Discover the benefits of open banking, its origin, estimated market size, and security measures. Learn how open banking works and it’s key use cases in this comprehensive guide.

Open Banking: What Is it and How Does it Work?
A true blue millennial trying to engineer her full time-career around the world of content. How cliché is that?
Table of Contents

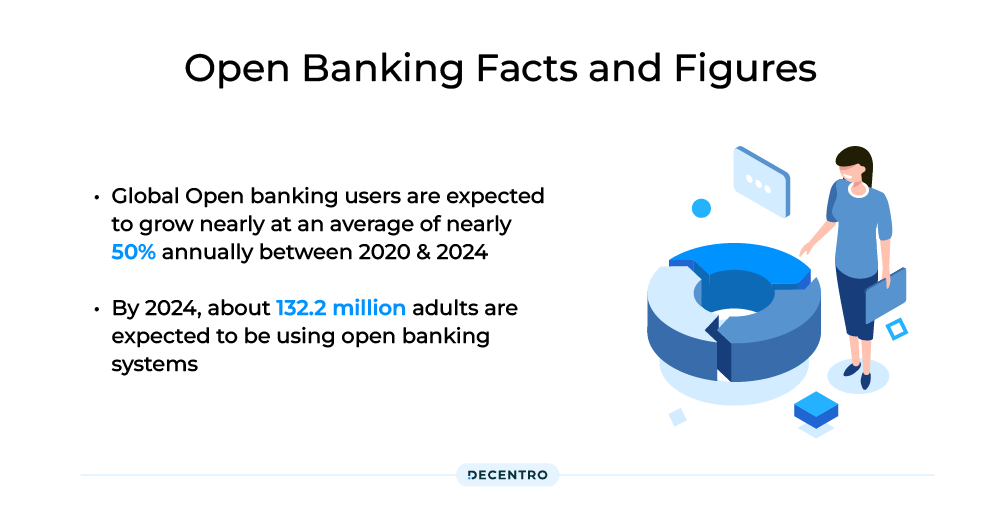
An industry study shows that the GDP of global economies that will facilitate sharing data for financial services will gain 1-5 percent by 2030.
According to a report by PwC, around 39% of clients are willing to share their data with third-party companies if it gives them a better experience.
Gone are the days when sharing information and banking experience were never said in the same breath.
The iron-clad banking world has seen a paradigm shift, where access, efficiency, and ease of execution of any action have become the primary drivers of their business use case.
According to the World Bank’s 2021 Global Findex Database, 1.4 billion adults globally cannot access formal financial services (unbanked).
And lack of access can only be combated with inclusivity, which presents as Open Banking.
What is Open Banking?
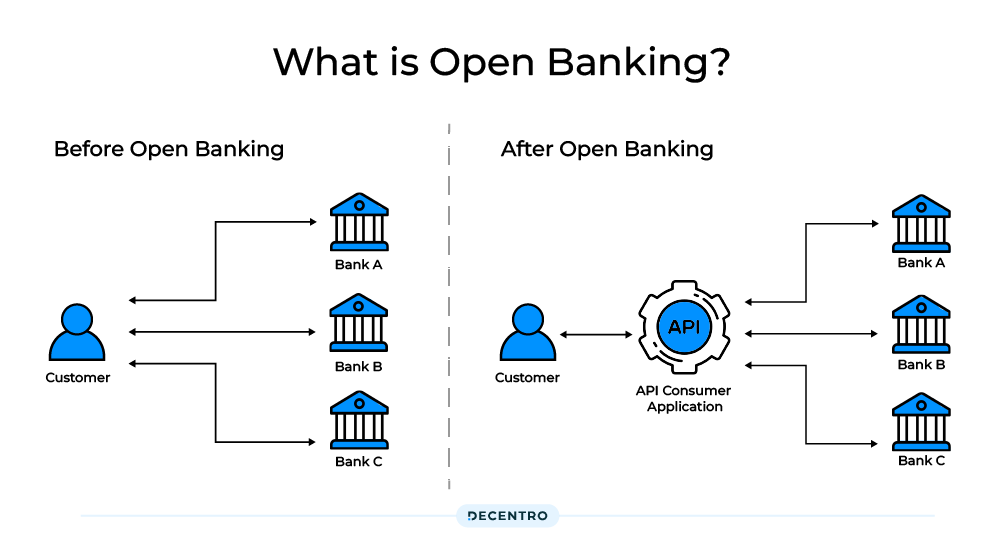
Open banking is a system where banks open their Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and allow third-party institutions to access certain financial information. This information includes but is not limited to transactions & banking information of account holders or clients.
Customers decide what information must be shared and what’s to be hidden securely, giving them higher financial transparency and control over their financial data. This will help the third-party institutions improve services, and the banks enhance the customer experience.
Open banking was created to improve customer financial services by opening up access to historically kept in-house data. New companies and products can enter the market to use this data in helpful, innovative ways.
So what does it all mean?
- For financial service providers — At the top of the chain, open banking will allow them to significantly innovate their product offerings to businesses.
- For businesses (large and small) — Those innovations made by financial service providers will mean more effective and efficient financial tools in your business — notably payments. This will mean more automation, freeing up more time, doing away with the headaches of manual tasks, and ultimately saving you money.
- For customers — Open banking will mean better ways to spend, borrow, and invest.
Where did Open Banking Originate?
The European Union first introduced open banking policies, and the United Kingdom has been hailed as the global leader of open banking.
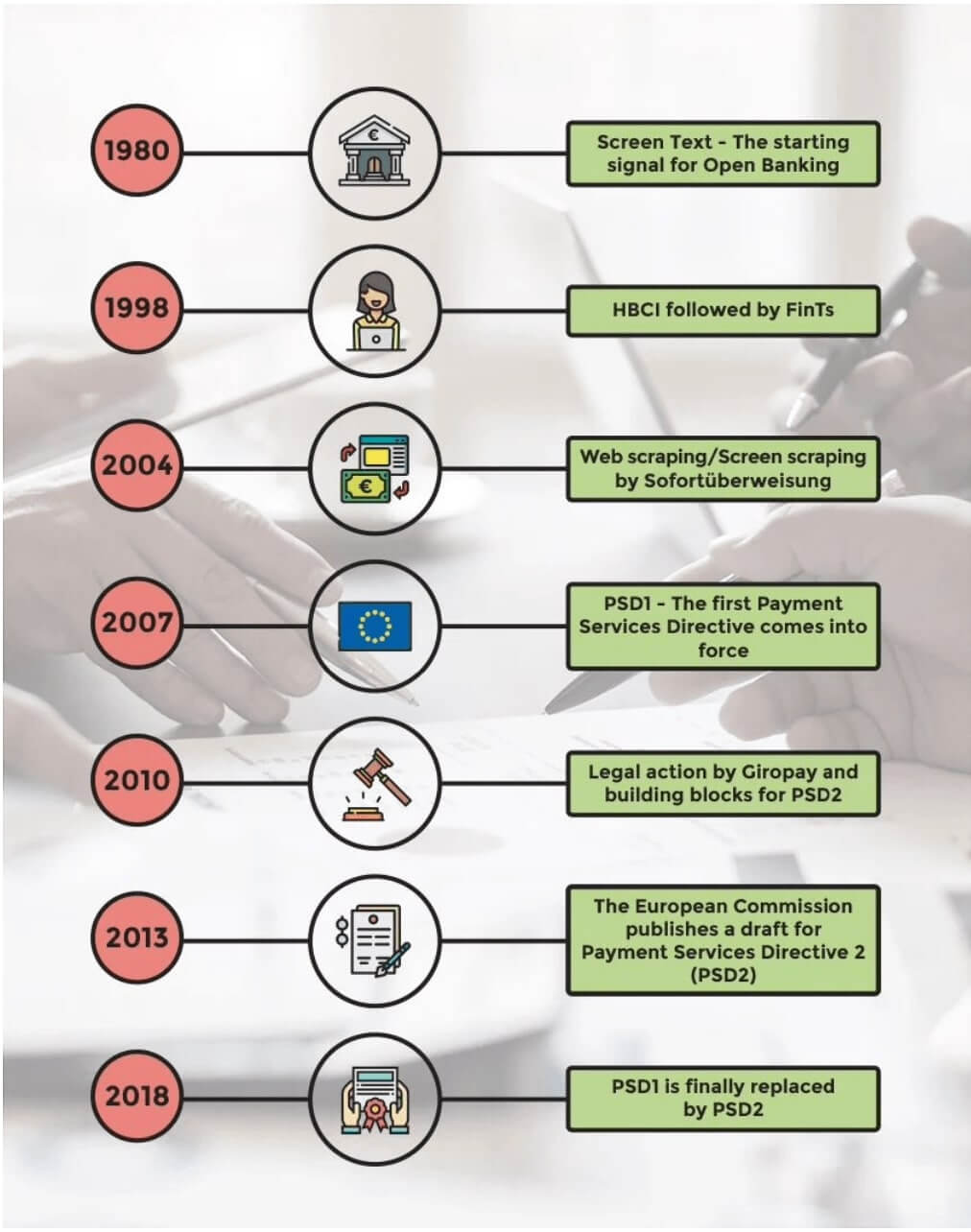
PSD1, or Payment Services Directive, was devised by The European Commission in 2007, but it was only until its successor PSD2 was enforced in January 2018 that open banking came into full throttle.
PSD2 made open banking mandatory in Europe – all banks had to furnish their APIs to third parties, giving customers higher control over their financials.
PSD2 categorises the TPPs into two categories.
- Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs): Regulated TPPs can initiate payments directly from customers’ accounts based on explicit consent.
- Account Information Service Provider (AISP): Regulated TPPs who access customer data and provide a single view of all their accounts for better financial management. Even this action requires the customer’s explicit consent.
PSD2 laid the groundwork for open banking, a practice that is very relevant, safe, quick, and easy to use.
Although European countries lead the scenario, others like the US, India, Australia, and Singapore are catching up quickly and being an essential part of the open banking system narrative.
The Estimated Market Size
In terms of size, the global open banking market is to grow from $27 billion in 2019 to $395 billion by 2026, per a report by a leading business consultancy.
India, which has already embraced various use cases of open banking (triggered by flagship UPI), has kickstarted its formal approach towards it.
According to a report published by the IMF, the Indian case of the rise of open banking consists of four layers (called India Stack) :
- The Presenceless Layer: Linking of Aadhar ID with bank accounts.
- The Cashless Layer: Enabling cashless transactions through UPI.
- The Paperless Layer: Enabling digital verification of scanned documents and KYCs.
- The Consent Layer: The layer of data fiduciaries facilitating open banking in the country. Examples: Banking-as-a-service, Neobanks, etc.
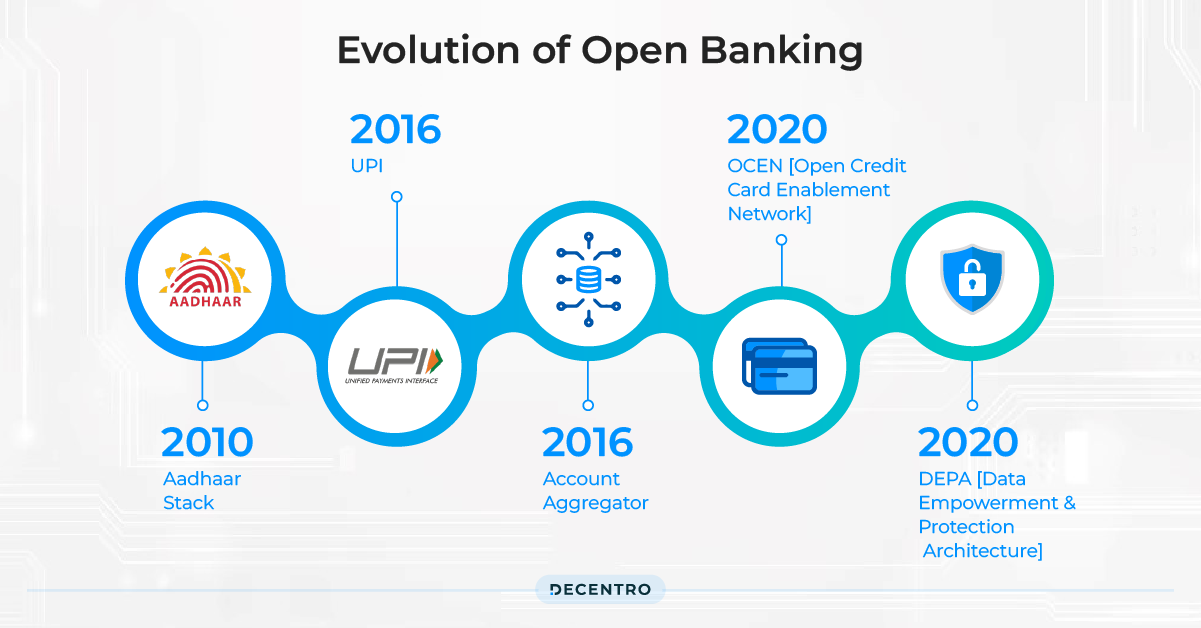
Let’s take a look at the timeline of how open banking has evolved over the years in the Indian Context:
2010 — Aadhaar Stack: A first foundational step for creating public digital infrastructure, with the launch of digital identity.
2016 — UPI: First launched for public use in the market, enabling access to any bank account from third-party apps using API protocols.
2016 — Account Aggregator: Framework launched by RBI to create consent managers and democratize financial data by empowering customers. The system went live in 2021.
2020 — OCEN [Open Credit Card Enablement Network]: It aims to change how credit is enabled to the end-customers by introducing new touchpoints for distribution.
2020 — DEPA [Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture]: This consent-based data-sharing framework launched by NITI Aayog aims for data democratization and financial inclusion. It complements the AA framework.
What Led to The Growth of Open Banking in API
Regulatory and market forces have combined to fuel the expansion of Open Banking APIs. Here are the two great reasons behind its growth:
- Open Banking API Growth is Being Driven by Regulation: As mentioned, every dominance has banking terms to meet the desired customer experience and benefits. The business finance sector is continuously working on technological advancement, and eventually, it has encouraged the usage of Open Banking APIs.
- Market Forces Driven Open Banking API Growth: New potential for cooperation between banks and outside developers has been made possible by developing new technologies and the growth of fintech businesses. The story of Open Banking has been fueled by banks’ ability to work with these developers to produce cutting-edge goods and services thanks to Open Banking APIs.
How Does Open Banking Work?
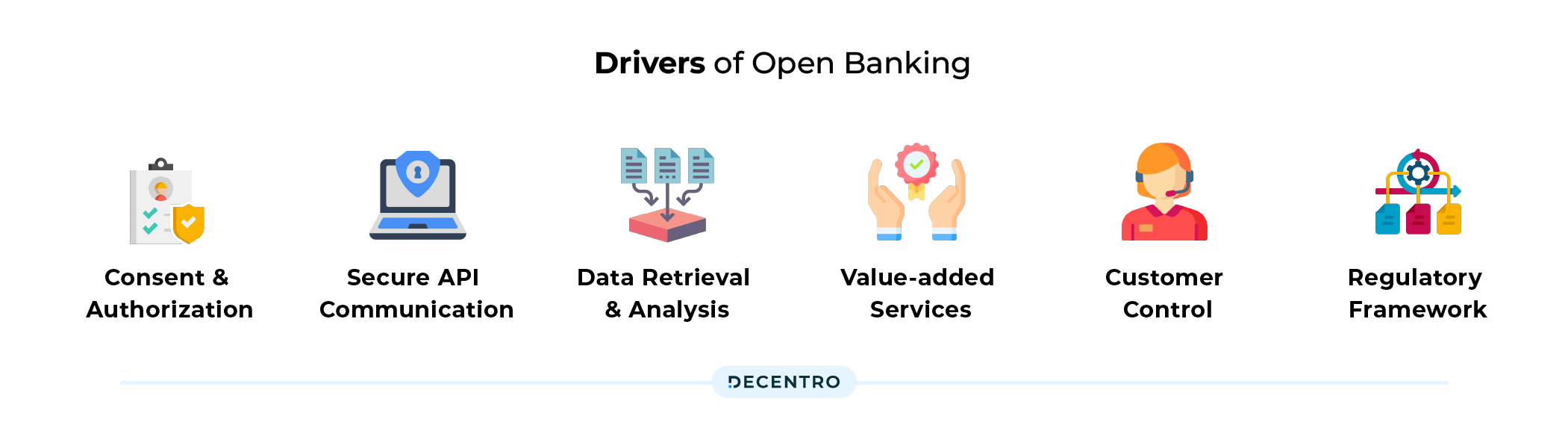
Technologically speaking, open banking relies on APIs (application programming interfaces). The following are the drivers of the Open Banking system,
- Consent and Authorization: The customer initiates the process by providing explicit consent to share their financial data with a Third-Party Provider [TPP]. Consent is typically given by linking their bank accounts to a specific TPP.
- Secure API Communication: Once consent is granted, the authorized TPP communicates with the customer’s bank or financial institution using secure APIs. The APIs facilitate the secure exchange of financial data between the customer’s bank and the TPP.
- Data Retrieval and Analysis: The TPP retrieves specific financial information, such as account balances, transaction history, and other relevant data, from the customer’s bank using the authorized APIs. The TPP then analyses this data to offer value-added services to the customer.
- Value-added Services: TPPs in India provide various value-added services to customers based on their financial data. This can include personalized financial management tools, expense tracking, bill payments, fund transfers, and other innovative services.
- Customer Control: Customers in India have control over their financial data and can manage the consent given to TPPs. They can revoke consent or modify access permissions at any time.
- Regulatory Framework: Open Banking in India operates within the guidelines and regulations set by the RBI and NPCI. These regulatory bodies ensure compliance, security, and data protection to safeguard customer interests.
What is API in Open Banking?
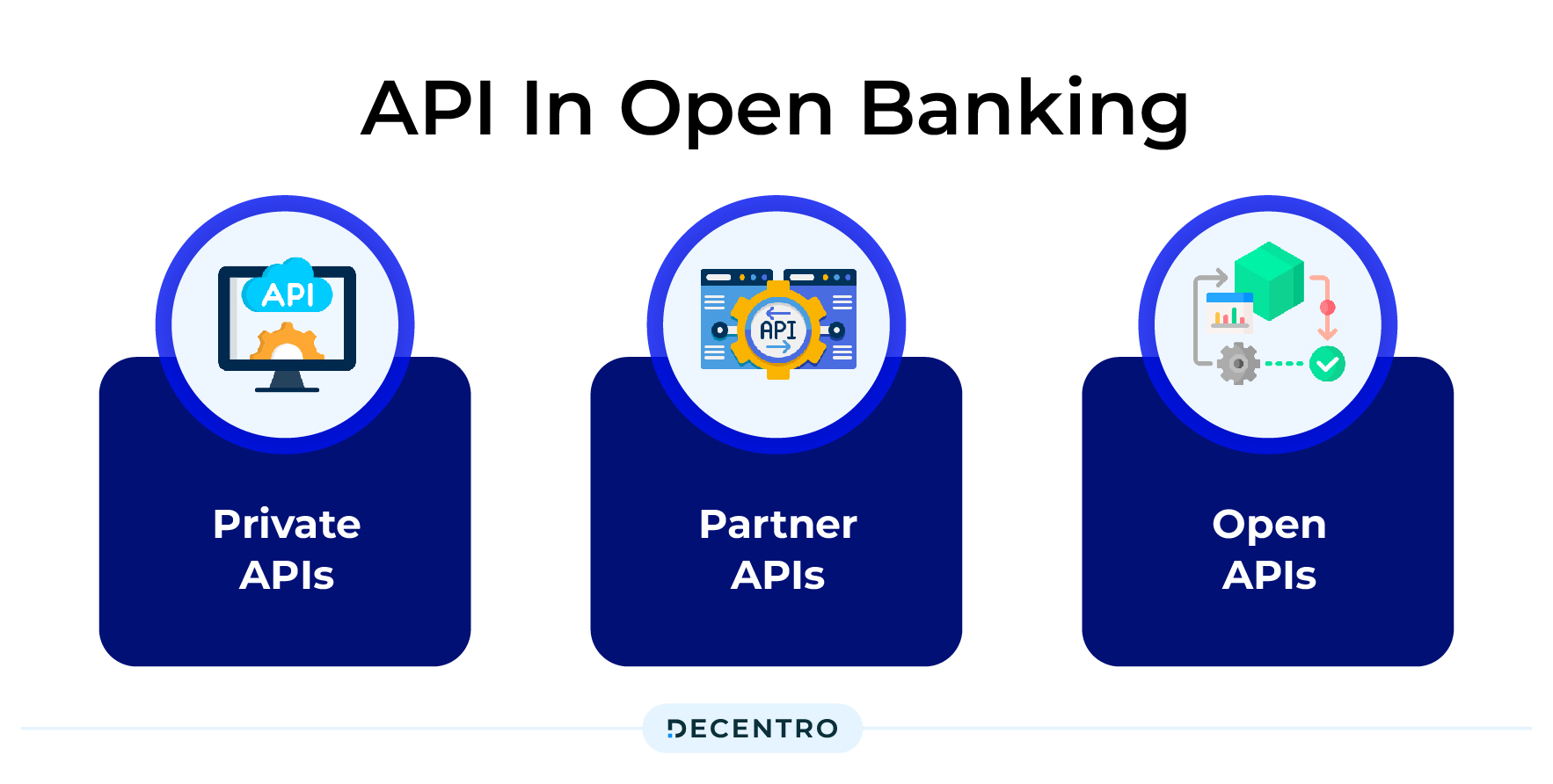
APIs are crucial elements for open banking, as they are the medium that allows communication between enterprises and banks. They enable third-party developers to access banking information and produce cutting-edge goods and services that meet unique customer requirements. There are 3 types of APIs when considering Open Banking.
Private (internal) APIs: These are utilised exclusively for information exchange within the enterprise, i.e. for internal banking systems. For data sharing, internal operations and departments of banks mostly use these APIs.
Partner APIs: These are used in collaboration with service providers and financial institutions. They enable banks to securely communicate customer information with their partners, which allows them to produce customised goods and services.
Open (public) APIs: Third-party developers can access financial data and create cutting-edge goods and services using open APIs, which are publicly accessible. These APIs must meet strict regulatory requirements for customer data security and protection.
Open Banking API
The API technology was designed to make information access, transfer, and management more secure, making Open Banking a safe option to carry out your transactions. Open Banking relies on these APIs to securely share information between financial institutions. This allows banks to securely share customer financial data with authorised third-party providers such as FinTech and other financial services providers. To ensure the integrity and privacy of this data exchange, data governance in the banking industry plays a crucial role in establishing clear policies, compliance frameworks, and accountability mechanisms.
This allows customers to access more innovative financial services, such as budgeting tools, loan comparison and advice services, and other innovative services.
Key Use Cases
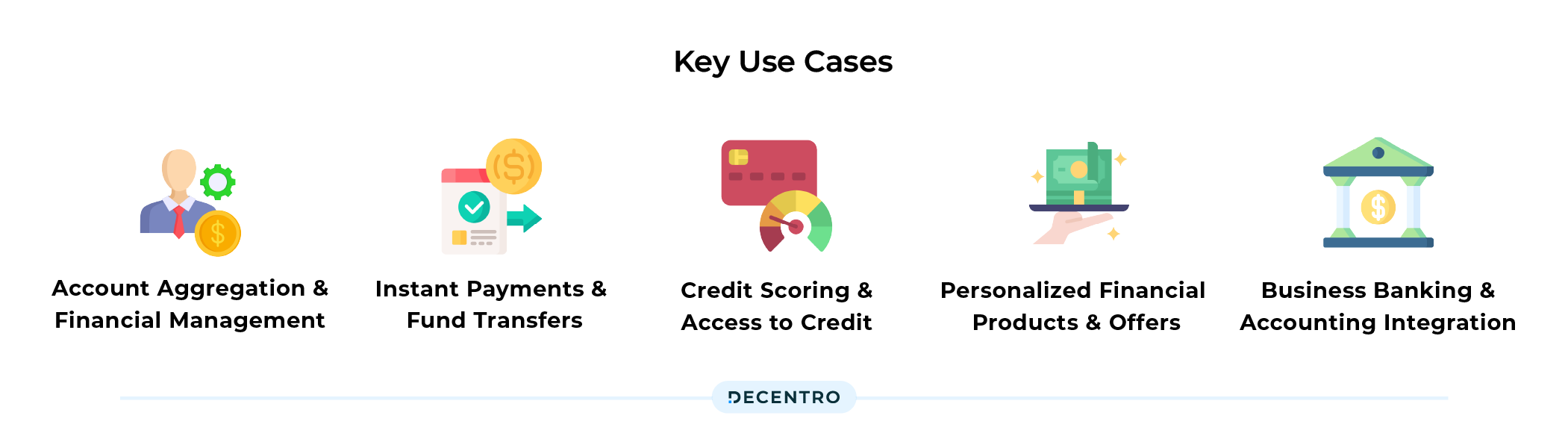
When it comes to Open Banking, the sky’s the limit for the application if the same. A few key examples include:
- Account Aggregation and Financial Management: Open Banking allows individuals to aggregate their accounts from multiple banks in a single platform or app. Users can view their account balances and transaction history and manage their finances more efficiently. It enables better financial planning, budgeting, and tracking of expenses across different accounts.
- Instant Payments and Fund Transfers: Open Banking facilitates real-time payments and fund transfers through the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) platform. Using UPI-enabled apps, users can initiate instant person-to-person transfers, merchant payments, and bill payments directly from their bank accounts. It provides a seamless and convenient payment experience.
- Credit Scoring and Access to Credit: Open Banking enables lenders and fintech companies to access customers’ financial data to assess creditworthiness. It can lead to more accurate credit scoring models, allowing individuals to access better loan terms, personalized lending options, and quicker loan approvals. Open Banking can improve financial inclusion by providing access to credit for individuals with limited credit history.
- Personalized Financial Products and Offers: With access to customers’ financial data, Open Banking can enable personalized financial product recommendations. Users may receive targeted offers for loans, insurance products, investment opportunities, or savings accounts based on their financial profile and preferences. It enhances the customization of financial services.
- Business Banking and Accounting Integration: Open Banking can facilitate seamless integration between banking services and accounting software for businesses. It allows businesses to automate financial processes, retrieve transaction data directly from bank accounts, reconcile accounts, and generate real-time financial reports. Open Banking streamlines business banking and financial management.
Benefits of Open Banking
And quite naturally, the myriad of applications paves the way for the following benefits:
You get Better Financial Transparency
Access all your financial data in one place; find better deals, open the right accounts, opt for better loan options, and plan better for your expenditures. The app you choose to share the details with is entirely your choice.
Quick & Efficient Payments
Transferring payments from one bank to another or a third-party app becomes effortless. Wish to recharge your phone bill? Cable bill? No worries there!
Improved Banking Experience
Open banking benefits customers with a better operating experience and helps the bank to amp up its offerings and expand its customer base.
Increased Referrals
The collaboration from open banking brings in referrals quickly—both for the third party and the bank.

Barriers to Adoption of Open Banking
Even at the level, Open Banking has seen in terms of adoption, there are a set of barriers that come with democratizing access to banking services, namely,
- Lack of customer awareness: Customers must be educated to familiarise themselves with the concept and generate buy-ins. Consumers will need time to become aware of and understand the benefits. Ultimately, the ability to engage customers will determine the success of Open Banking.
- Cost of transformation: For some banks, the incremental cost to enable, roll out, and maintain Open Banking is a barrier to adoption, especially if they do not have a strategic view; it’s unclear how much they can profit from this.
- Legacy systems: Banks’ core and legacy systems have become complicated and can challenge interoperability with Open Banking APIs.
- Data security and fraud: Open Banking relies on data sharing. Regarding Open Banking, banks are particularly concerned about data security and customer privacy because they can be held liable, resulting in hefty fines and a loss of customer trust. Concerns over fraud and data security inhibit customer adoption.
- Data sharing anxiety to competitors: Banks face a dilemma on how much customer data they should expose to make Open Banking meaningful without losing control over customer data and product cannibalisation.
- Better entrenched competition: Today, banks face competition from FinTechs, neobanks, and technology giants like Amazon, Google, and Facebook that are improving existing financial services by enhancing capabilities, improving convenience, or lowering prices and fees for consumers. Banks that don’t proactively think about their strategy could face eroded market share, increased customer churn, and increased pressure on margins.
Open Banking Security: How Safe Is Your Data?
Now for addressing the elephant in the room.
With the conversation sharing of sensitive information, especially in banking and payments, security and compliance become a huge risk factor.
However, Open banking security is designed to protect and keep your data safe. Banks use various measures such as encryption, authentication, and authorization to protect the data shared between you and the bank.
Banks will also often use two-factor authentication to ensure that it is you who is trying to access your account.
Additionally, data is also encrypted in transit between the two parties.
The API technology was designed to make information access, transfer, and management more secure, making Open Banking a safe option to carry out your transactions.
At Decentro, we’re firm believers in Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) innovation and wish to extend banking workflows to all kinds of customers. Companies have started differentiating themselves by building personalized user workflows in a hyper-personalized world.
Our Fabric and Flow modules offer a full-stack payment and embedded banking experience catering to your evolved requirements.
The Flow module aims to ease the money movement journey for your platforms. The full-stack payment suite enables you to automate payment collections and money transfers via any bank-to-bank protocol (e.g., UPI, IMPS, NEFT, RTGS), enable reconciliation via virtual accounts, and help set up recurring payment methods such as NACH & UPI Autopay.
On the other hand, the Fabric module is a first-of-its-kind module offering a comprehensive Banking as a Service (BaaS) stack. The module embeds a fully orchestrated KYC, onboarding, and credit into your platform or workflow.
To put things into perspective, in just a matter of two years, our KYC stack has been churning solid numbers.
With over 400+ Identity validations, 250+ Image recognitions, and 300+ Repository fetches happening via Decentro’s KYC stack per hour, we’re more than equipped to enable your verification and validation journey.
Besides absorbing the complex banking workflows, our platform handles the underlying regulations while dealing with each module.
Curious to know exactly what these modules have in store for you?


