Uncover the key trends driving SME lending in India and how digital platforms are transforming access to financing for small businesses.

The Importance of Effective Underwriting in SME Lending
Avi is a full-stack marketer on a mission to transform the Indian fintech landscape.
Table of Contents

The Indian economy is heavily bolstered by the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector, a key driver of India’s GDP, employment, and exports.
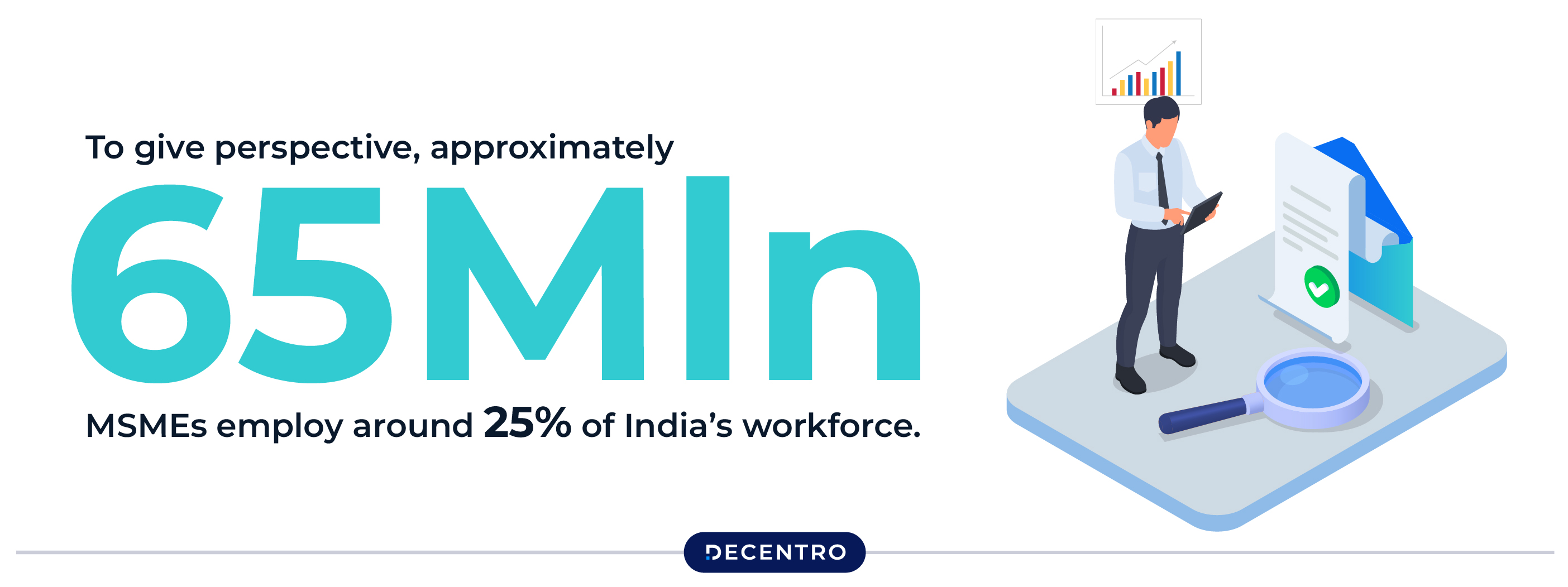
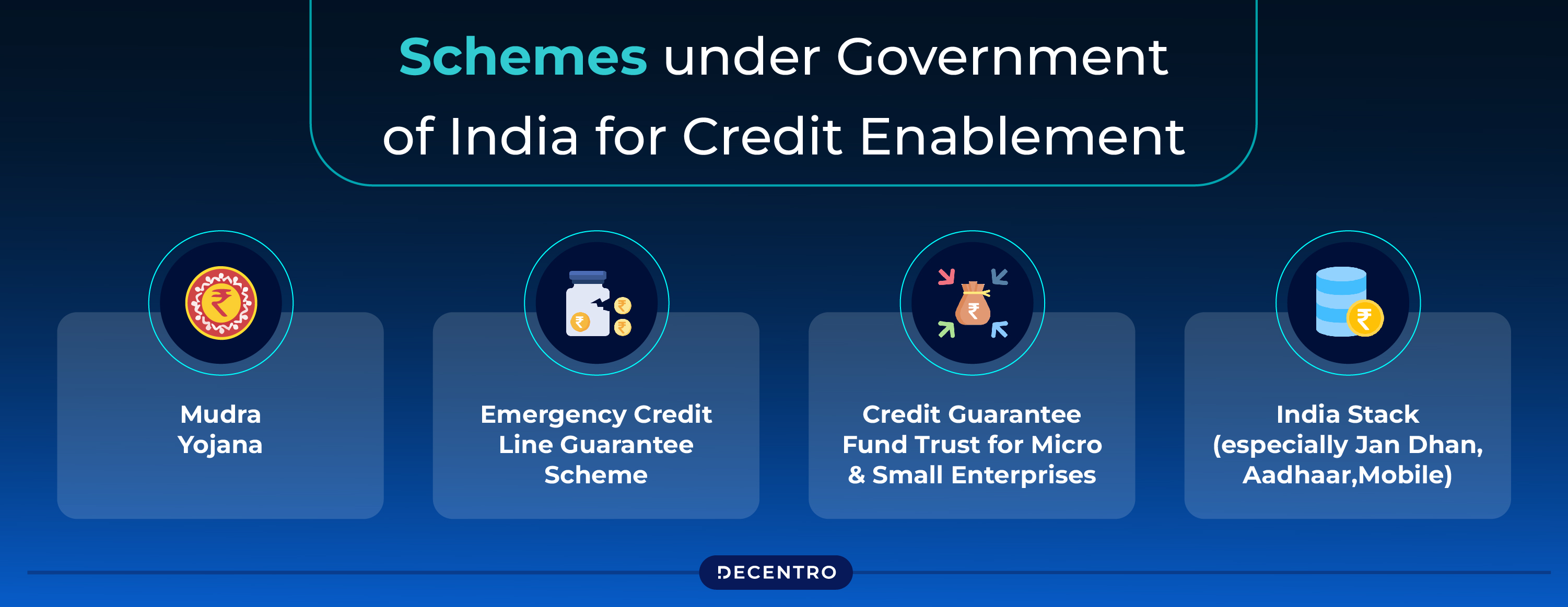
To give perspective, approximately 65 million MSMEs employ around 25% of India’s workforce. Therefore, the growth of SMEs will be a huge driver in India’s overall economic growth, both directly and indirectly. However, in recent years, SMEs in India have encountered significant barriers in accessing the credit required for growth. Despite the various measures by the Govt. of India to address this gap by introducing the Mudra Yojana, Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme, Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises, and India Stack (especially Jan Dhan-Aadhaar-Mobile), the huge requirement for capital remains unsatiated. This has limited the sector’s ability to contribute to the nation’s economic potential fully. Bridging this gap is essential to unlocking the MSME sector’s growth potential and fostering a more resilient and self-reliant economy.
With advancements in digital innovation and financial technology, there is a renewed opportunity to close the credit gap and capital requirement. In this blog, we explore the complexities of SME lending in India and how new-age lending and underwriting solutions can simplify risk management, driving greater impact across the financial landscape.
Challenges in SME Lending in India

Below are the current set of challenges faced by SMEs/ MSMEs w.r.t loans and financing in India:
- Limited Access to Formal Credit – Many MSMEs in India struggle to access formal credit through traditional financial institutions. This is primarily due to a lack of proper documentation, limited credit history, and insufficient collateral, all of which hinder their ability to meet the eligibility criteria set by lenders.
- Collateral Requirements—Traditional lenders typically require collateral to secure loans, making it difficult for small and micro-enterprises that often lack valuable assets to obtain the necessary capital for growth and operations. This requirement poses a significant barrier for these businesses.
- High Interest Rates—MSMEs often face higher interest rates compared to larger enterprises due to the perceived risk associated with smaller businesses. As a result, the cost of borrowing becomes prohibitive for many, further limiting their ability to access affordable financing.
- Lack of Financial Literacy – Many MSME owners lack a deep understanding of financial processes and formal lending procedures. This lack of financial literacy is a significant barrier, preventing them from navigating the complexities of securing credit and making informed borrowing decisions.
- Inadequate Credit Information—Another key challenge is the absence of reliable credit information about MSMEs. Lenders struggle to accurately assess the creditworthiness of smaller businesses, often leading to conservative lending practices or outright denial of credit, further exacerbating the funding gap.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from government bodies, financial institutions, and MSMEs. Solutions such as digital lending platforms, credit guarantee schemes, and improved financial literacy programs are crucial for enhancing the lending ecosystem for MSMEs in India.
Trends Shaping SME Lending in India
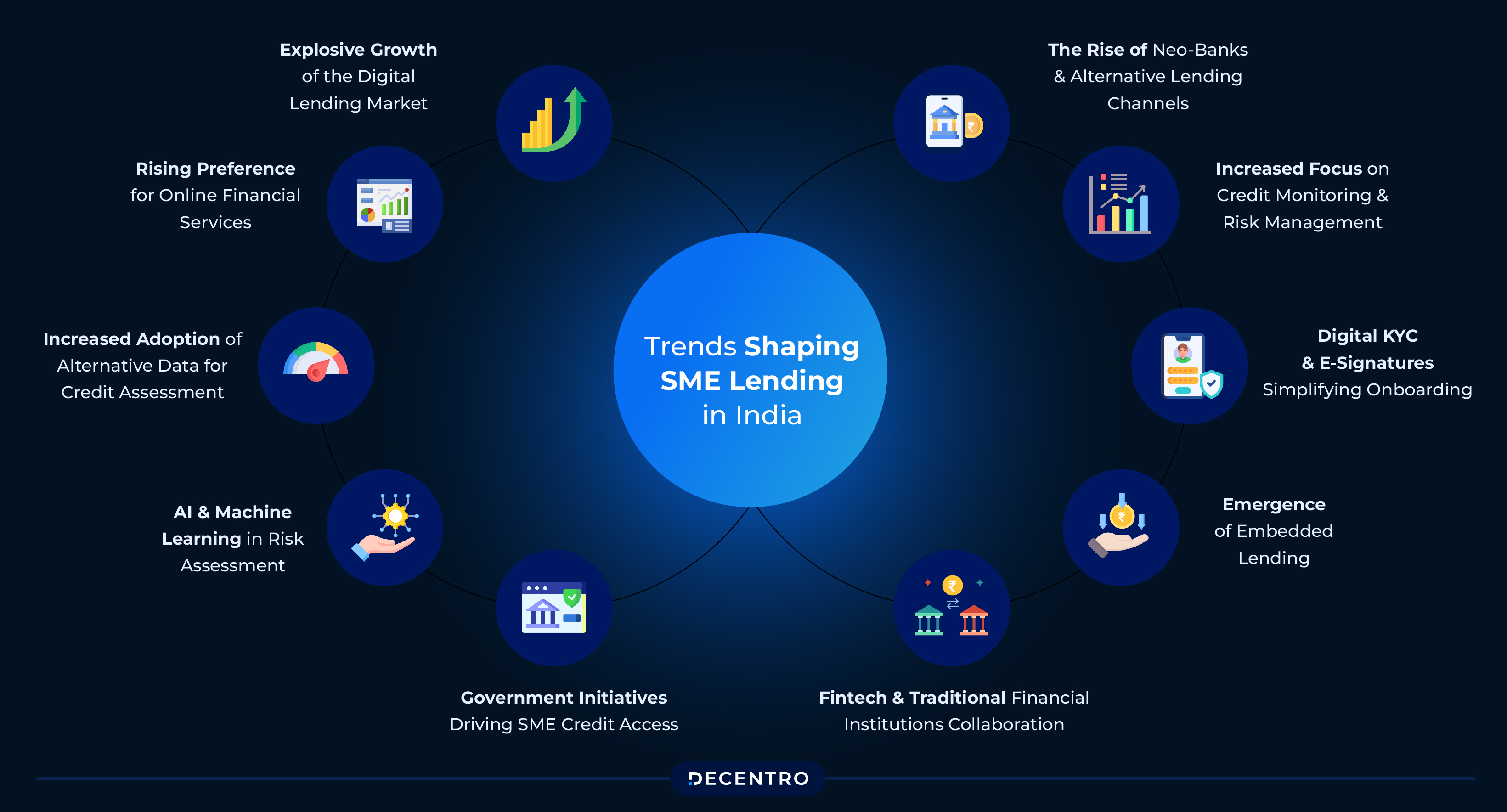
The SME lending landscape in India is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by a combination of technological advancements, policy interventions, and evolving consumer preferences. As traditional lending models struggle to keep pace with the growing needs of SMEs, digital lending has emerged as a game-changer, providing quicker, more accessible, and data-driven credit solutions. Here are some key trends that are shaping SME lending in India:
Explosive Growth of the Digital Lending Market
The digital lending market in India has witnessed remarkable growth over the past decade. As of 2023, the market value was estimated at around USD 75 billion and is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 22%, reaching USD 515 billion by 2030 (6Wresearch).
Rising Preference for Online Financial Services
As more people access the internet and smartphones, the preference for online financial services has surged. This shift is particularly impactful for SMEs as it enables them to apply for loans online, receive quicker decisions, and access a wider array of financial products tailored to their specific needs.
Increased Adoption of Alternative Data for Credit Assessment
One of the most significant trends in SME lending is using alternative data for credit assessments. Traditional credit scoring models often rely on formal financial documentation and credit history, which many SMEs, particularly first-time borrowers, may not have. To assess creditworthiness, digital lending platforms now leverage alternative data sources such as transaction histories, utility bill payments, and even social media behaviour.
AI and Machine Learning in Risk Assessment
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming risk assessment and underwriting processes in SME lending. These technologies can analyse vast amounts of data in real-time, helping lenders make more accurate and faster credit decisions. Using AI-driven algorithms, lenders can identify patterns in borrower behaviour, predict default risks, and offer tailored loan products.
Government Initiatives Driving SME Credit Access
The Indian government has been actively supporting SME lending through various initiatives to improve access to credit. Programs such as the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) and the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) have provided a safety net for lenders, encouraging them to extend loans to SMEs without the need for collateral.
Fintech and Traditional Financial Institutions Collaboration
Fintech platforms collaborate with traditional financial institutions to drive SME lending. Banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) are partnering with fintechs to leverage their digital infrastructure and technology-driven lending processes.
Emergence of Embedded Lending
Embedded lending is another growing trend in which lending services are integrated directly into platforms that SMEs already use for their daily operations. For example, e-commerce platforms, payment gateways, and accounting software can now offer SMEs access to credit without requiring them to switch between different applications.
Digital KYC and E-Signatures Simplifying Onboarding
The adoption of digital KYC (Know Your Customer) processes and e-signatures is streamlining loan approval and onboarding processes for SMEs. These innovations reduce the documentation burden on SMEs and eliminate the need for physical visits to bank branches.
Increased Focus on Credit Monitoring and Risk Management
As the digital lending market matures, there is an increased focus on real-time credit monitoring and risk management. Lenders invest in technologies that track SME financial health in real time, providing early warning signs of potential defaults. This proactive approach enables lenders to take corrective measures early.
The Rise of Neo-Banks and Alternative Lending Channels
Neo-banks and other alternative lending channels are significantly impacting SME lending. These digital-only banks offer innovative financial products specifically designed for SMEs, including short-term loans, credit lines, and invoice financing. They offer a much more agile and user-friendly experience than traditional banks.
The Regulatory Push and Open Digital Ecosystems Driving MSME Lending
India’s digital lending landscape has experienced rapid growth, fueled by a strong regulatory framework and the adoption of open digital ecosystems like Aadhaar and India Stack. These innovations are the backbone of the country’s financial inclusion initiatives, particularly for MSMEs.
Lending Guidelines & Account Aggregator (AA) Framework
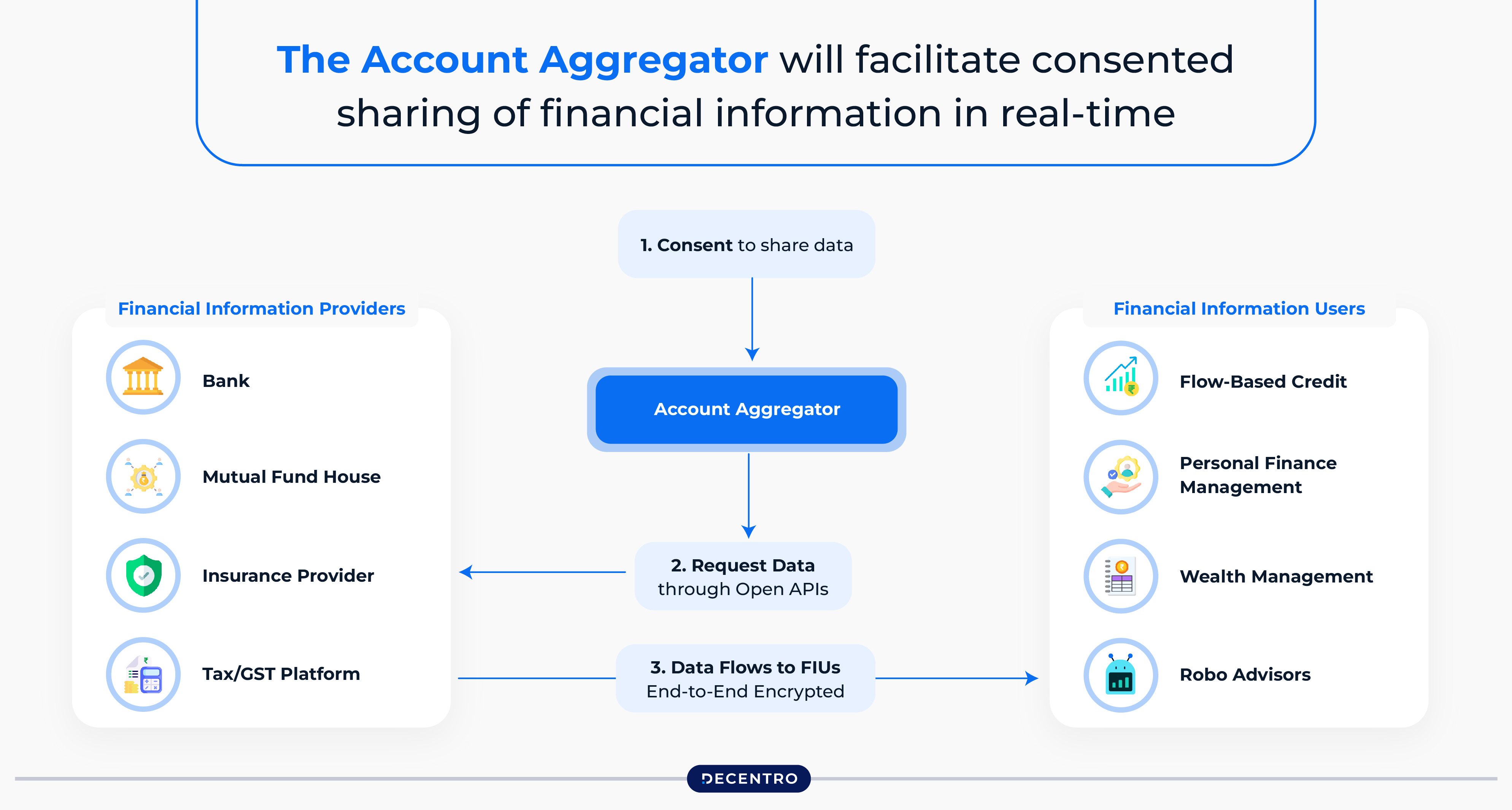
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other regulators have introduced specific lending guidelines to ensure transparency, customer protection, and financial inclusion. One of the pivotal innovations in this space is the Account Aggregator (AA) framework, which allows MSMEs to securely share their financial data with lenders in a consent-based, efficient manner. This open access to reliable financial information is vital for lenders when assessing the creditworthiness of businesses that lack traditional credit histories. Fintech platforms like Decentro are seamlessly integrating with the AA framework to simplify credit decisions for MSMEs.
The Role of India Stack and Aadhaar in Digital Lending
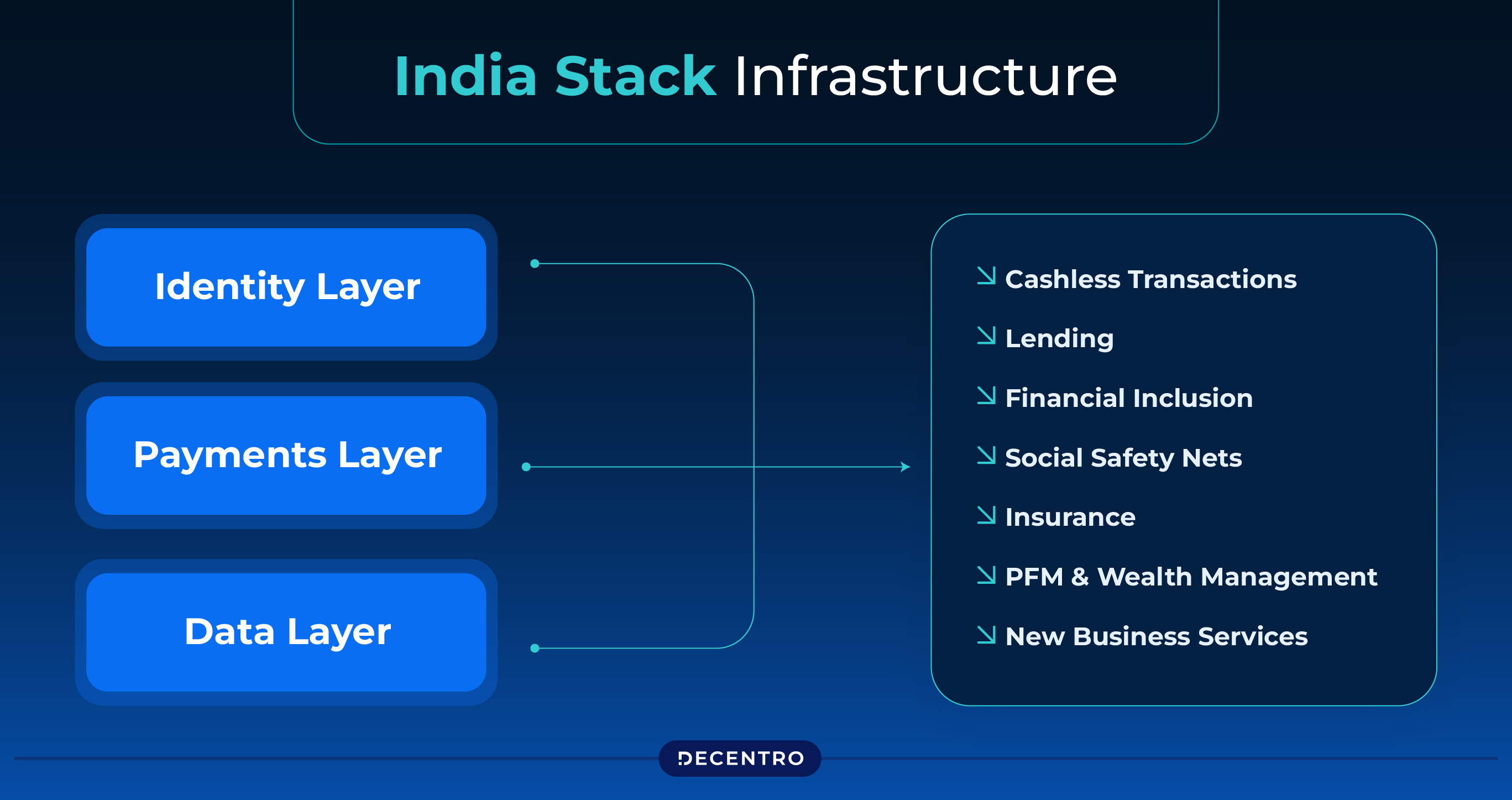
Platforms like India Stack and Aadhaar have revolutionised digital lending, creating an open digital ecosystem that enables rapid onboarding, verification, and credit assessment. The Aadhaar-based KYC process, digital signatures, and consent architecture ensure fast and reliable identity verification. These tools allow fintech companies like Decentro to build efficient and scalable lending processes, reducing onboarding times and minimising risks related to identity fraud.
Proliferation of Digital Lending
Integrating digital public goods, like Aadhaar, e-KYC, Unified Payment Interface (UPI), and DigiLocker, into the financial system has made digital lending more accessible to MSMEs nationwide. Lenders can now quickly assess and verify borrower profiles, even for businesses with limited traditional financial histories. This shift empowers more MSMEs to access unsecured credit, fostering their growth and development.
India’s forward-thinking regulatory environment and the power of open digital ecosystems are setting the stage for a more inclusive lending landscape. Fintech platforms like Decentro are harnessing these innovations to streamline lending processes, making it easier for MSMEs to secure the financial backing they need to grow.
The Importance of Effective Underwriting for SMEs
Lenders assess SMEs’ borrowing capability through underwriting. The process decides whether or not a particular loan and amount should be granted to the borrower. Traditionally, underwriting was carried out using resource-intensive methods such as checking a borrower’s credit score, debts and liabilities. However, these methods carried some issues like:
- Depth of Information—Traditional documents such as bank statements and salary slips provide only a fraction of the information about these SMEs.
- First-time Borrowers – For first time borrowers, there is no credit history or other documented proofs with traditional bureaus. This has created a huge gap in terms of credit information for first time borrowers and young professionals.
The above factors may lead to poor credit penetration and smaller loan book sizes, which in turn reduce revenue and profits.

For effective underwriting, three points must be defined in-depth for better decision-making. These are:
- Intent to Repay – Relies on the behaviour, personality traits, and character of the SME leader.
- Capacity to Repay – Depends on the SME’s income and financial health.
- Stability to Repay – Linked to the stability of the SME’s industry. For salaried employees, this includes factors such as industry growth prospects, CAGR, and hiring or firing trends within the industry.
Here is where alternative data-based underwriting comes in. Fintechs have increasingly adopted credit underwriting engines to automate and streamline the credit underwriting process, leveraging alternative data sources. These engines use sophisticated algorithms and risk models to analyse data from various sources, such as credit bureaus, bank statements, and even social media profiles, to assess the creditworthiness of loan applicants. Credit underwriting engines are advanced software programs that utilise this data to make informed lending decisions.
Why Lenders Should Choose Alternative Data Underwriting
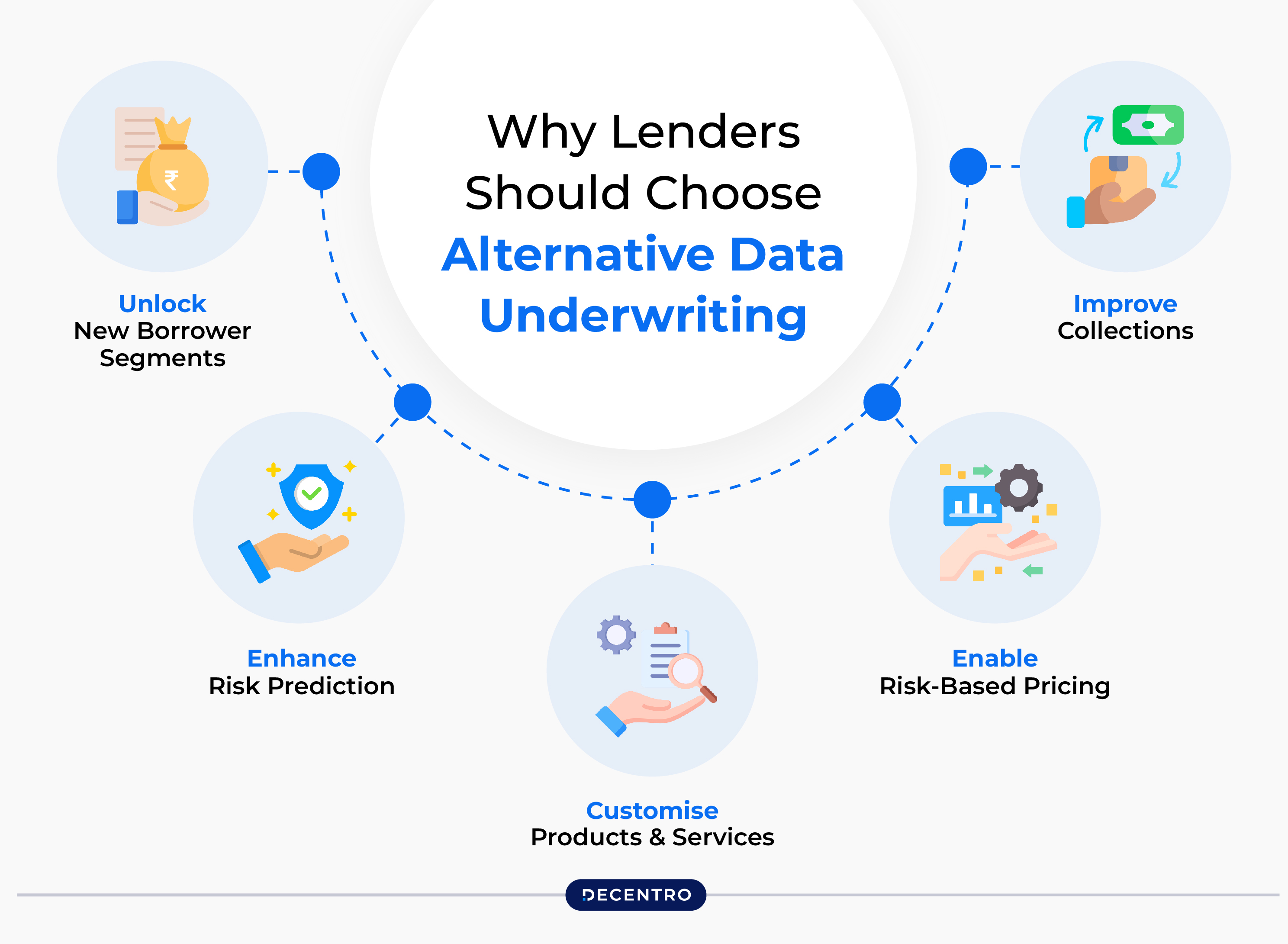
Lenders and NBFCs should use alternative data underwriting to significantly grow their loan books without compromising on the borrower repayment capability:
- Unlock New Borrower Segments: Tap into India’s untapped borrower potential by leveraging non-traditional data like utility payments, online behaviour, and social media, expanding access to formal credit.
- Enhance Risk Prediction: Integrating alternative data can boost Gini Coefficient scores and improve loan repayment predictions. A single-point increase can save banks up to USD 10 million per billion in loans.
- Customise Products and Services: Use diverse data sources, including social media, to better assess creditworthiness, enabling personalised lending terms that maximise value for both lenders and borrowers.
- Enable Risk-Based Pricing: Achieve precise credit assessments with alternative data, allowing for personalised loan pricing that reflects each borrower’s risk profile and troubleshooting for fraud.
- Improve Collections: Enhance collection efficiency and reduce costs with alternative data-driven strategies, prioritising borrowers by risk and significantly increasing recovery rates.
Evaluating a Credit Engine to meet your business needs
When selecting a robust underwriting engine, key considerations should include integrating multiple data sources efficiently through a single API, customisation options to meet specific business needs, and a user-friendly interface that allows for easy navigation and workflow adjustments. Additionally, evaluating costs about expected ROI is crucial, along with ensuring technical support and training availability to maximise the software’s effectiveness. These factors together enable a well-informed decision, ensuring the chosen underwriting engine aligns with business requirements and budget while supporting accurate and efficient lending decisions.
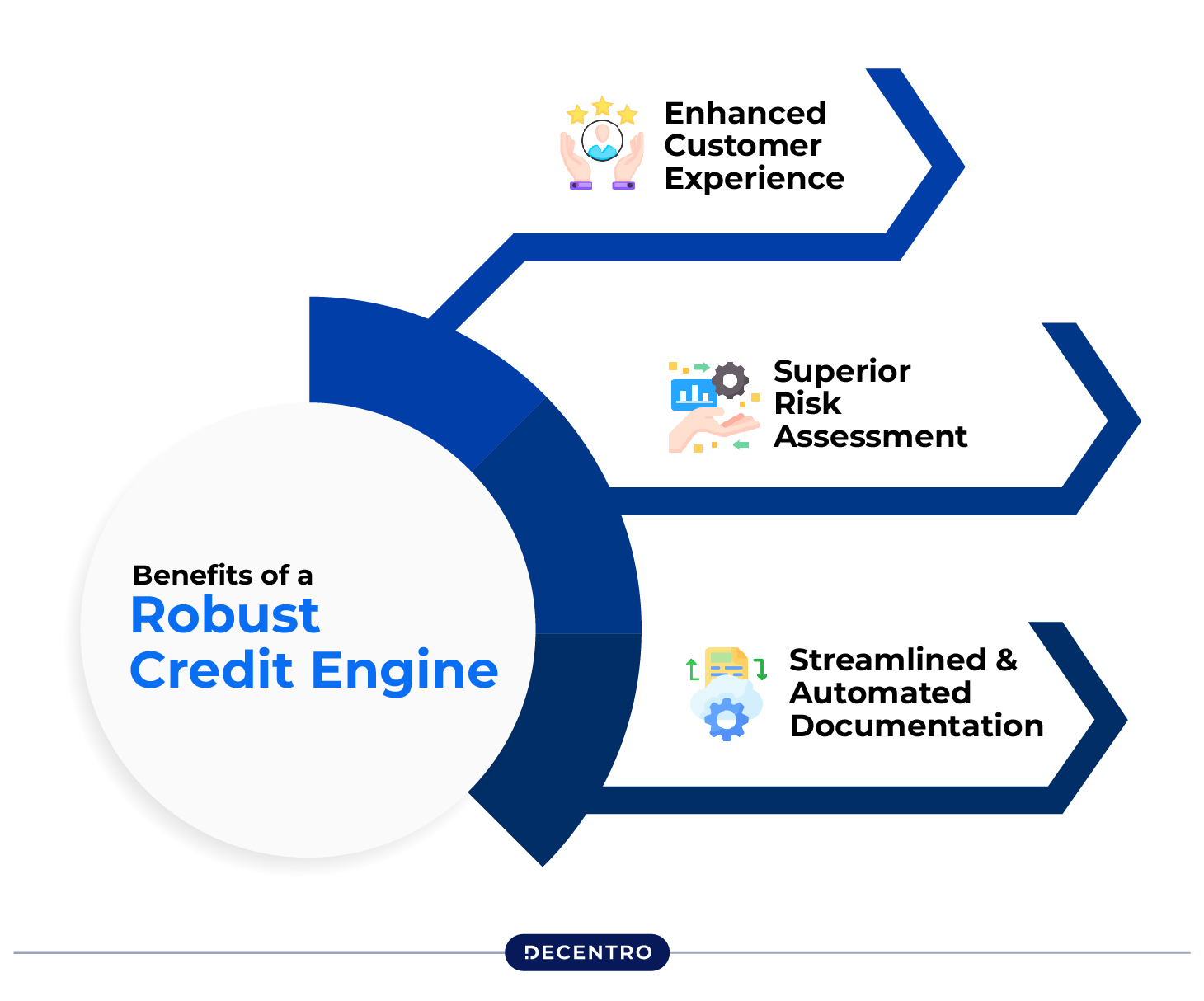
A robust underwriting credit engine offers several key benefits, including:
- Enhanced Customer Experience – By leveraging a customer’s risk profile, lenders can tailor credit products to meet individual needs while considering underlying risk factors. This not only improves the customer experience but also increases closure rates for lenders.
- Superior Risk Assessment – AI-powered underwriting transforms unstructured data into structured data, automating the analysis process to prevent potential losses and significantly reduce manual errors.
- Streamlined and Automated Documentation – AI-driven underwriting can extract crucial information from unstructured documents and provide document management solutions, allowing lenders to store and assess customer documents for risk evaluation efficiently.
The Future of SME Lending and Underwriting in India
The MSME sector accounts for 30% of India’s GDP, and the need for accessible credit has never been more critical. Many MSMEs in India lack a solid financial history, which remains a significant barrier to securing unsecured credit from lenders or investors. This challenge is even more pronounced for small, homegrown, and emerging businesses if they lack a valid credit history, a company credit card, or previous loan experience.
Fintech companies like Decentro, are helping lenders turn to alternative data sources for credit underwriting, aiming to bridge the credit gap in the country. Studies have shown that potential borrowers are 70% more likely to provide additional financial information if it improves their chances of obtaining credit. By leveraging alternative financial data such as bill payments, digital footprints, and social media footprints, lenders can build highly comprehensive credit profiles for these businesses. These will provide a complete and clear picture of the creditworthiness of these businesses compared to traditional underwriting practices.
Achieving financial inclusion for MSMEs and other entrepreneurial ventures depends on making the lending process more navigable. Fintech platforms like Decentro are at the forefront of this transformation, enabling lenders to adopt a multi-faceted underwriting approach that paves the way for more inclusive and efficient lending.
Ready to transform your underwriting process and support the growth of MSMEs? Explore how Decentro can help you bridge the credit gap and revolutionise your lending practices.


