Dive into our concise guide exploring the various types of KYC, along with the pros and cons for hassle-free customer verification. Build your onboarding journey with Decentro today.

Types of KYC: A Quick Guide to Various Verification Methods
Table of Contents
Annually, an estimated $800 billion to $2 trillion USD is believed to be laundered globally, comprising 2-5% of the entire world’s GDP. Notably, banks and financial institutions serve as prevalent conduits for this illicit activity, including other forms of illegal practices such as terrorist financing. Consequently, implementing multiple layers of anti-money laundering (AML) techniques is imperative to dissuade, identify, and safeguard against financial crimes.
Last month, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) tightened customer diligence norms by introducing a risk-based approach to the KYC process. This basically entails driving their customer verification processes by adjusting verification levels based on risk factors. This means low-risk customers are accepted more quickly, whereas higher-risk customers may require additional verification procedures.
This brings us to an understanding of the process of KYC and the different types of KYC prevalent in India. Read our guide to understand which form of KYC can be relevant to you or your business and the pros & cons around each of these.
| KYC Type | Benefits | Challenges |
| Physical KYC | Greatly helpful in remote areas such as villages and tier-3 cities. | Complexities associated with storing and handling physical documents. |
| Aadhaar Offline e-KYC | High accessibility for all private BFSI entities. | May lead the service provider to go for additional identification due to masking. |
| Aadhar e-KYC | Better user experience and better conversions. | After every subsequent year, full KYC must be performed to use a minimum KYC account. |
| Digital KYC | Highly cost-effective. | Can lead to inefficiencies and subjectivity at times. |
| Central KYC (CKYC) | Enhanced accessibility and convenience. | High compliance requirements can lead to operational complexity. |
| Video KYC (V-KYC) | 90% reduction in costs for financial institutions. | Needs high technological infrastructure. |
What is KYC?
KYC stands for Know Your Customer. It involves verifying the identity of every customer, client, individual, or third party as part of the onboarding or verification process and during transactions. The Reserve Bank of India has made KYC compulsory for all financial institutions, including banks that conduct financial transactions.

In fiscal year 2022, more than 11 billion of cumulative e-KYC (Know Your Customer) authentication transactions took place in India.

Holders of Aadhaar alone carried out nearly 2.31 billion authentication transactions in March 2023. With the large demographic and high number of financial institutions in India, a robust KYC system is becoming increasingly important for risk management, maintaining compliance-related requirements and profitability.
KYC Guidelines as per the UIDAI
UIDAI has established KYC regulations to safeguard customers and businesses against criminal activities and mitigate the risk of fraud. In India, regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) oversee the BFSI industry, implementing specific policies to authenticate individuals’ identities.
These measures enable companies to understand better their customers’ financial transactions for improved service and more effective risk management.
The guidelines necessitate the following processes:
- Identity verification
- Address verification
- Biometric verification
- OTP verification
The regulatory bodies may also do risk profiling, and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks for additional safety.
Why is KYC Needed?
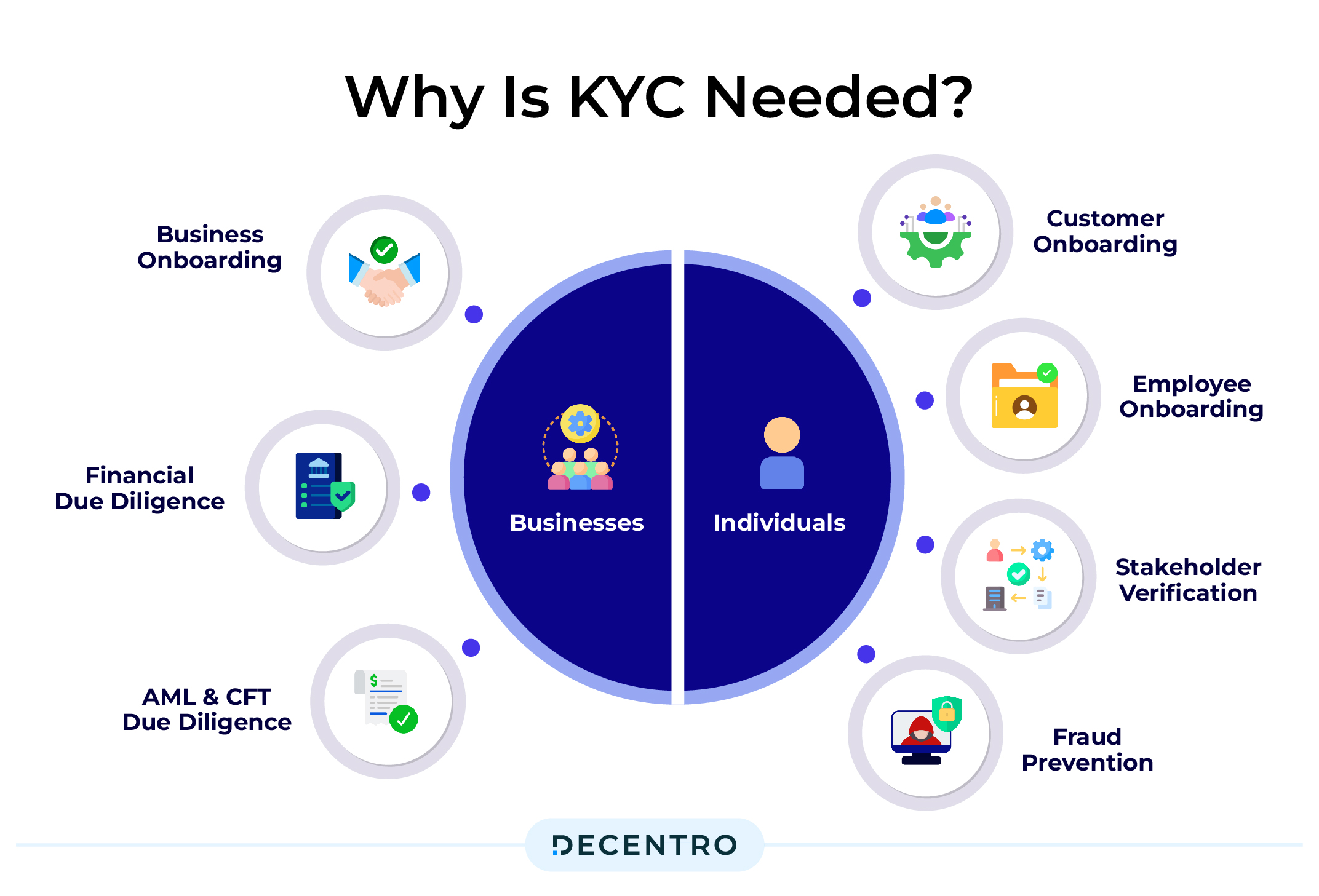
For individuals:
- Customer Onboarding: Financial institutions use KYC to verify customer identities, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering regulations and mitigating legal and reputational risks.
- Employee Onboarding: KYC includes background checks for new hires to maintain a secure workplace, safeguard sensitive information, and uphold company integrity.
- Stakeholder Verification: Businesses utilise KYC to validate key stakeholders’ legitimacy, such as clients, partners, and investors, ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
- Fraud Prevention: KYC aims to minimise the risk of fraud, protecting organisations from financial losses, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
For businesses:
- Business Onboarding: KYC/KYB compliance safeguards against illegitimate ventures, ensuring informed decision-making and protecting against reputation, corruption, or money laundering risks.
- Financial Due Diligence: Leverage KYC/KYB solutions to assess the financial health of partners, preventing potential ROI, time, and reputation losses.
- AML & CFT Due Diligence: A robust KYC process is essential for AML and CFT compliance, combating fraud, and preventing money laundering and terrorist financing.
Documents required for KYC
Under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002, KYC compliance is mandatory to establish customer identity. KYC documentation includes
Uniform KYC: Documents recommended by the Central KYC registry.
Additional KYC: Extra information requested by the financial intermediary.
List of KYC documents:
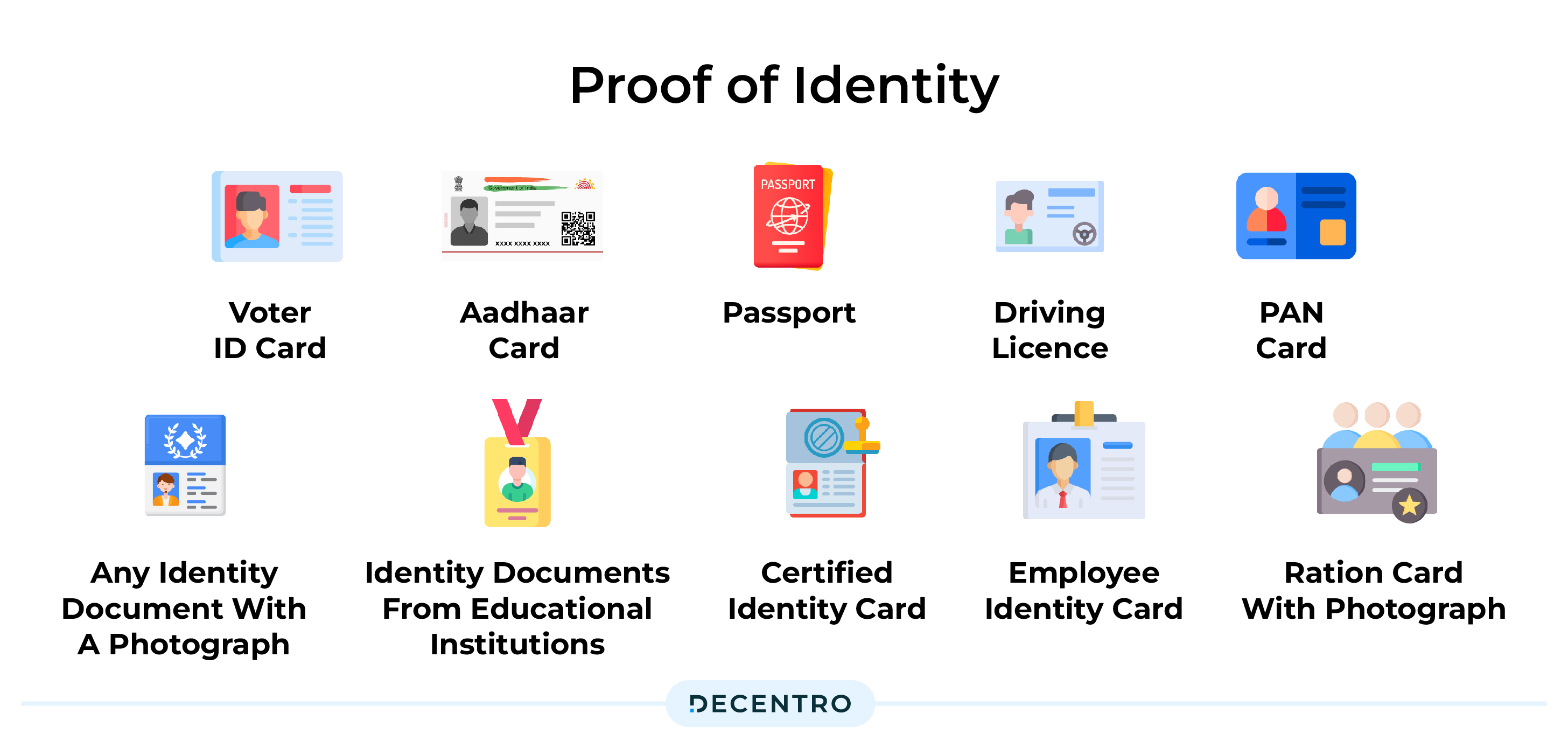
Proof of Identity:
- Voter ID card
- Aadhaar card
- Passport
- Driving Licence
- PAN card
- Any identity document with a photograph issued by Regulatory/Authorities/Statutory, State or Central Government, and related Departments
- Identity documents from educational institutions affiliated with Professional Bodies (ICSI, ICWAI, ICAI, Bar Council)
- Certified identity card from Scheduled Commercial, Public or Private Financial Institutions
- Employee identity card from a public or private sector organization
- Ration card with photograph
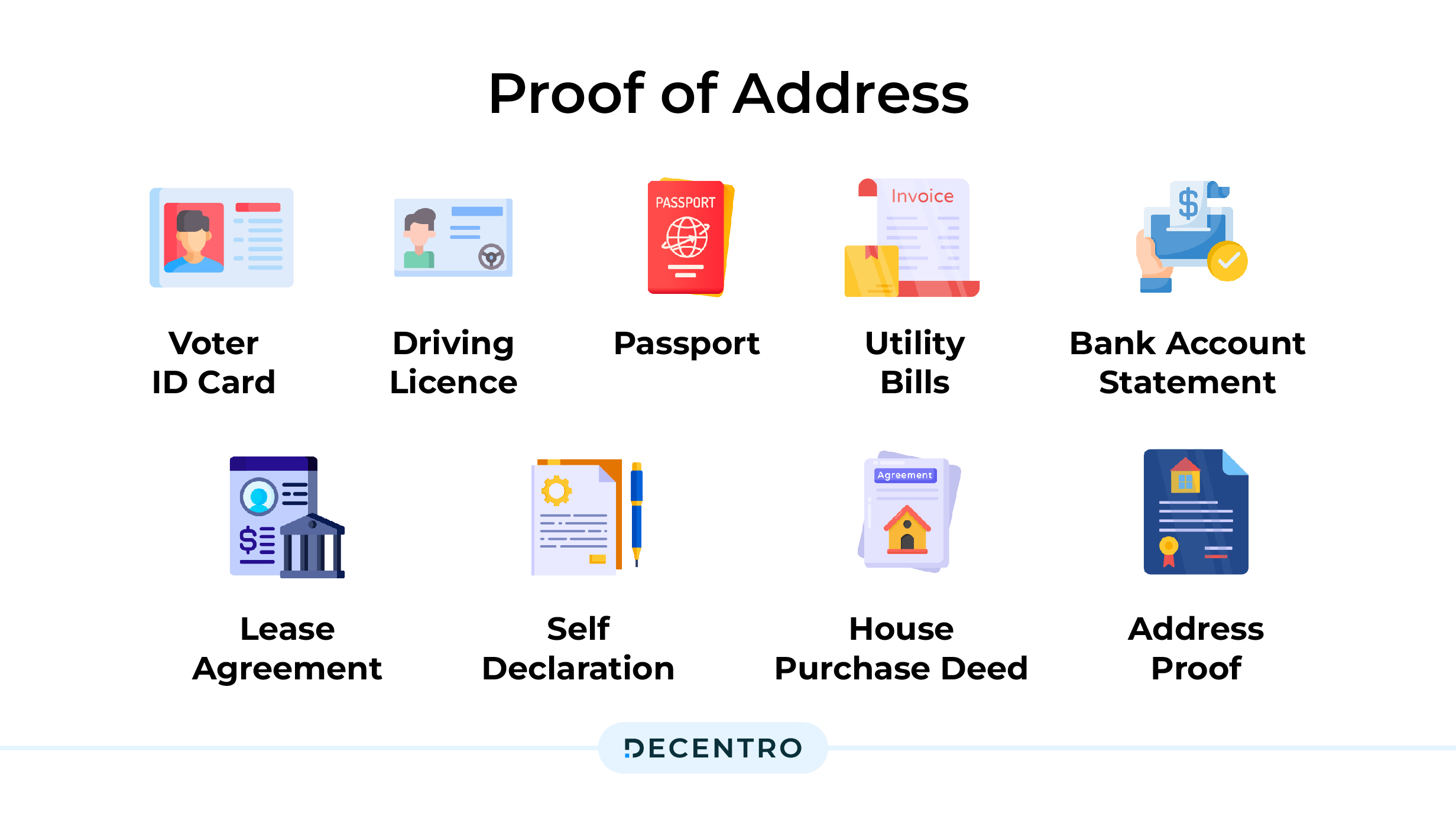
Proof of Address:
- Voter ID card
- Driving licence
- Passport
- Utility bills (not more than 6 months old): Telephone, Electricity, Water consumption, Gas receipt/connection card
- Bank account statement
- Lease agreement with the last 3 months’ rent receipt
- Self-declaration by a Supreme or High Court justice (for convicted individuals)
- House purchase deed
- Address proof issued by entities like multinational foreign banks, bank managers of Scheduled Commercial banks, gazetted officers, Parliament, Notary public, Government or Statutory Authority-certified document, Scheduled co-operative bank, elected representatives to the Legislative Assembly

Proof of Income:
- Income Tax Returns (last 2 years)
- Bank Passbook (with transaction updates for the past 6 months)
- Salary Slips (last 3 months)
Additionally, financial institutions may request other documents for consumer authentication.
Types of KYC APIs
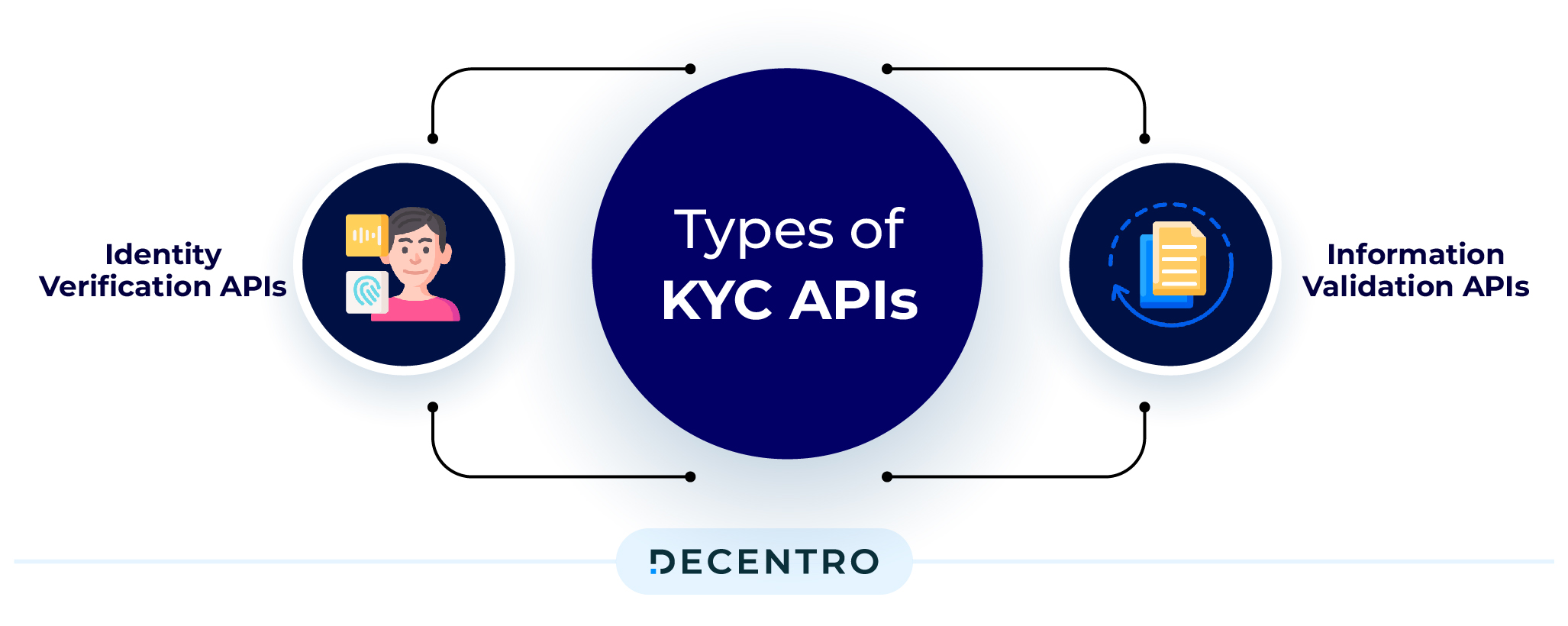
Identity Verification APIs: Identity Verification API is a robust solution for document authentication and real-time identity verification. By validating credentials and identity proofs it ensures the legitimacy of entities and businesses involved in various processes, leaving no room for fraudulent activities such as false authorizations, identity theft, money laundering, and other financial crimes.
This API not only aids in preventing verification errors but also establishes a secure end-to-end KYC verification process. Specifically, it accommodates the following features:
- Aadhaar Paperless Verification with OTP (restricted to Banks and telecommunication sectors)
- Verification via Digilocker
- Verification via CKYC
- Officially valid documents, including PAN, Driving License, and others.
Information Validation APIs: These act as validators for the verification information received from the Identity Verification APIs. These help validate the documents using the customer’s biometrics and other details to confirm the authenticity of the documents shared.
- Face Match API is an advanced solution employing facial recognition technology for identity verification. This API meticulously assesses live or recorded images of individuals, comparing them with a reference ID to analyse biometric data such as facial features, proportions, and patterns, ensuring a robust match determination.
- Liveness Check API elevates the verification process by confirming the physical presence of an individual. It employs real-time analysis of facial and body movements to detect and prevent the use of fraudulent or pre-recorded images.
- OCR technology serves as a formidable tool against document forgery and tampering. It differentiates between genuine and fraudulent applications and streamlines onboarding processes through automated data capture.
- Match Engine feature rigorously validates the authenticity of official documents such as passports and IDs. Through comprehensive analysis of text, images, and document elements, it identifies any signs of tampering or forgery. Cross-referencing with government databases and authoritative sources increases the verification process’s credibility.
In essence, Decentro’s suite of KYC solutions prioritises security, accuracy, and efficiency in identity verification protocols.
Types of KYC
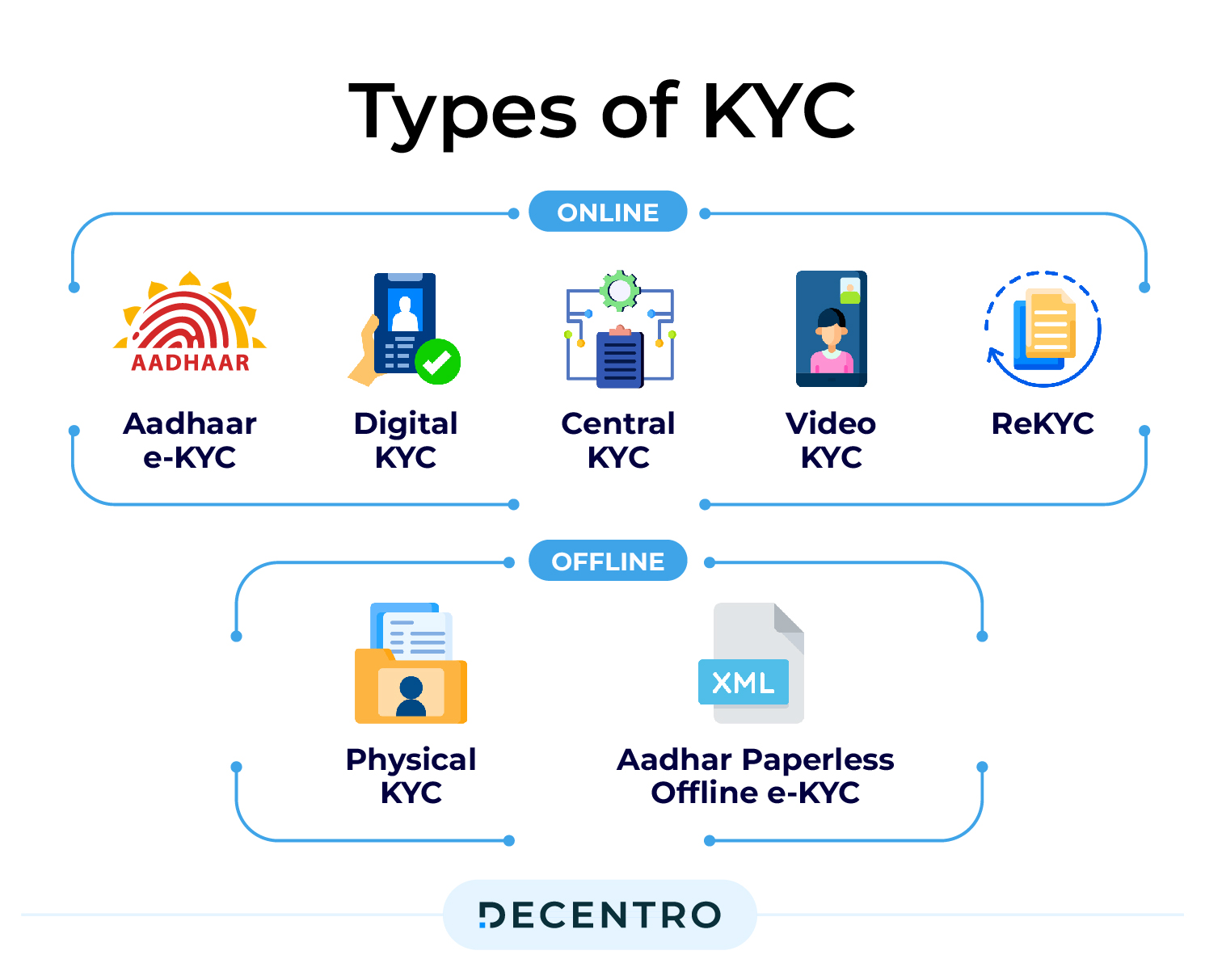
Here are the various KYC types employed in the customer identification process.
Offline KYC:
Physical KYC: Physical KYC or paper-based KYC refers to the process of submitting customer-attested copies of Proof of Identity (POI) and Proof of Address documents to the respective financial institutions. This requires the customer to be present at the bank branch or financial institution at the time of submission.
- Benefit: This form of KYC can be greatly helpful in remote areas such as villages and tier-3 cities where customers and institutions might not have been digitised.
- Disadvantage: The apparent disadvantages of physical KYC are the operational complexities and inefficiencies associated with storing and handling physical documents.
Aadhar Paperless Offline e-KYC: Aadhaar Offline e-KYC comprises users generating a password-protected XML file containing their Aadhaar data from the UIDAI website. The file is then shared with the verifying organisation along with the password.
- Benefit: The most significant advantage of Aadhaar Offline e-KYC is its accessibility for all private BFSI entities. Users can simply download the XML file and share their consent to use the file to verify themselves.
- Disadvantage: The Aadhaar number is masked on the XML file and may lead the service provider to go for additional identification.
Online KYC:
Aadhaar e-KYC: There are two ways to conduct Aadhaar verification in two ways: OTP-based and Biometric-based. For OTP-based Aadhaar verification, users must have their mobile numbers linked to their Aadhaar. For Biometric-based verification, users must go through UIDAI-approved biometric scanners to authenticate themselves.
- Benefit: Aadhar e-KYC verification does not need user involvement, thereby leading to better user experience and, eventually, better conversions.
- Disadvantage: Accounts initiated through Aadhaar eKYC are categorised as limited or mini-KYC accounts. After every subsequent year, full KYC must be performed to use a minimum KYC account.
Digital KYC: Digital KYC usually involves capturing a live photo of the customer along with Officially Valid Documents (OVDs). As expressed by the RBI, authorised officials must be physically present during the verification process and geo-tagging the documents.
- Benefit: This method can be highly cost-effective since it’s majorly digital while providing a seamless journey to users by creating a pre-defined digital journey for them.
- Disadvantage: Since it requires the physical presence of the authorising officer, the process is not entirely digital in nature. This can also lead to inefficiencies and subjectivity at times.
Central KYC (CKYC): The Central KYC Registry is a centralised repository of KYC records managed and maintained by the Central Registry of Securitisation Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest of India (CERSAI). With CKYC, users need to do a KYC check only once and are assigned a KYC Identification Number (KIN), which is unique, after the check.
- Benefit: Financial institutions benefit from enhanced accessibility, and customers avoid the need to provide the same information, ultimately enhancing their convenience.
- Disadvantage: Financial institutions must adhere to various regulations when utilising the CKYC database, making compliance an operational complexity.
Video KYC (V-KYC): VKYC involves onboarding customers over a video call. The process is two-legged: the first is the video call, where the customer submits their documents, and the second includes reviewing the call while approving or rejecting the KYC.
- Benefit: It can reduce the customer onboarding time from days to minutes and result in up to a 90% reduction in costs for financial institutions.
- Disadvantage: Video KYC requires a higher technological infrastructure with high investments.
ReKYC: ReKYC involves periodic updating of information by banks to have updated KYC records of their customers at specific intervals. For changes in customers’ addresses or other details like phone numbers, the customer details should always be up to date as enabled by the ReKYC process.
Need for KYC in different industries
| Industry | Prevalent KYC Usecases |
| Financial Institutions | Physical KYC and Digital KYC are both used by FIs to verify and onboard their customers. |
| Fintechs | Fintechs prefer using online KYC like Digital KYC with liveness checks for maximising their customers’ user experience. |
| Investment Platforms | Investment platforms like Zerodha and Groww use Liveness check combined with PAN and Aadhaar verification for customer onboarding. |
| Online Gaming and Trading | Gaming and trading companies can leverage online KYC, liveness checks, and OCR to accelerate their onboarding processes at scale. |
| Marketplaces | Marketplaces generally use Online KYC verification methods including CKYC and Digilocker. |
| Real estate | Real estate agents use Identity Verification APIs for verifying the customer’s identity using Aadhaar, PAN, etc. while also using OCR for document verification. |
| Insurance | Insurance providers generally use Aadhaar-based KYC along with V-KYC and CKYC. They might also use Digital KYC for OVDs. |
| Legal Sector | Legal entities are required to upload all customer KYC data to CKYCR. They use both Identity Verification APIs for KYC completion of their customers. |
| Precious metals and art dealers | Broker dealers use AML Checks with KYC to comply with regulatory requirements while verifying their customers at the same time. An escrow account could also be a good addition here. |
How can Decentro help?
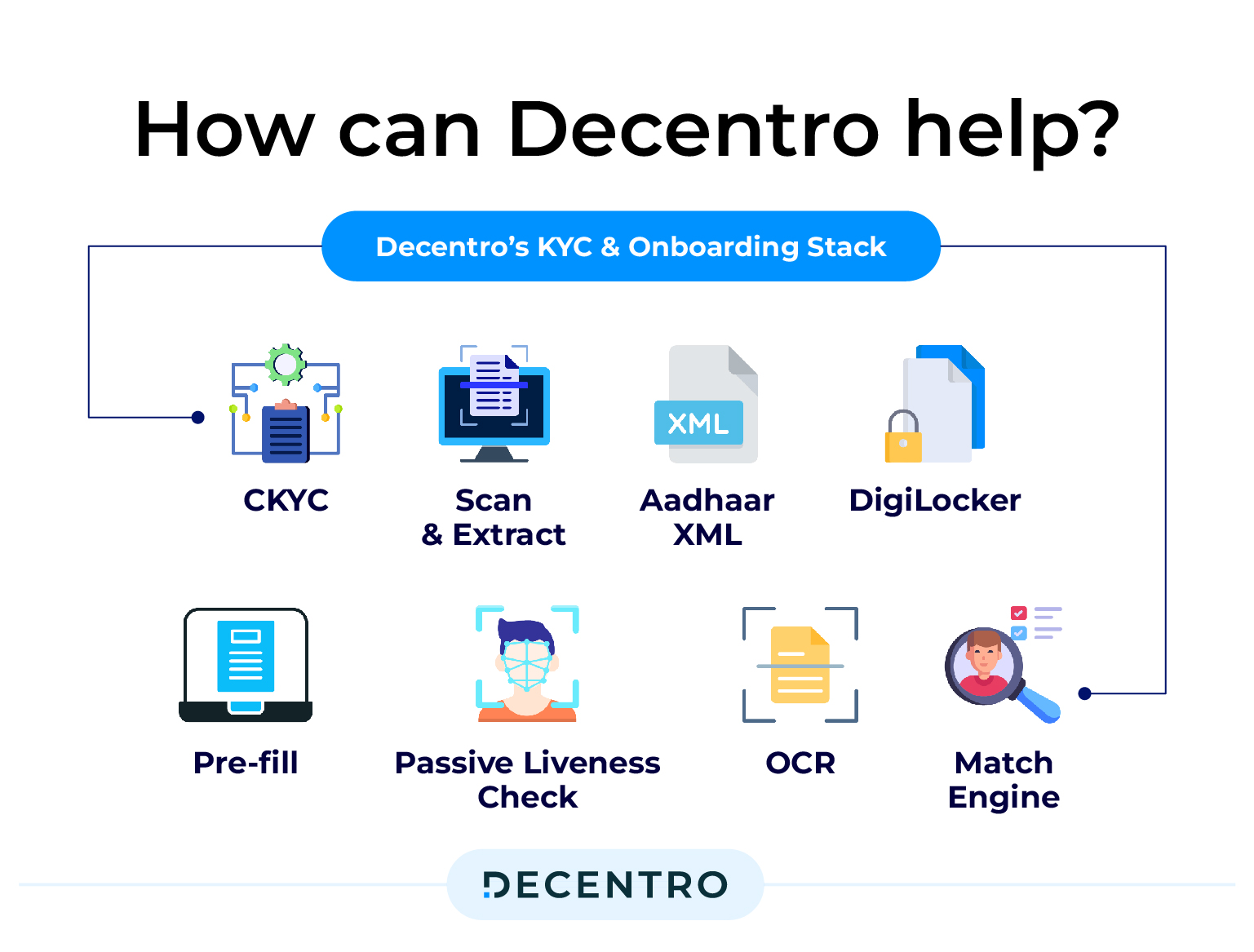
Decentro’s KYC and Onboarding stack can help businesses conduct instant background verifications with real-time KYC and KYB checks. We work with businesses like Rupyy from Cardekho, NewTap Finance, CashE, and MoneyTap, helping 800+ businesses grow and scale.
Doing 800+ ID validations per hour and 500+ OCR & extractions per hour, Decentro fully understands the importance of enabling faster customer onboarding, helping businesses reduce drop-offs and save costs.
In order to enable this, we have introduced several new additions to our existing KYC stack:
- Pre-fill – You can now use name and phone number to fetch details like DOB, Age, ID numbers such as PAN, Aadhaar, Passport, etc., in a matter of seconds, only with Decentro’s Consumer Pre-fill feature.
- Passive Liveness Check – Our Passive Liveness solution requires no specific actions from the user. Being an AI-driven identity verification, it offers near-instant verification and a confidence score matching a person’s face and checking for liveness.
- OCR – With Decentro’s Scan and Extract module, you can scan and extract customer information from KYC documents and verify the same from the associated public repository.
- Match Engine – Decentro’s Match Engine ensures accurate matching but also a comprehensive understanding and handling of Indian honorifics and a plethora of salutations across different government IDs.
With Decentro, you get:
- A fully flexible API-based flow for verification, extraction, and onboarding of customers
- A single platform to cater to all your KYC needs across ID verification, KYC OCR, CKYC, Digilocker and Aadhaar XML
- Higher success rates with multiple partners integrated on our backend
- Fully compliant with KYC, UIDAI, and other governmental regulators
Ready to explore how Decentro can revolutionise and accelerate your KYC and onboarding process by 10X?



Drop a Comment