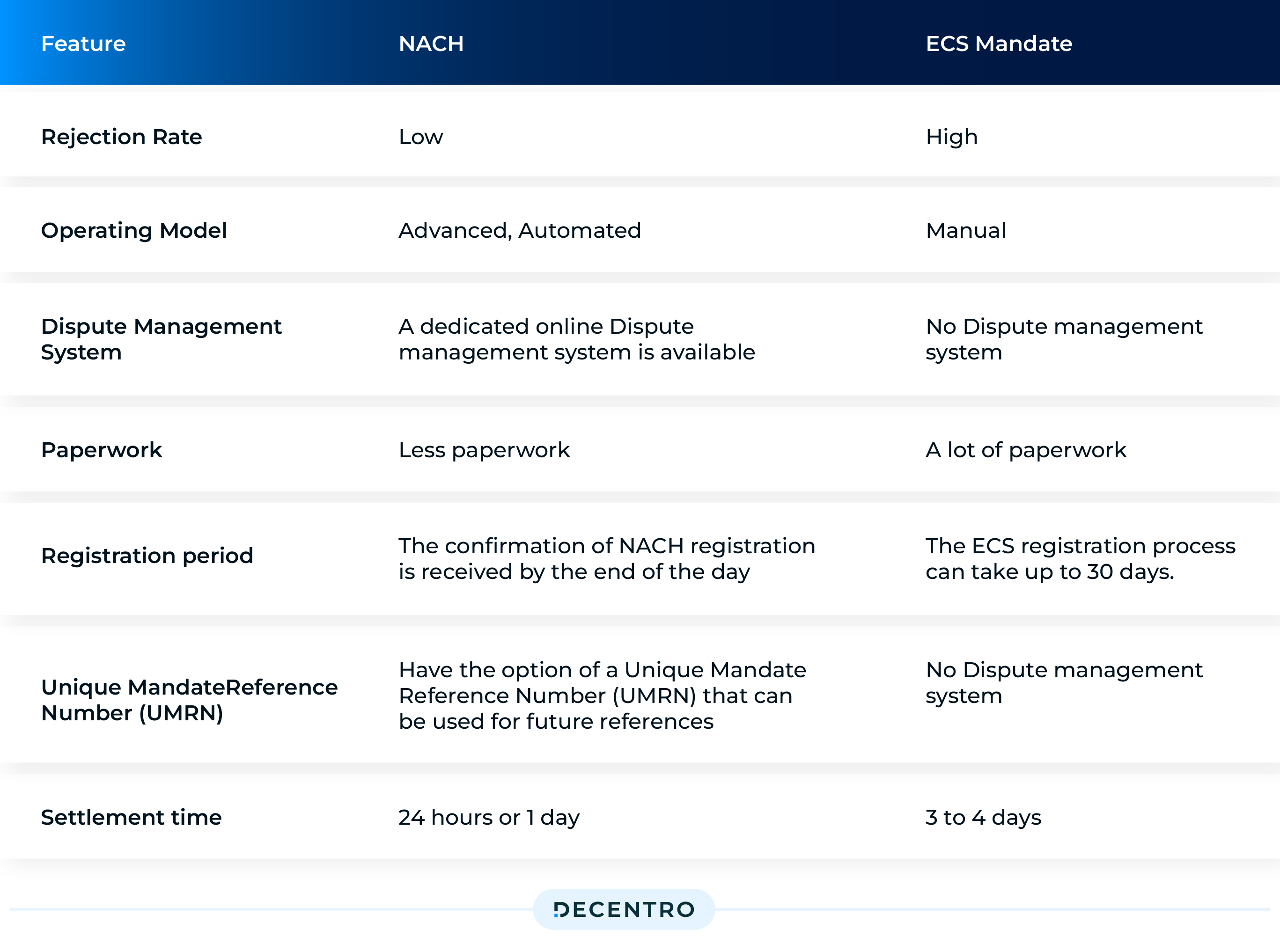
A lot. The NACH platform is a relatively mature and standardised platform across all the central banks in the country, including public and private sector banks.
ECS, or the Electronic Clearing System, was the preferred platform for regular and periodic fund transfers. However, there were many limitations with ECS, which considerably slowed the speed of bulk transactions.
ECS also had a limited reach and was available at only 89 centres. Of the total, 15 were maintained by the RBI, while commercial banks maintained the rest. On the other hand, NACH is operational at more than 82,000 banks branched across the length and breadth of the country. Even smaller banks can cover eNACH and provide instant confirmation of mandate registration compared to ECS, which takes a few days. eNACH provides considerable flexibility compared to UPI in terms of transaction limits.
eNACH mandates are well regulated by RBI and have higher success rates than card mandates, which are still being developed and not offered by all the banks in the country. The industry is still working on credit card mandates.
What is ENACH?
NPCI introduced the ENACH concept for facilitating NACH registration using digital means instead of the traditional way of signing on physical NACH mandate files. ENACH is an enhanced version that brings the same benefits as the conventional NACH mandate.
Electronic NACH, simply put. A popular variant of NACH mandates is the electronic form, popularly known as ENACH, which can be set up using APIs with slightly different limitations.
ENACH can be created by a payer authorizing using Netbanking credentials or Debit card information on an NPCI page, thus ensuring security and making sure mandates are not registered without due authorization.
What are eMandate and ENACH?
ENACH and e-Mandate are services that help customers and businesses manage recurring payments. Both produce the same results, but they differ slightly in terms of structure. Since
NPCI implements ENACH, which includes over 40 banks, and only a few offer e-Mandates. If you choose to use ENACH, you must submit an online form on your bank’s website and have the destination bank approve it. By completing a one-time transaction for authorization on the merchant website, you can set up an e-mandate immediately.
What are the benefits of ENACH?
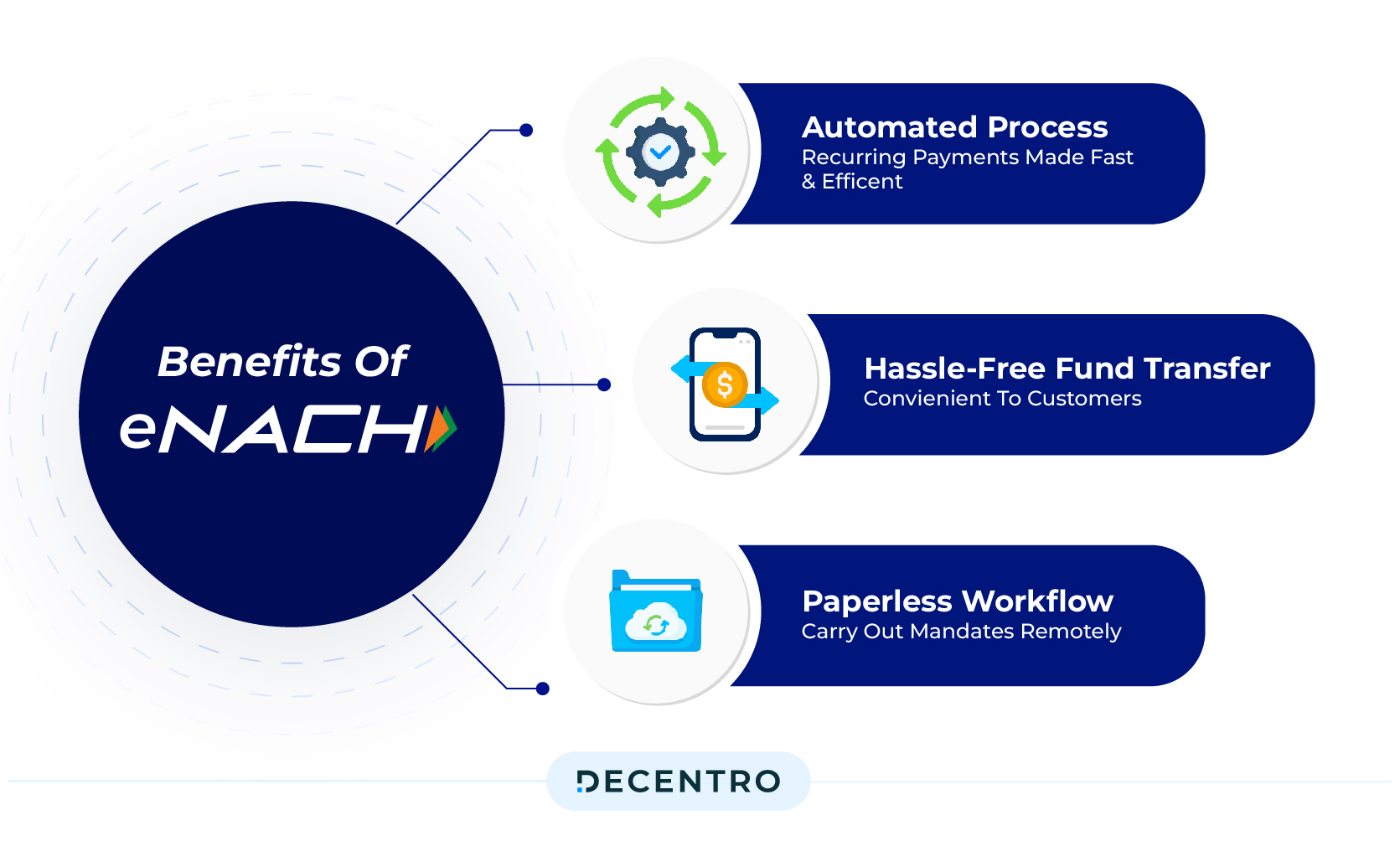
ENACH is not just an electronic form of NACH – it builds on the benefits of traditional NACH to provide a better way of registering mandates.
ENACH registration, which sets up the mandate, requires no physical processes or manual intervention from the payer. This results in instant confirmation compared to physical NACH, which takes at least a week for confirmation and can get rejected due to signature mismatch or account information being incorrect, etc.
ENACH registration also benefits from avoiding fraud as the payer needs to key in confidential account information, thus avoiding any scenarios of the fraudulent mandate being registered or registration happening without consent.
Apart from convenience and compliance, we also have the following benefits attached to ENACH:
Improves your Customer Retention
The auto-recurring nature of ENACH and a one-time ENACH authentication ensure a seamless service experience and better customer retention.
Ensures Frictionless Payments
The one-time set-up system with ENACH is a clear winner when ensuring fricitonless payments and a better customer experience.
Helps Cut Administrative Costs
Because the payments are auto-debited, your employees don’t have to notify the customers about the payments continuously. This cuts down the operational efforts and, thus, administrative costs.
Auto-Reconciliation
Using ENACH, most details about the payments made are recorded online. This makes reconciling easy as your financial data is aligned with your bank and speeds up the overall accounting process.
More Flexibility
With ENACH, the business have the authority to change or modify the payment, which can be done conveniently and almost instantly should the need arise. This helps ensure a good relationship between the business and the customer.
Do all Banks Support ENACH Mandates?
No, but most major banks do. The ENACH platform of NPCI requires the sponsor bank (where the payee has an account) and the destination bank (where the payer has an account) to be live on the platform.
ENACH platform has onboard all the leading private and public sector destination banks live on Debit card or Netbanking authorization modes, with 39 banks live with a debit card, 33 on the net banking, and 28 banks live with both modes.
Essentially, what it means is if your insurer is with HDFC Bank and you have an SBI account, you can register a mandate using either your net banking credentials or debit card for your premium.
What are the Steps in an ENACH?
Two steps, basically. Like all recurring mandates, NACH has 2 steps –
- Registration, which is setting up the mandate
- Presentation, which is the actual debit of a mandate
NACH registration involves the payee mentioning some critical parameters like amount, frequency, and collecting the bank account information of the payer. Post this, the payer authorizes which generates a unique mandate ID if successful.
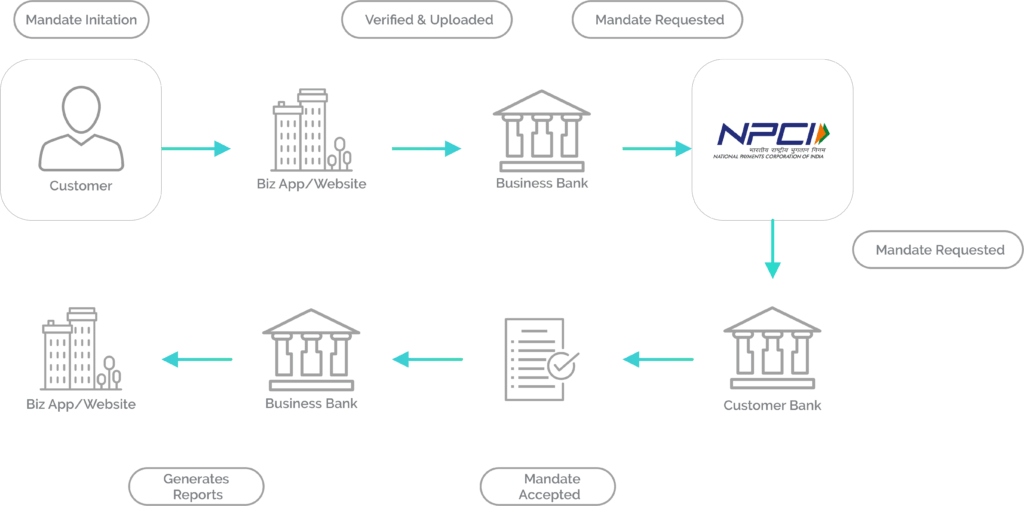
NACH presentation is the actual debit of the funds from the payer’s account on a specified date mentioned at the time of mandate registration. Typically, the transaction is successful if funds are available in the payer’s account.
The following entities are involved in the ENACH process:
- NPCI is a regulatory body constituted by the government of India to oversee all retail payments in India. It was set up with the guidance and support of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA).
- Sponsor Bank: These banks are empanelled with the NPCI to facilitate the eMandate process.
- Destination Bank: The bank where the customer holds their account from which the automatic debit is made.
- Corporate: The company or bank for which the eMandate is requested to enable auto-debits from the customer’s bank account.
- Customer: The person who registers and authorizes the eMandate
The working ENACH
NACH mandate has smooth functioning and works via linking the Aadhar or PAN with the e-NACH.The system relies on transferring all the relevant data like the details of EMI, Loan, etc. The verification process is entirely online, and there is no physical interface. We will explain the work in the following steps:
The process begins with Person X filling out the e-mandate form for recurring payments to the corporation/financial institution Y, i.e., the body receiving the money.
- After filling out the form, Person X submits the e-mandate form to the corporation or financial institution Y. The money-receiving body verifies the details of the payments and transfers.
- Once Y verifies the details, the e-mandate form is transferred to the bank with NPCI.
- After the verification process is completed, Y’s bank account is enabled to receive payments from X’s account for recurring payments.
- There is a provision for X to cancel the payments at any time. However, it is not a blanket rule, and there can be cases where the payment-receiving body might have explicitly disallowed the discontinuation of the payments. Some banks and mutual funds don’t allow the cancellation of recurring payments.
Are There Limits on NACH Mandates?
Yes. NPCI places limits on the registration amount at a mandate level. NACH limits are presented to protect the payer from excessive mandates and help avoid misuse of funds. The debit is rejected if the amount presented exceeds the registered or maximum amount.
Here are a few limits you can keep in mind –
- There are no limits on the registration amount set for physical NACH.
- ENACH registrations have a limit of 10,00,000 per mandate. NPCI increased this limit to the existing limit of 1,00,000, which was maintained from inception.
- The limits for the execution of e-mandates without the Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) have been raised from Rs. 15,000 to Rs. 1 lakh per transaction. This limit has now been increased for mutual funds, insurance premium subscriptions, and credit card repayments.
- Given the growing liquidity requirements of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and requests from industry, the NACH mandate limit for Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) settlements has been increased to ₹3 crore.
Who Can Start Using ENACH Mandates?
NPCI allows businesses to register as corporates and start using ENACH or even physical NACH through a sponsor bank, typically a scheduled commercial bank.
Businesses typically can use the services of an aggregator like Decentro to piggyback on their corporate code to collect payments, where Decentro audits the use-case of the mandates.
Businesses can also choose to register with NPCI as a corporate and use the service of a service provider like Decentro to integrate with a sponsor bank to facilitate ENACH registration and presentation flows.
Can Payers Cancel NACH Mandates?
Yes. Payers can contact the concerned payee or the corporate facilitating the payments to have a mandate cancelled or modified based on a genuine justification.
Cancellation and modification of NACH mandates are subject to mutual agreement between the payer and payee in most scenarios like lending. The lender might not cancel the mandate until the loan is repaid.
Payees or corporates typically cancel mandates once the product or service for which the mandate has been registered is completed or fully delivered, like loan repayment or when an insurance policy matures.
How Can Decentro Help Your Business with ENACH?
Decentro has integrated with NPCI, a leading banking partner, to simplify the entire ENACH integration process, from registration to presentation.
Businesses can just use the plug-and-play APIs to Decentro to integrate with NPCI and go live within a couple of weeks. Decentro, on its own, manages the integration with NPCI and the constant maintenance and connectivity.
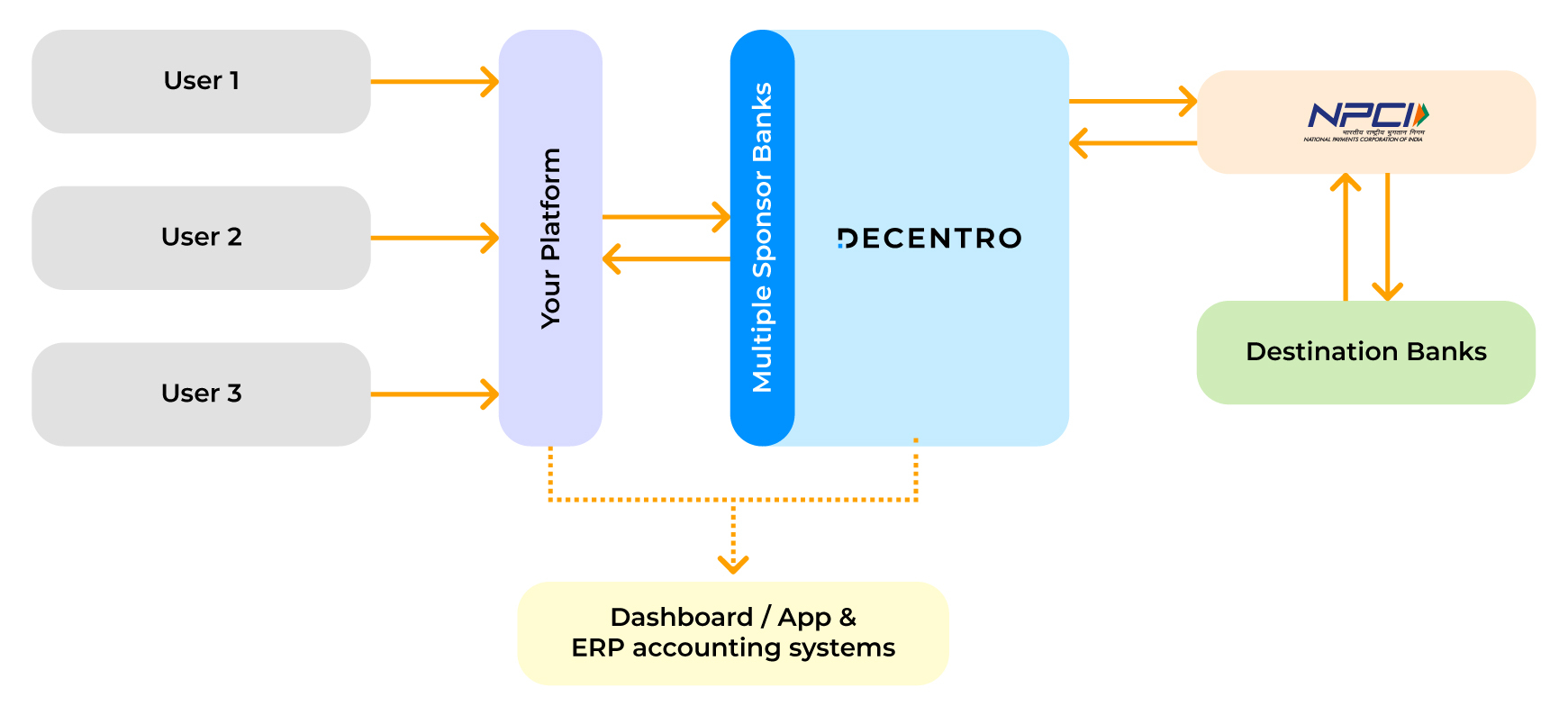
Businesses who are looking to set up the ENACH service on their account can also integrate using Decentro to facilitate collections into their collections account, with Decentro acting as a technology partner.
For Your Customers
With Decentro, enable your customers with the following.
- Instant confirmation on registration.
- Uninterrupted payment cycle.
- Secured and assured PAN India acceptance.
How will Decentro’s banking APIs to facilitate recurring payments help your product? Let’s see!
For Your Product
- Facilitates mandate processing with multiple sponsor banks.
- Provides configurable mandate form to platforms.
- Enable recurring payments up to ₹1 Crore
For Your Engineering Team
How about the engineering team who’s hard at work? Would you like to provide them ENACH APIs that make things easier and enable them to build quickly and ship faster? Our APIS have:
- 99.9% Uptime
- Require only a single endpoint or multiple sponsors bank
- Enables swift mandate processing to and fro.
For Your Ops Team
Not just the tech part of things, create an ecosystem for your ops team to function better!
- Real-time tracking and status updates.
- A single view of mandate generated, status, and frequency for debit.
- 8x reduced manual effort.
If you’d like to enable the same for your business, we’re just a chat away at hello@decentro.tech.


